What is Communication?
Communication is the process of passing information (sending) and understanding (receiving) the same from one person to another through verbal and non-verbal means. Thus, communication means to understand information, facts or opinions of someone.
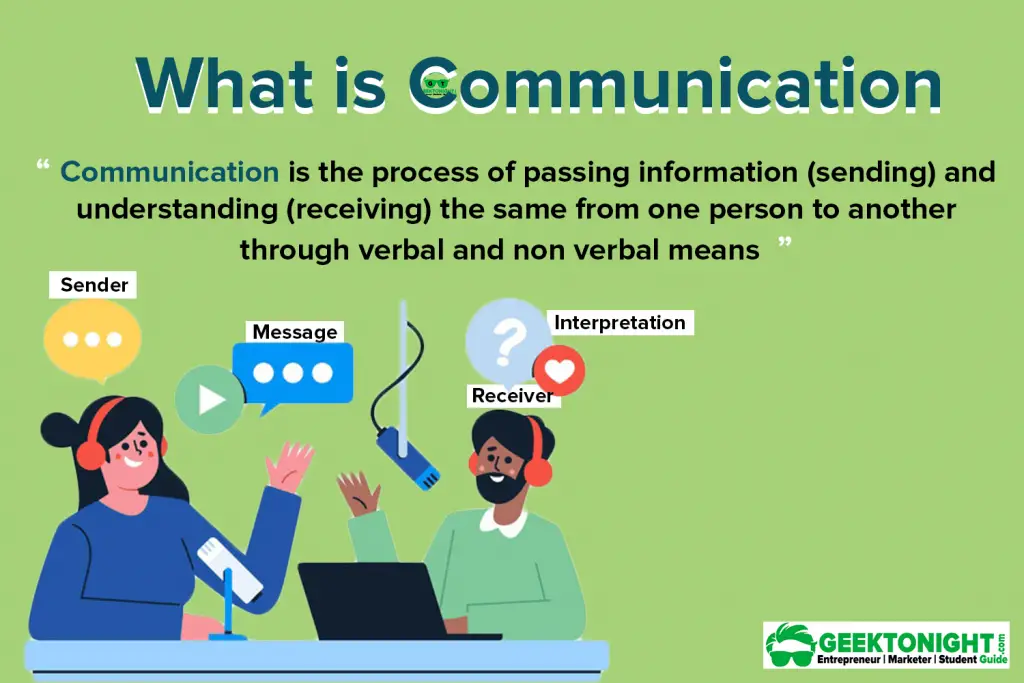
Communication is the giving and receiving of feedback between individuals and/or groups for the purpose of exchanging information.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Communication?
- 2 Communication Meaning
- 3 Communication Definition
- 4 Need for Communication
- 5 Purpose of Communication
- 6 Importance of Communication
- 7 Forms of Communication
- 8 Process of Communication
- 9 Elements of Communication Process
- 10 Objectives of Communication
- 11 Nature of Communication
- 12 7 C of Communication
- 13 Barriers To Communication
- 14 Business Communication Notes
- 15 Reference
Communication Meaning
The word communication originates from the Latin word “communis” which means “Common”. This means that we try to establish “commonness” with someone in communication.
Literally, communication means to inform, to tell, to show, or to spread information. Thus, it may be interpreted as an interchange of thought or information to bring about understanding and confidence for good industrial relations.
Communication Definition
The word “Communication” has been defined differently by different management thinkers and experts. Some of these definitions of communication are given below:
Need for Communication
What is communication Need? Today every organization small or multinational needs an effective communication.
According to Koontz and Weihrich, communication is needed to:
- Increase employees job performance and effectiveness by updating their knowledge
- Promote employees sense of belonging and commitment
- Effect changes smoothly
- Motivate and create a sense of identification with organization and its goals
- Inform and convince employees about decisions and the reasons behind those decisions
- Develop employees clear understanding of future growth opportunities in the organization
- Empower employees with information on development and relevant activities
Purpose of Communication
What is communication Process? Communication could have many purposes depending on the context and person involved. Communication within a family, seminar, theatre, office has different purposes that have to be achieved.
Purpose To inform
The basic purpose of Communication is to keep the people informed. Various important facts and information are required to be given on time.
Peter F. Drucker has stated,” “The manager has a specific tool: Information ……….”.
Thus, communication may be to inform the people about ideas, views, suggestion etc. Managers need complete, accurate and precise information to plan and organise. Employees need it to translate planning into reality.
To persuade
Persuasion may be defined as an effort to influence the attitudes, feelings or beliefs of others.
Persuasion consists of four important steps:
- Analysis of situation
- Preparing the receiver
- Delivering the message and
- Prompting action
All these depend on effective communication. It is not enough to inform the people, along with it they need persuasion to attain common goals. Thus, communication is to pursue people so that they ensure their efforts in right direction.
To educate
Communication may have a purpose to educate the people. It is very conscious process of communication. It involves both teaching and learning with an object to widen knowledge as well as improve skills.
For the purpose knowledge, skills and attitude are developed among the people by communication.
