What is Economics?
Economics is the science that deals with production, exchange and consumption of various commodities in economic systems. It shows how scarce resources can be used to increase wealth and human welfare. The central focus of economics is on the scarcity of resources and choices among their alternative uses.

Table of Content
Economics is broadly classified into two types
- Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behaviour of individual consumers and organisations in the market. It focuses on the demand and supply, pricing, and output of individual organisations.
- Macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole and deals with issues related to national income, employment pattern, inflation, recession, and economic growth.
Managers should have a clear understanding of different economic concepts, theories, and tools. Business economics or managerial economics is a specialized discipline of economics that undertakes a study of various economic theories, logic, and tools used in business decision making.
Also Read: Difference Between Micro and Macro Economics
Meaning of Economics
In the meaning of economics, the term ‘Economics’ owes its origin to the Greek word ‘Oikonomia’, which can be divided into two parts: oikos means home and nomos means management.
Thus, in earlier times, economics was referred to as home management where the head of a family managed the needs of family members from his limited income.
Till the 19th century, Economics was known as ‘Political Economy.’ The book named ‘An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations’ (1776) usually abbreviated as ‘The Wealth of Nations’, by Adam Smith is considered as the first modern work of Economics.
Also Read: Laws of Economics
Economics Definition
Defining economics has always been a controversial issue since time immemorial. Definition of economics by different economists have different viewpoints. Some economists had a viewpoint that economics deals with problems, such as inflation and unemployment while others believed that economics is a study of money,
Therefore, a simple definition of economics is defined by taking four definition

Wealth Definition of Economics
This is a classical definition of economics by Adam Smith, who is also considered as the father of modern economics.
Economics is the study of the nature and causes of nations’ wealth or simply as the study of wealth.
Adam Smith
Key Features of Wealth economics definition
- The main objective of Economics is to gain maximum wealth as possible
- The core of economic activity: are production, distribution and consumption.
- It deals with the causes of the creation of wealth in an economy.
- The term ‘wealth’ used in this definition referred to material wealth.
Welfare Definition of Economics
It is a neo-classical definition of economics by Alfred Marshall.
It is the study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. It enquires how he gets his income and how he uses it. In one view, it is a study of wealth and on other hand it is part of study of man.
Alfred Marshall
Key features of Welfare economics definition
- It defines Economics as the study of activities related to a human being and their material welfare.
- Marshall clarified that Economics is related to incomes of individuals and its uses for creating material welfare.
- Collectively incomes of a group of individuals form the wealth of a nation and ultimate goal is to increase welfare of individual by their routine activities.
Scarcity Definition of Economics
It is a pre-Keynesian definition of economics by robbins in his book ‘Essays on the Nature and Significance of the Economic Science’ (1932).
Economics is a science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.
Lionel Charles Robbins
Key features of Scarcity economics definition
- It recognized that Economics is a science deal with the economic behaviours of a human being.
- It also focuses on optimum utilisation of scarce resources.
- It provides three basic features of human existence, which are unlimited wants, limited resources, and alternative uses of limited resources
- There is a need for efficient use of scarce resources, and the primary objective of Economics is to ensure efficiency in the use of resources with a purpose to satisfy human wants.
Growth Definition of Economics
This is the modern perspective definition of economics by Samuelson. He provided the growth-oriented definition of economics.
Economics is the study of how man and society choose with or without the use of money to employ the scarce productive resources, which have alternative uses, to produce various commodities over time and distributing them for consumption, how or in the future among various person or groups in society.
Paul Samuelson
Key features of Growth economics definition
- It deals with the allocation of scarce resource to be used in productive purposes.
- The selection of the most efficient use of the resources from alternative ways.
- The growth of economies will depend upon the consumption and production in the economy.
- This definition also points towards Economics as a study of an economic system.
Economics have different definition of economics by different economists and social thinkers with different objectives and contexts. All these definitions are correct and none can be taken as universally acceptable.
Also Read: Economies of scale and Diseconomies of Scale
Scope of economics
The scope of economics has been broadened to many and some area are mentioned below:
- Microeconomics
- Macroeconomics
- International arena
- Public finance
- Welfare
- Health
- Environmental studies
- Urban and rural development

