What is Downward Communication?
Downward Communication flows from a top-level to a low level in an organisation is known as downward communication.
In other words, communication that takes place from superiors to subordinates in a chain of command is a downward communication.
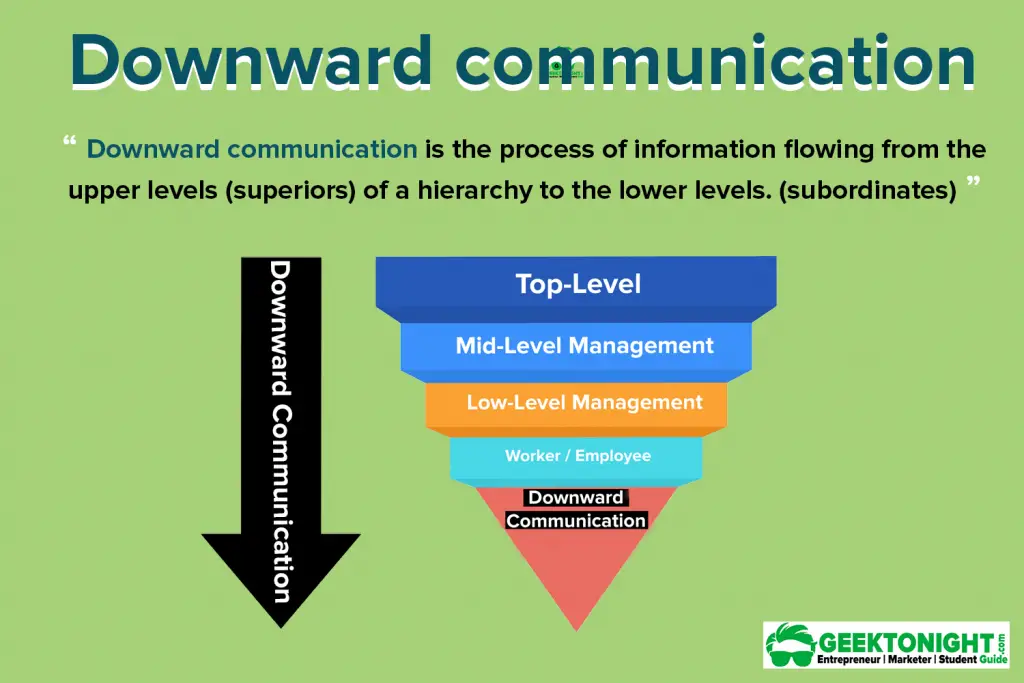
Table of Content
This flow of communication is used by the managers to convey work-related information to the employees at lower levels. Employees require this information for carrying out their jobs and for meeting their manager’s expectations.
It may include efficiently managing the tone of the message, and also showing skill in a delegation to make sure the job is done efficiently by the right person.
Importance of Downward Communication
Importance of Downward Communication are:
- To give an idea
- To encourage
- To maintain discipline
- To inform job rationale
- To explain about change
- To give direction
- Assignment of job
- To control
- To evaluate
To give an idea
With the help of downward communication objectives, policies, rules are explained to the subordinates by superior to give complete understanding.
To encourage
Employees are required to be motivated to work more to achieve organisational objectives. Management has to resort to downward communication to encourage lower-level employees.
To maintain discipline
Such communication follows the organisational hierarchy, so every section unit or department must follow the set rules or procedure. As a result discipline is ensured.
To inform job rationale
An important objective of this type of communication is to give information regarding the rationale of the task assigned and its relation to other organisational tasks.
To explain about change
Changes are dependent to circumstances. When there is any change in respect of plans, policies, procedures or rules etc. such are communication with explanation through downward communication.
To give direction
To direct any assignment, job or task to the subordinates, superior makes downward communication.
Assignment of job
To assign job according to efficiency of the workers, superior makes justification through downward communication.
To control
Since necessary instructions are forwarded through downward communication, employees are very much aware about their task and activities. Therefore such communication can act as a control tool.
To evaluate
Downward communication helps supervisors to evaluate works performed by the employees. Downward communication is used to inform the employees of their evaluations.
Advantages of Downward Communication
The advantages of downward communication are as follows:
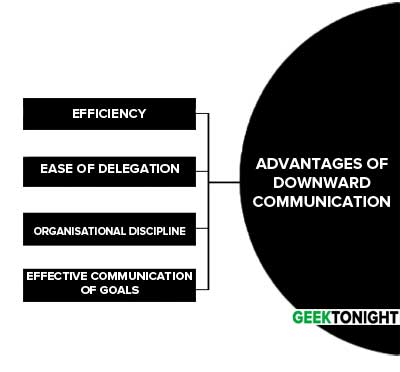
Efficiency
Downward communication offers efficiencies because instructions and information come from the sources in power that are able to coordinate activities from the top of the organisation.
Ease of delegation
Delegation is much easier if the delegation comes directly from the vertical communication structure representing the chain of command.
Organisational discipline
Downward communication follows the organisation’s hierarchy, meaning that organisational discipline and member compliance is much easier to maintain.
Effective communication of goals
Upper management can easily communicate goals and assign responsibilities regarding achieving those goals.
Disadvantages of Downward Communication
The disadvantages of downward communication are as follows:

