What is Barriers to Communication?
Barriers to business communication refer to any obstacles or challenges that impede the effective exchange of information between individuals or groups within an organization or between different organizations. These barriers can prevent the transmission of messages or ideas, leading to misunderstandings, errors, and reduced productivity.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Barriers to Communication?
- 2 Barriers To Business Communication
- 3 Overcome Barriers To Communication
- 3.1 Fostering Good Relationships
- 3.2 Purposeful and well focused communication
- 3.3 Coordination between superiors and subordinates
- 3.4 Avoid technical language
- 3.5 Accuracy
- 3.6 Feedback
- 3.7 Clarity in message
- 3.8 Communication of organizational philosophy
- 3.9 Flat organizational structure
- 3.10 Division of Labour
- 3.11 Minimize SemPantic Problems
- 3.12 Organization policies
- 3.13 Proper communication channels
- 3.14 Right feedback
- 4 Business Communication Notes
- 5 Reference
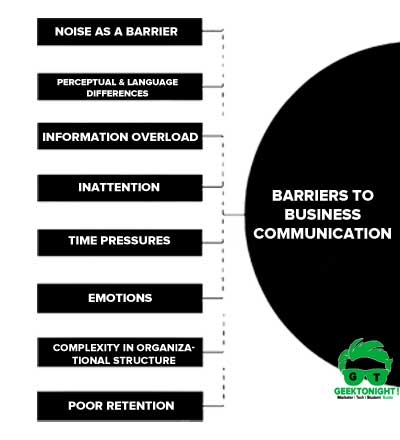
Barriers To Business Communication
The barriers to business communication may also be defined as obstructions or blockades or hurdles, stoppages and bottlenecks ineffective system of communication.
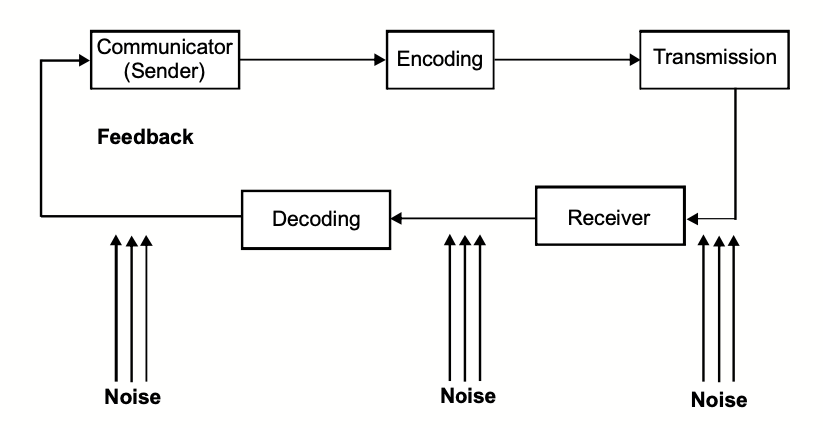
The figure below shows the concept of an obstacle to communication.
- Noise as a Barrier
- Perceptual and Language Differences
- Information Overload
- Inattention
- Time Pressures
- Emotions
- Complexity in Organizational Structure
- Poor Retention
Noise as a Barrier
“Noise” is the disruption or hindrance in communication process anywhere along the way as shown in the figure. It can occur at any point in the communication process.
Noise can be the sound of someone coughing, a truck driving by, or two people talking close at hand. It can also include disruptions such as a letter being lost in the mail (either traditional or electronic), a telephone line going dead, or one of the participants in a conversation being called away before the communication process is completed.
Perceptual and Language Differences
Perception is in general how each individual interprets the world around him. People generally want to receive messages which are significant to them.
Example: A person is on leave for a month due to personal reasons (family member being critical). The HR Manager may be in confusion whether to retain that employee or not, the immediate manager might think of substitute because his team’s productivity is being hampered, the family members might take him as an emotional hold.
Information Overload
Managers are bordered with a pool of information. It is necessary to control this information flow else the information is likely to be misinterpreted or forgotten or overlooked. As a consequence, communication is less effective.
Inattention
At times we just not listen, but only hear
Example: A traveller may pay attention to one “NO PARKING” sign, but if such sign is put all over the city, he no longer listens to it. Therefore, repetitive messages should be dismissed for effective communication.