Also Read: Scope of Economics
Nature of Economics
There are a number of controversial issues related to its nature. Let us now understand the true nature of economics.
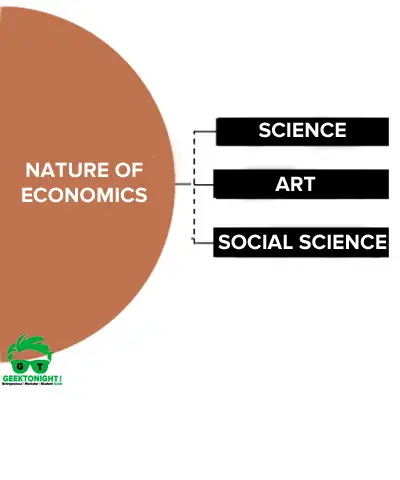
Also Read: Nature of Economics
Assumptions in Economics
There are certain assumptions in economics about an economic situation to happen in the future. Economists use assumptions to break down complex economic processes and advocate different theories to understand economic variables.
Three important assumptions in economics, are as follows:
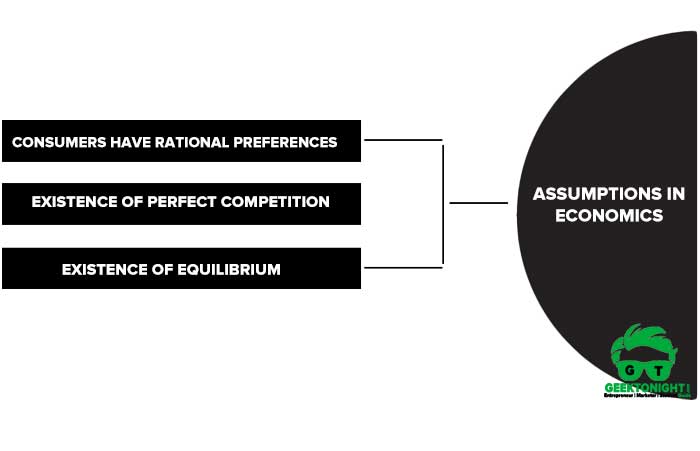
Consumers have rational preferences
This assumption states that consumers act in a rational manner and focus on satisfying their needs.
It is also assumed that the tastes of consumers remain constant for a long period. For instance, a consumer who is vegetarian may not change his/her preferences in the near future.
Existence of perfect competition
According to this assumption, there is perfect competition in an economy, wherein there are numerous buyers and sellers.
It is assumed that homogenous products exist in the market and both buyers and sellers cannot affect prices.
Existence of equilibrium
As per this assumption, equilibrium exists wherein both consumers and entrepreneurs achieve maximum satisfaction.
In a market, there can be two types of equilibrium: industry equilibrium and firm’s equilibrium. An industry is at equilibrium if profits achieved are normal. On the other hand, a firm is at the state of equilibrium if its profits are maximum.
Also Read: What is Business Cycle?
Difference Between Economics and Business Economics
| Economics | Business Economics |
|---|---|
| Economics is a traditional subject that has prevailed from a long time. | Business economics is a modern concept and is still developing. |
| Economics mainly covers theoretical aspects. | Business economics covers practical aspects. |
| In economics, the problems of individuals and societies are studied. | In Business economics, the main area of study is the problems of organisations. |
| In economics, only economic factors are considered. | In business economic, both economic and no-economic factors are considered. |
| Both microeconomics and macroeconomics fall under the scope of economics. | Only microeconomics falls under the scope of business economics. |
| Economics has a wider scope and covers the economic issues of nations. | Business economics is a part of economics and is limited to the economic problems of organisations |
Also Read: Production in Economics
Business Economics Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Economics Tutorial? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on What is Economics | Business Economics in the comments section.
Business Economics Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)