Interpretative problems
Downward communication presents interpretation problems because of the distortion effect and the slow feedback for message clarification.
Distortion
Ever played the grapevine game? Downward communications can become distorted as it proceeds through multiple levels of the organisation.
Not motivating
Given slow feedback and the dependence on formal channels of communication, this method of communication doesn’t really help with motivation.
Slow feedback
It takes time for messages to go down the organisation and then up the organisation and then back down again. This means that feedback can be slow, resulting in problems, especially in a dynamic environment.
Lowers morale
Given the time communication takes and the problem with distorted messages, downward communications can have a negative impact on organisational morale.
Purpose of Downward Communication
Canary (2011) has identified five general purposes of downward communication:
- Implementation of goals, strategies, and objectives
- Job instructions and rationale
- Procedures and practices
- Performance feedback
- Socialization

Implementation of goals, strategies, and objectives
Communicating new strategies and goals provides information about specific targets and expected behaviors. It gives direction for lower levels of the school/school district, community college, or university.
For example: “The new reform mandate is for real. We must improve the quality of student learning if we are to succeed.”
Job instructions and rationale
These are directives on how to do a specific task and how the job relates to other activities of the school organization. Schools, community colleges, or universities need to coordinate individual and departmental objectives with organization-wide goals.
We often fail to provide enough of this kind of information, leaving it to the individual staff member to get the big picture.
Procedures and practices
These are messages defining the school organization’s policies, rules, regulations, benefits, and structural arrangements in order to get some degree of uniformity in organization practices.
In school organizations, this information is transmitted to staff members through board and organization-wide policy manuals, handbooks, and the day-to-day operation of the school organization.
Performance feedback
Departmental progress reports, individual performance appraisals, and other means are used to tell departments or individuals how well they are doing with respect to performance standards and goals.
For example: “Mary, your work on the computer terminal has greatly improved the efficiency of our department.”
Every school organization tries to motivate staff members to adopt the institution’s mission and cultural values and to participate in special ceremonies, such as picnics and United Way campaigns. It is an attempt to get a commitment, a sense of belonging, and a unity of direction among staff members (Lunenburg & Ornstein, 2008).
For example: “The school thinks of its employees as family and would like to invite everyone to attend the annual picnic and fair on May 30.”
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Reference
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company.
- Business Communication: “M.K. Sehgal, Vandana Khetrapal, Excel Books.
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons.
- Fred C. Lunenburg (2010). Formal Communication Channels: Upward, Downward, Horizontal, and External Retrieved 3 Feb, 2021
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Downward Communication | Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?













This is so good
Gooe information
Thank you
Well written