What is Oral Communication?
Oral communication is transfer of information from sender to receiver by means of verbal and visual aid. Examples of oral communication include presentations, speeches, discussions, etc.
Though the message is conveyed through words, most of the times oral communication is effectively carried out with the help of non-verbal communication like body language and tone modulations. Oral communication is also at times mixed with visual aid to help establish the conveyed message in a clear manner.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Oral Communication?
- 2 Oral Communication Definition
- 3 Modes of Oral Communication
- 4 Advantages of Oral Communication
- 5 Disadvantages of Oral Communication
- 6 How to Make Oral Communication Effective?
- 7 Importance of Oral Communication
- 8 Principles of Oral Communication
- 8.1 Clarity
- 8.2 Simplicity
- 8.3 Source of information
- 8.4 Adequacy
- 8.5 Consistency
- 8.6 Principle of time
- 8.7 Balance between uniformly and adaptability
- 8.8 Emotional Appeal
- 8.9 Consultation
- 8.10 Feedback
- 8.11 Purpose
- 8.12 Empathy
- 8.13 Rehearsal
- 8.14 Selection of main idea
- 8.15 Introduction
- 8.16 Easiness
- 8.17 Researching the topic
- 8.18 Summary
- 9 PAIBOC Model
- 10 Business Communication Notes
- 11 Reference
- 12 FAQ
Oral Communication Examples include usage of presentations in a seminar or meeting to put across the message in a clear manner. Oral communication can also be mixed with written communication methods to ensure that maximum effectiveness is achieved.
Oral Communication Definition
Oral communication takes place in face-to-face conversations, group discussions, telephone calls and other circumstances in which spoken word is used to express meaning.
Ricky W. Griffin
Oral communication takes place when spoken words are used to transfer information and understanding form on person to another.
S. K. Kapur
Modes of Oral Communication
Research studies have shown that 80% of communication by executives of a company is in the oral form. The modes of Oral Communication include:
• Telephone/Cellular phone
• Messages
• Intercom
• Face-to-face discussion
• Meetings/Conferences
• Presentation
• Dictaphone/Dictation
• Conversation
• Radio
• Teleconferencing
• Speeches
• Brainstorming sessions
• Grapevine
• Interview
Advantages of Oral Communication
Advantages of oral communication are mentioned below:
- Immediate Feedback
- Time Saving
- Economical
- Personal Touch
- Flexibility
- Secrecy
- Group Communication
- Effectiveness
- Persuasive power

Immediate Feedback
The biggest advantage of oral communication is that it provides immediate feedback to both the sender and the receiver. Each can therefore ask for clarification and elaboration on the spot.
The speaker can immediately understand the reaction of the audience or group, s/he is addressing while the hearers get a number of clues about how their behaviour is being perceived by the speaker.
Time Saving
Oral communication is very fast. It saves the time involved in writing the message and delivering it through a channel like the postal or courier services.
Economical
Oral communication saves the money spent on stationery and the channel of communication.
Personal Touch
Oral communication builds up a healthy climate in the organization by bringing superiors and subordinates closer. It is also an effective tool for persuasion.
Flexibility
Oral communication provides an opportunity to the speaker to correct himself and make himself clear by changing his voice, pitch, tone, etc. A number of other factors like context, body language, etc. can be used to reinforce and modify what is spoken through the words.
Secrecy
Oral messages can be more easily kept confidential than written messages. All one has to do is to ensure that there is no one within the hearing or recording distance.
Group Communication
Oral communication is extremely useful for communicating with groups in meetings, conferences, etc. No classroom teaching would be possible without oral communication.
Effectiveness
Because oral communication involves the real or virtual presence of both the parties, therefore, the message transfer is more effective and that helps in achieving the goal of the communication more efficiently.
Persuasive power
Persuasion is the process of guiding people toward the adoption of an idea, attitude or action by rational means. It relies on “appeals” and convincing arguments. We live in a world where persuasive oral messages are around us.