To train
Training is the act of increasing the knowledge and skill for a particular task, communication is an integral part of training. To achieve proficiency in a particular field instructions, lectures, demonstrations, practices and discussion are required which are part of communication.
To motivate
Motivation is creating and releasing work energy within an individual. High level of morale and motivation is a must to ensure high-level of achievements. Communication provides a mean to keep people motivated.
Besides money, various factors such as job satisfaction, prestige, a sense of belonging, recognition can also motivate a person to work sincerely and effectively. Motivation as a form of communication deals with these factors.
To integrate
where large number of people working altogether, communication helps them to work in an integrated manner. Exchange of views, problems and other information can create better understanding among them, which is resulted into integrated efforts by them.
To relate
As human being is a social creature. They require good relationship. Communication is not only building relation but also nurturing mutually beneficial relationship.
communication may have a purpose to entertain. Communication also facilitates social bonding. It also helps in creating pleasure events which entertain the human being and relive them from tension.
Importance of Communication
What is communication Importance? Communication is a vital force, it is an important aspect of effective business organization
Importance of Communication are:
- Efficient functioning of the undertaking
- Facilitates decision making
- Proper planning
- Minimize organisational conflicts
- Job satisfaction and higher productivity
- Democratic management
- To establish better labour relations
- Effective organizing
- Enhance motivation and morale
- Sound human and industrial relation
- Efficient functioning of the undertaking: The efficient performance of employees of an organization depends on effective communication within the organization.
- Facilitates decision making: Desired results of an organization largely depends on the right decision at the right time. A communication system is a prerequisite for making a sound decision.
- Proper planning: Communication is required not only for effective planning but also to ensure its better implementation.
- Minimize organisational conflicts: Proper communication reduces conflicts by developing understanding. Communication helps them to know the views, problems, and thoughts of others.
- Job satisfaction and higher productivity: Effective communication promotes better performance as people are able to understand their jobs and roles in a better manner.
- Democratic management: Modern business organization are following democratic system of management. It requires good channels of communication so that employees, consumers and other stakeholders share information and participate in the discussion, consultation and decision making.
- To establish better labour relations: Effective communication creates better management and labour relationship.
- Effective organizing: Organizing involves delegation of authority, assigning liability, decentralization and establishes the relationship between the members which cannot be done in the absence of communication.
- Enhance motivation and morale: Communication helps in enhancing the morale of the employees because they are aware of their role in the business firm.
- Sound human and industrial relation: The basic reason for disputes between labour and management is a communication gap. With the help of effective communication, sound relations can be maintained as it promotes mutual understanding, cooperation and goodwill.
Forms of Communication
Communication implies an exchange of information. It may be in various forms, it may be classified on the following basis:
3 Forms of Communications are:
- On the basis of Organisational Structure
- On the basis of Direction
- On the basis of Mode of Expression
- Organisational Structure
- Formal Communication
- Informal Communication
- Direction
- Downward Communication
- Upward Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Diagonal Communication
- Mode of Expression
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Oral Communication
- Written Communication
Process of Communication
What is communication Process? Communication is a process, generally a two-way process. The process is a concept that is dynamic and ever-changing.
The process, in fact, is both times dimensional as well as space dimensional in which action unfolds in a continual manner towards some goal.
In other words, communication being a process attempts to provide information to the receiver and also to persuade the concerned person according to the sender of the message.
The two-way communication process is superior to one-way communication in the following respects:
- Two-way communication is more effective than one-way communication. The feedback allows the sender to refine his communication so that it becomes more precise and accurate.
- Receivers self-confidence is higher in case of two-way communication as they are permitted to ask questions and seek clarification from the senders.
Sequencing of Communication Process
- Ideation: Conceiving of the idea by the sender or source
- Encoding: Encoding the message
- Transmission: Transmission of message
- Receiving: Receiving of the message by receiver
- Decoding: decoding the message
- Action: Behavior or action on the message
The process of communication is further refined as
Figure shows that there are six phases in the entire communication process. At phase I, the sender has an idea or information. At phase II, the sender encodes the idea for transmission and at phase III, the encoded idea is transmitted by the sender through the strategically selected channel or medium of transmission.
At phase IV, the receiver gets the message, at phase V, the receiver decodes the message and finally at phase VI, the feedback is sent by the receiver.
Mary Ellen Guffey says that, “we cannot just glance at another person and transfer meaning directly from mind to mind, we engage in a sensitive process of communication that involves five steps”. These steps are depicted in Figure.
Elements of Communication Process
The main elements that are also human as the concepts or the components of the process of communication are discussed to draw the basic understanding of the communication process.
Elements of Communication Process are:
- Message
- Sender
- Encoding
- Medium and Channel
- Receiver
- Decoding
- Feedback
- Message: It is information, written or spoken, which is to be sent from one person to another. Here, the word person stands for the two ends of a system and may represent an individual, or a group of individuals, or even electronic machines.