Time Pressures
Frequently in an organization, the targets have to be achieved within a specified time period, the failure of which has adverse consequences. In a haste to meet deadlines, the formal channels of communication are shortened, or messages are partially given, i.e., not completely channelled. Thus ample time should be given for effective communication.
Emotions
Emotional state at a peculiar point of time also affects communication. If the receiver feels that communicator is angry he understands that the information being sent is very bad.
Complexity in Organizational Structure
Greater the power structure in an organization (i.e. more the number of managerial levels), more are the chances of communication getting lost. Only the people at the top level can see the overall picture while the people at low level just have knowledge about their own area and a little knowledge about other areas.
Poor Retention
Human memory cannot function outside a limit. One can’t always retain what is being told especially if he is not interested or not attentive. This leads to communication collapse.
Overcome Barriers To Communication
How to overcome barriers in communication? Constant work is required to overcome barriers which unconsciously sneak up in the process of communication. Barriers can be overcome if sufficient effort is put into the communication process and it is wanted that communication be effective and efficient.
Following are some of the measures to overcome barriers to communication:
- Fostering Good Relationships
- Purposeful and well focused communication
- Coordination between superiors and subordinates
- Avoid technical language
- Accuracy
- Feedback
- Clarity in message
- Communication of organizational philosophy
- Flat organizational structure
- Division of Labour
- Minimize SemPantic Problems
- Organization policies
- Proper communication channels
- Right feedback

Fostering Good Relationships
Strong relationships must be forged between the employer and employee in order to avoid misunderstandings and accept each other’s view in order to remove the barriers and to help proper communication in the organization.
Purposeful and well focused communication
Communication should be purposeful and aimed at an individual. At the end of the communication, the receiver should not be left to feel that communication had been meaningless or useless.
Coordination between superiors and subordinates
In case, the superior thinks at a level, which is different from that of the subordinate and vice-versa, it will impact the effectiveness of communication. Thus, there should be good and proper coordination and co-operation between the superior and subordinate for effective communication.
Avoid technical language
Specialized language should be avoided. Efforts should be made to use language commonly understood by the receiver and sender of the message. There should be least use of technical jargon in the communication process.
Accuracy
There should be accuracy in the message to be carried between both parties for the communication to improve its effectiveness.
Feedback
The selective percept of receiver should be minimized through proper feedback. The drawback of the selective perception should be explained to minimize the barriers.
Clarity in message
The message to be transferred should be clear, practical accurate and without any equivocalness.
Communication of organizational philosophy
Efforts have to be made in a planned way to sensitize people with the organizational philosophy. It should be properly communicated to its employees so that it allows proper attention in their day-today communication.
Flat organizational structure
The organization should have a clear-cut and simple organizational structure. Tall hierarchical structures should be removed, and changed to flat structures to avert excessive control of information. Wrong information transferred to anyone in the organization can prove detrimental. Proper restyle of organizational structure will trim down the status gap.
Division of Labour
There should be proper division of labour between people in order to reduce information overload and keep delay in information transfer.
Minimize SemPantic Problems
People use either the same word in different ways or different words in the same way. One will be surprised to know that there are 15 different meanings of the word ‘charge’ in the English language. They also occur when people use jargons or professional shorthand which they expect others to understand, or use language that is outside the other’s vocabulary.
Organization policies
The organization should devise its policies in such a way that it will give full advantage to all members of the organization. It should be flexible and easy to implement. While the organization’s goal must be clear, everyone must know about his position in the organizational communication process.
Proper communication channels
If one wants immediate action from the receiver, there is no need to send a lengthy discussion report. One can pick up the telephone or go to his office to tell him what to do. Also remember that a picture is worth a thousand words, and in this age of computer graphics, information can be produced more rapidly in this way too.
Right feedback
Although one-way communication is quicker, two-way communication is more exact. In complex situations, it helps both sender and receiver to measure their understanding and improves their joint commitment towards the task. It alters both parties to describe and clear misunderstandings leading to a higher quality of reception and acceptance.
Thus, in order to communicate effectively, there is need to overcome all barriers and also develop skills to improve existing communication abilities.

Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Reference
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company.
- Business Communication: “M.K. Sehgal, Vandana Khetrapal, Excel Books.
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons.
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Notes? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Barriers To Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
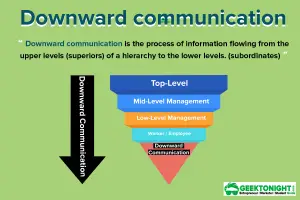
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?