Disadvantages of Oral Communication
Disadvantages of oral communication are explained below:
- Poor Retention
- No Record
- Time Consuming
- Misunderstanding
- Lengthy Messages
- Lack of Responsibility
- Imprecise
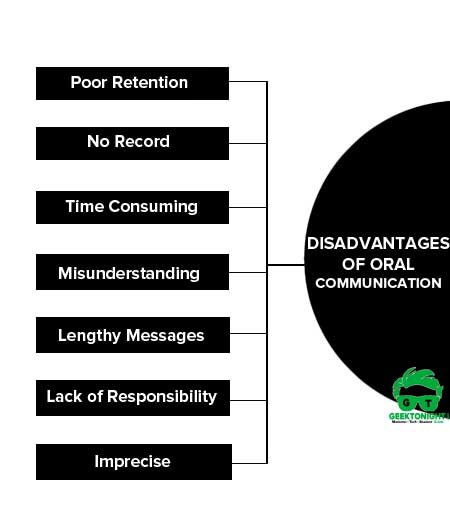
Poor Retention
The listener cannot retain oral messages in his memory for a long time. The speaker himself may not recall what he actually said.
No Record
Oral communication does not provide any record for future reference. In the absence of a record, oral messages have no legal validity.
Time Consuming
Oral communication may not always be time saving. Precisely because there is no binding medium like a page or a book, this form of communication is virtually endless. Sometimes meetings continue for a long time without arriving at any satisfactory conclusion.
Misunderstanding
Oral communications are likely to be misunderstood due to poor expression and noise. The speaker may not be able to make himself quite clear or the listener may be inattentive. This is likely to be truer when the two individuals are not on good terms with each other.
Lengthy Messages
Oral communication is not suitable for transmitting lengthy messages. Some parts of vital importance may not receive adequate attention.
Lack of Responsibility
Oral messages are not recorded. Therefore, it becomes difficult to hold persons responsible for mistakes, inaccuracy or falsity in oral communication.
Imprecise
People usually take less care when speaking than when writing. Therefore, spoken words tend to be less precise than written words. Often the exact point the speaker is trying to make is lost in a mass of words.
How to Make Oral Communication Effective?
The following steps should be taken to make oral communication effective:
- Clarity
- Brevity
- Precision
- Right words
- Avoid Hackneyed Phrases
- Understand the Listener
- Natural Voice
- Logical Sequence
- Conviction

Clarity
The speaker should pronounce his words “clearly” and “correctly”. He must talk distinctly and slowly. When a person speaks fast or munches words the oral message is likely to be misunderstood.
The way a person speaks his dialogue exercises much influence on the audience. Clarity of expression is the aim at all times.
Brevity
Oral communications often suffer from too much of talking. When a speaker keeps on talking for long, his message is lost in a sea of words and his listeners tend to become inattentive.
Therefore, the message must be kept as short as possible. However, the speaker should not appear unclear, abrupt or discourteous.
Precision
An oral message becomes more effective when it is precise and concise.
Example: It is better to say ‘cut down costs by 100 instead of saying ‘reduce costs’. The message should not be vague or incomplete. Words ought to mean clearly what they are intended to say.
Right words
The first caution is to ensure that you know the meaning of the words that you use. Some words have more than one meaning while some others carry different meanings for different persons. Be sure about what your words will convey to a trained reader.
Example: City, town and metropolis are three different words and care should be exercised before using them. You will find that the word ‘metro’ has at least three different meanings in day-to-day usage. Find them out for yourself.
Therefore, words should be chosen carefully and their meaning clarified in the context of usage. The speaker should not presume that the listener would mean the same thing from a word, which s/he means.
Avoid Hackneyed Phrases
Speakers often use hackneyed phrases and clichés like ‘you know’, ‘I see’, ‘you see’, ‘what I mean’, ‘isn’t,’ etc.
Such phrases interrupt the flow of speech and obstruct the quick grasp of meaning besides causing boredom. Speakers should ensure that they do not use these phrases unconsciously or consciously.