The most important characteristic of a message as an element of communication is that it is organized, structured, shaped and selective. It exists in the mind of the sender (communicator). - Sender: The person who transmits, spreads, or communicates a message or operates an electronic device is the sender i.e., one who conceives and initiates the message. The sender transmits the message with the purpose of informing/persuading/influencing/ changing the attitude, opinion, or behaviour of the receiver (audience/listener).
- Encoding: The method by which a message is expressed is called encoding. Message arises in the mind in the form of Idea. That idea is transmitted by the sender to receiver in the form of words, symbols, pictures, day-to-day language, etc. Otherwise, it may not be possible for the receiver to understand it.
Keeping in view, the purpose of communication, selection of words or symbols for encoding should be such as make the receiver understand the communication correctly. - Medium and Channel: The method or channel means by which a message is transmitted by a sender to a receiver called medium or channel. For instance, a letter is a medium and postal or couriers service a channel. If a message is communicated by telephone, then an oral message is a medium and the telephone a channel.
- Receiver: The receiver of communication is a person or a group or an organization that receives the message. He is the destination of the message. In its absence, the process of communication is incomplete.
He not only receives the messages but also understands what is implied in it. He is a decoder of the message responds to it or gives necessary feedback. - Decoding: Decoding is a mental process by which the receiver draws meanings, from the words, symbols or pictures of the message. The receiver does decoding or understands it. That is the reason he is also called a decoder. If the receiver understands the meanings of the words or the symbols correctly, then his decoding is perfect.
- Feedback: Feedback is the receiver’s response to the message. Feedback is the final link in the communication process. On its receipt, the receiver expresses his response by way of acknowledgement to the sender.
Feedback is the key element in the communication process because it enables the sender to evaluate the effectiveness of the message.
Objectives of Communication
John G. Glover in his book on “Fundamentals of Top Management’ has given the following objectives of communication in an organisation:
- To keep the employees acquainted with the company’s progress and development programmes.
- To provide employees with necessary orders and instructions in connections with their rights, duties and responsibilities.
- To solicit information from the employees which may help the management in decision making.
- To express the interest of management to its personnel.
- To minimize labour turnover.
- To motivate the employees towards his job and to create interest in the work of the company.
- To indoctrinate employees with the will to work and the benefits from their association with the company.
- To instil each employee with personal prestige and pride in being a member of the corporate body.
Nature of Communication
- Communication is a process of encoding, sending and decoding.
- It is the essence of leading, it is the basis for action and cooperation.
- It is a two way process, there must be at least two people i.e. sender and receiver.
- Communication is not a constant as it is dynamic in nature and ever changes as per the circumstances.
- It is a universal activity which is equally useful and necessary in politics, religion and economy.
- It may be verbal or non-verbal
- It is an exchange of facts and opinion
- It means, not an end as its primary purpose is to motivate response and the end results are understanding.
- It is a continuous process as it does not finish after one message.
- It may be formal or informal.
- It may be oral, written or even gestural.
- It is an interactive process.
7 C of Communication
There are 7 C of effective communication which are relevant to both written as well as oral communication.
7 C of Communication are as follows:
- Completeness: The communication must be complete. It should convey all facts required by the audience.
- Conciseness: means communicating what you want to express in the least possible words without forgoing the other C’s of communication.
- Consideration: implies “stepping into the shoes of others”. Effective communication must take the audience into consideration.
- Clarity: implies stressing on a particular message or goal at a time, rather than trying to achieve too much at once.
- Concreteness: Concrete communication means being particular and clear rather than fuzzy and general. Concreteness strengthens confidence.
- Courtesy: in message entails the message should show the sender’s expression as well as should respect the receiver. The sender of the message should be sincerely polite, judicious, reflective and keen.
- Correctness: in communication means that there are no grammatical errors in communication.
Barriers To Communication
What is communication barriers? The barriers to business communication are anything that interferes in the communication process
- Noise as a Barrier: “Noise” is the disruption or hindrance in communication process anywhere along the way
- Perceptual and Language Differences: Perception is in general how each individual interprets the world around him. People generally want to receive messages which are significant to them.
- Information Overload: Managers are bordered with a pool of information. It is necessary to control this information flow else the information is likely to be misinterpreted or forgotten or overlooked. As a consequence, communication is less effective.
- Inattention: At times we just not listen, but only hear
- Time Pressures: Frequently in an organization, the targets have to be achieved within a specified time period, the failure of which has adverse consequences.
- Emotions: Emotional state at a peculiar point of time also affects communication. If the receiver feels that communicator is angry he understands that the information being sent is very bad.
- Complexity in Organizational Structure: Greater the power structure in an organization, more are the chances of communication getting lost.
- Poor Retention: Human memory cannot function outside a limit. One can’t always retain what is being told especially if he is not interested or not attentive. This leads to communication collapse.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Reference
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company.
- Business Communication: “M.K. Sehgal, Vandana Khetrapal, Excel Books.
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons.
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on What is Communication? | Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
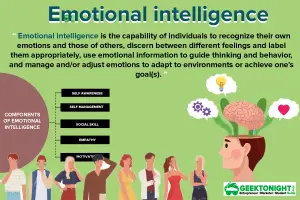
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?