What is Demand Function?
Demand function represents the relationship between the quantity demanded for a commodity (dependent variable) and the price of the commodity (independent variable).
Table of Content
Demand Function Formula
Mathematically, a function is a symbolic representation of the relationship between dependent and independent variables.
Let us assume that the quantity demanded of a commodity X is Dx, which depends only on its price Px, while other factors are constant. It can be mathematically represented as:
Dx = f (Px)
However, the quantitative relationship between Dx and Px is expressed as:
Dx = a – bPx
Where a (intercept) and b (relationship between Dx and Px) are constants.
Also Read: Law of Demand
Types of Demand Function
2 types of demand function are:
Linear demand function
In the linear demand function, the slope of the demand curve remains constant throughout its length. A linear demand equation is mathematically expressed as:
Dx = a – bPx
In this equation, a denotes the total demand at zero price.
b = slope or the relationship between Dx and Px
b can also be denoted by change in Dx for change in Px
If the values of a and b are known, the demand for a commodity at any given price can be computed using the equation given above.
For example, let us assume a = 50, b = 2.5, and Px= 10:
Demand function is:
Dx = 50 – 2.5 (Px)
Therefore, Dx = 50 – 2.5 (10)
or Dx= 25 units
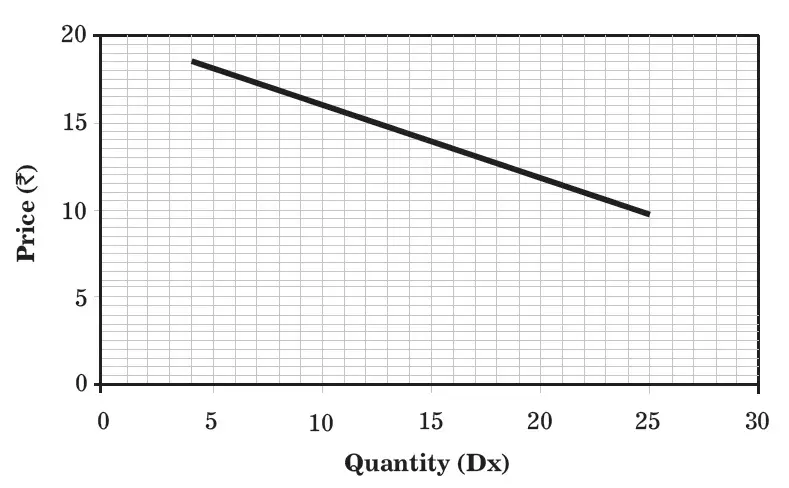
The demand schedule for the above function is given in Table
| Quantity Demanded of Commodity X | Price Levels of Commodity X |
|---|---|
| 5 | 18 |
| 10 | 16 |
| 15 | 14 |
| 20 | 12 |
When the demand schedule is plotted on a graph, it produces a linear demand curve, which is shown in Figure below.
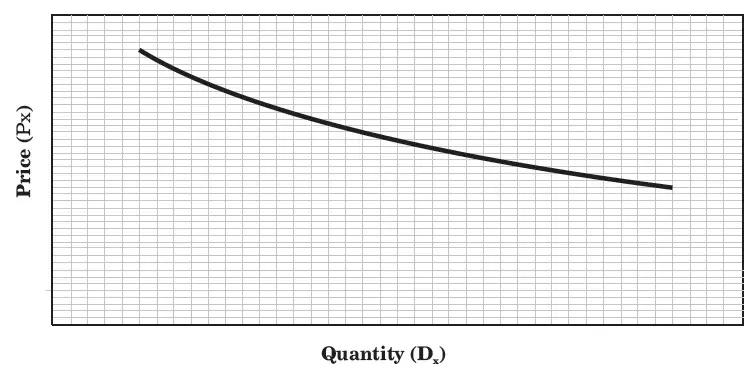
Non linear demand function
In the non linear or curvilinear demand function, the slope of the demand curve (ΔP/ΔQ) changes along the demand curve. Instead of a demand line, non-linear demand function yields a demand curve.
A non-linear demand equation is mathematically expressed as:
Dx = a (Px)-b
Or of a rectangular hyperbola of the form
Dx = (a/Px + c) b
where a, b, c> 0
Exponent –b of price in the non-linear demand function refers to the coefficient of the price elasticity of demand.
Figure, represents a non-linear demand function:
Also Read: What is Demand?
Business Economics Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Economics Tutorial? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Demand Function | Business Economics in the comments section.
Business Economics Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)