Most of us use them as connectives, filling up a gap when we do not have the correct word/phrase. Keeping them consciously out of your usage would mean that you will have to remain silent for those gaps. But don’t worry. Once you stop using fillers like those, appropriate words will come to you with a little effort at articulation.
Understand the Listener
A good speaker must understand the listener before talking. People vary in terms of their education, culture, intelligence level, maturity, etc.
Natural Voice
The speaker should use his natural way of speaking. In order to look sophisticated, some speakers use a foreign accent. This reduces the effectiveness of communication.
Logical Sequence
Before speaking, different ideas to be conveyed should be arranged in a logical order. It helps to make the speech forceful.
Conviction
A speaker must have conviction in what he says. Careful understanding, the sincerity of speech, and intelligent planning are required to develop conviction in speech.
Importance of Oral Communication
The importance of oral communication can be discussed in the following points:

Importance for a scholar
The art of oral presentation is of immense significance for an academician or a student who is needed to defend his/her thesis in a seminar or a conference.
Importance for a professional
At times, managers or executives in a company are required to prepare a report and then give an oral presentation on that report. Their performance can make or mar their career.
Importance for business
Oral communication are of huge significance in today’s business environment. It’s simply because nothing has more impact, or is quite as impressive, as a well-delivered oral presentation.
Properly executed and in the right context, they can inform, motivate and convince more effectively than any other single form of communication. As a result, employers place great value on presentation skills.
As a marketing tool
Ability to deliver oral presentation is one of the most effective tools of marketing. For instance, consider these two typical situations where oral presentation skill will be needed as a marketing strategy:
Go to Section:
What is Oral Communication | Oral Communication Definition |
Modes of Oral Communication | Advantages of Oral Communication | Disadvantages of Oral Communication | How to Make Oral Communication Effective | Importance of Oral Communication | Principles of Oral Communication |
Principles of Oral Communication
The following are the main principles of oral communication:
- Clarity
- Simplicity
- Source of information
- Adequacy
- Consistency
- Principle of time
- Balance between uniformly and adaptability
- Emotional Appeal
- Consultation
- Feedback
- Purpose
- Empathy
- Rehearsal
- Selection of main idea
- Introduction
- Easiness
- Researching the topic
- Summary
Clarity
In oral communication the meaning of the words and the language should be clear so that the audience does not misunderstand it. One should avoid the use of technical, very difficult or literary words.
Simplicity
The communication should be simple so that every type of audience finds it easy to understand.
Source of information
The sources of information used in the communication should be reliable and the audience should be informed about the source to increase their confidence.
Adequacy
The quantity, weightage, expansion and the subject matter should be decided in a wise manner, communication that are lengthy, too detailed and difficult are boring. Over abundance of information puts strain on the mental ability. Thinking and working of the audience.
Consistency
The figures and information used in the communication should not be in conflict with the policies, objectives and programmes of the institutions.
Principle of time
The communication should not take more time that intended. Principle of time leaves a good impression on the audience.
Balance between uniformly and adaptability
On the one hand uniformity of message in the communication should be attempted and on the other due importance should be given to the changer in today’s fast business. In other words one should try to strike a balance between uniformity and changeability or adaptability of words. h. Principle of Audience Analysis
To develop a mutual understanding with the audience and to remove the unnecessary difficulty of meanings the presenter should keep in mind the age, education, ability, knowledge and organizational position of the audience.
Emotional Appeal
In some communication there is a lack of logic and intellect therefore there should be an emotional appeal in the communication so that a positive response can be taken from the audience.
Consultation
To make a communication effective the communicator should consult all the related people. This way one can get some new advice and ideas.
Feedback
After communication the communicator should try to find the views, Ideas, opinions, objections and feelings of the audience. This develops an understanding between the two and the objective of communication is also fulfilled.
Purpose
In the communicator mind the purpose of the communication should be absolutely clear and defined. Objectives could be one or more. The purpose of the communication could be to inform, encourage, sympathies and entertain.
