What is Business Communication?
Business communication is the process of expression, channelling, receiving and interchanging of ideas in commerce and industry.

In simple words, Business communication is the process of sharing information between people within and outside a company in order to promote an organization’s goals, objectives, aims, and activities, as well as increase profits.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Business Communication?
- 2 What is Communication?
- 3 Business Communication Definition
- 4 Types of Communication
- 5 Success of Business through Communication
- 6 Importance of Business Communication
- 6.1 Efficient functioning of the undertaking
- 6.2 Facilitates decision making
- 6.3 Proper planning
- 6.4 Minimize organisational conflicts
- 6.5 Job satisfaction and higher productivity
- 6.6 Democratic management
- 6.7 To establish better labor relations
- 6.8 Effective organizing
- 6.9 Enhance motivation and morale
- 6.10 Sound human and industrial relation
- 7 Role of Communication in Business
- 8 7 C of Communication
- 9 Role of Communication in Business
- 10 Tools of Business Communication
- 11 Barriers To Communication
- 12 Characteristics of Non-verbal Communication in Organization
- 13 Business Communication Notes
- 14 Reference
What is Communication?
Communication is the process of passing information and understanding the same from one person to another. Thus, communication means to understand information, facts or opinions of someone.
Business Communication Definition
According to Ricks and Gow, Business communication is a system that affects change within the total organization.
According to W. H. Meaning, The exchange of ideas, news and views in connection with the business among the related parties is called business communication.
According to Prof. J. Haste, Communication occurred between two or more businessmen for organizing and administering business efficiently is called business communication.
According to Brennar, Business communication is the expression channelling, receiving and interchanging of ides in commerce and industry.
Types of Communication
Communication implies an exchange of information.
3 Forms of Communications are:
- On the basis of Organisational Structure
- On the basis of Direction
- On the basis of Mode of Expression
- Organisational Structure
- Direction
- Mode of Expression
Success of Business through Communication
Business communication may make relations or may break relations. Business communication asserts, sustains and animates business relations.
It can figure out the problems of the organization and it can produce problems if the executives are not perfect in communication with employees, suppliers and customers.
Business communication can contribute to industrial turbulence and at the same time can bring industrial peace. Following summarized points further rationalize the need or implication of communication.
Communication is:
- Basis of planning
- Basis of decision making
- Creating coordination and cooperation
- Establishment of effective leadership
- Development of human relations
- Helpful in building image
- Helpful in achieving peace and effective control
- Leading to high morale and motivation
- Unseen infrastructure of an organization
- Helpful in delegation of authority.
Importance of Business Communication
Communication is a vital force, it is an important aspect of effective business organization
Importance of Business Communication are:
- Efficient functioning of the undertaking
- Facilitates decision making
- Proper planning
- Minimize organisational conflicts
- Job satisfaction and higher productivity
- Democratic management
- To establish better labour relations
- Effective organizing
- Enhance motivation and morale
- Sound human and industrial relation
Efficient functioning of the undertaking
Every type of organization whether small or big, public or private, communication plays a vital role. It is said that “good communication is good business.” The efficient performance of employees of an organization depends on effective communication within the organization.
Facilitates decision making
Desired results of an organization largely depend on the right decision at the right time. A communication system is a prerequisite for making a sound decision.
The quality of decision-based on the availability of data, facts, reports discussions and other means of communication. It is also essential to communicate a decision to the person concerned for effective implementation.
Proper planning
Communication also facilitates effective planning According to Koontz and O’Donnell “Effective planning occurs when everyone responsible for it has access to complete information affecting areas of planning.” Thus, communication is required not only for effective planning but also to ensure its better implementation.
Minimize organisational conflicts
In an organisation where various employees are working at different level, the conflicts arise due to one or more reasons. Proper communication reduces the conflicts by developing understanding. Communication helps them to know the views, problems, and thoughts of others.
Shobhana Khandwala writes “most of the conflicts in a business are not basic but are caused by misunderstanding and ignorance of the facts, proper communication between the interested parties reduce the point of friction and minimize those that inevitably arise.”