Empathy
The communicator should put himself in the place of audience while doing the communication. This brings about a similar opinion and creator mutual understanding.
Rehearsal
Before communication one should rehearsal atleast thrice. This increases self confidence and makes the communication easier.
Selection of main idea
The main idea or should be decided before hand. This makes the communication easier and interesting.
Introduction
It is said that first impression is the best impression. Thus, the communicator should introduce the communication with expertise, patience, cleverness and effectively that the audience can connect to it right till the end.
Easiness
A friendly behaviour should be used with the audience. As a result he can say opinion with ease and the audience too will accept it.
Researching the topic
Information, figures and other facts related to the communication should be collected so that some new ideas can be joined with the basic thought that is change should be acceptable.
Summary
At the end of the communication the main points should be revised which make the audience will remember the basic thought of the communication
PAIBOC Model
PAIBOC is an acronym devised by Kitty Locker and Stephen Kaczmarek. The PAIBOC model can be an instrumental tool for effective communication, specifically with speeches. PAIBOC refers to purpose, audience, information, benefits, objections and context. In an organisation, it is important to have a set process when initiating any business correspondence. PAIBOC is explained as follows:
P
It stands for purpose, which infers the purpose for initiating communication or writing a document. For example, the credit card division of a bank decides to send a formal e-mail to its credit card holders to make them understand the policy of moratorium period during Covid-19 Pandemic.
The purpose of the communication in this case is to educate its customers on the responsible use of credit cards and to use debt responsibly.
A
It stands for an audience, which explains who is the target audience or recipient of the communication. Having an insight into the target audience is cardinal for the success of communication. For instance, the target audience of communication via e-mail is the credit cardholders.
I
It stands for information, which infers what information the message should contain. The information that is shared relies on the audience. If the audience is not aware, then they need to be familiarised with facts.
For instance, the E-mail would involve information about the relaxation provided during the moratorium period; consequences of irresponsible use of credit; ways to manage credit/debt; and reasonable expectations of the use of credit.
B
It stands for benefits, what benefit both the sender and the receiver will derive from the exchange of communication.
For example, assessing how much interest they need to pay on the credit taken, how much interest customers have to pay during and after the moratorium period. In such a case, the bank can ensure that its customers are aware about the relaxation period and time limit to which they have to pay the bill.
O
It stands for objections, what objections can be raised by the receiver and how to overcome those objections tactfully. For instance, credit card holders can raise requests to extend the moratorium period in order to pay less interest on a credit card.
C
It stands for context, which refers to what is the relationship with the receiver. Context can also relate to morale in the organisation, the economy, the time of year and any special situation.
For instance, a formal e-mail can exchange important information with the customers and they will be more aware about the payment policy and procedure.

Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Reference
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company
- Business Communication: “M.K. Sehgal, Vandana Khetrapal, Excel Books
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Oral Communication | Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends
FAQ
What is Oral Communication?
In oral communication, spoken words are used. It includes face-to-face conversations, speech, telephonic conversation, video, radio, television, voice over internet.
Read Complete Article: Oral Communication
What is Business Communication?
Business communication is the expression, channelling, receiving and interchanging of ideas in commerce and industry.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
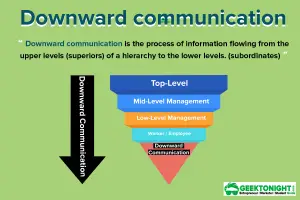
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
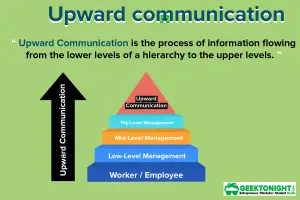
- Upward Communication
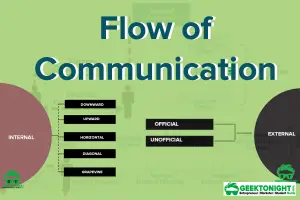
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?








I’m satisfied from this notes.
Thank you.
The best for research purposes