Job satisfaction and higher productivity
Effective communication promotes better performance as people are able to understand their jobs and roles in a better manner. Various sources of production such as machine, material, money does not resulted into productivity unless highly motivated men are there, and it is done with the help of co
Democratic management
Modern business organization are following democratic system of management. It requires good channels of communication so that employees, consumers and other stakeholders share information and participate in discussion, consultation and decision making.
To establish better labor relations
Industrial peace is the need of the day. An effective communication creates better management and labour relationship. Labour communicates their problems, suggestion and expectations to the organizational head, on the other hand manager share their policies, programmes with subordinate and explain them that and how they are beneficial to them also. It results into better labour relationship.
Effective organizing
Organizing involves delegation of authority, assigning liability, decentralization and establishes relationship between the members which cannot be done in absence of communication.
According to Dale Yoder “Communication is at the very heart of the process of organising.” Thus, communication is important for effective organization as success or failure of organization depends on it.
Enhance motivation and morale
Communication helps in enhancing morale of the employees, because they are aware of their role in business firm. It awakens a sense of security and encourages them to work. Effective communication plays critical role in enhancing the motivation and morale of employees.
Sound human and industrial relation
Robert D. Berth states “It is impossible to have human relations without communication.” The basic reason of disputes between the labour and management is communication gap. With the help of effective communication sound relations can be maintained as it promotes mutual understanding, cooperation and goodwill.
Role of Communication in Business
Peter Ferdinand Drucker (November 19, 1909–November 11, 2005) was an Austrian-born American management consultant, educator, and author, whose writings added to the philosophical and practical foundations of the advanced business corporation.
He was also a leader in the development of management education, and he devised the concept known as Management by Objectives (MBO).
Communication is not just significant for business. It is essential for the very existence and operation of any business or any other coordinated effort.
- Communication Dimensions
- Communication With Your Directs
- Communication With Your Peers
- Communication With Your Boss
Communication Dimensions
According to Drucker, there are three dimensions to being an effective communicator in all spheres of management. They are as follows:
Communication With Your Directs
A manager’s success is decided by the level of output from his/her directs. The first rule of understanding is do they understand their JD (job description) and the value they provide to the organization?
For if this is not determined, any communication will be hard to process and applied to work more slowly. In a worst case scenario a manager can misdirect, rather than direct if the employee does not realize their contribution.
Communication With Your Peers
Communicate what you are working on and what is going well and not as well. Your peers may not report to you, but they can render valued assistance and expertise. Inquire if there is anything you or your team is doing to keep them back.
If one department is doing well at the expense of others, the organization cannot improve and loses traction. With this question about feedback, your peers may also ask you what they are doing to hold you back. This criss-cross communication will assure you both have the information needed to improve yourselves and your teams.
Communication With Your Boss
Determine what communication techniques your boss finds effective. Are they a reader or a listener? Do they value verbal communication or hardcopy communication? Sending weekly reports to a boss that understands more verbally will be ineffective for the both of you, as you’ll keep writing and he’ll keep on deleting not knowing what to look for.
Invite feedbacks: Discover what you or your team could work on, what the priorities are and if there is any news that can affect you or your team.
For without direction, you will be mistaken. Your boss will most likely ask the same question with feedback, part your insights and ask for possible answers for the future. Once there is an understanding of what you and your manager need or do not require to perform on key targets, the question that follows is always: “Why didn’t we share each other’s feedback before?”
Success in an organization depends on all three spheres of communication: your directs, your peers and your boss. Drawing these spheres closer to the centre so they overlap more and more with uninterrupted communication and improvement will result not only in you being successful, but everybody around you as well.
7 C of Communication
There are 7 C of effective communication which are relevant to both written as well as oral communication. These are as follows:
- Completeness: The communication must be complete. It should convey all facts required by the audience.
- Conciseness: means communicating what you want to express in the least possible words without forgoing the other C’s of communication.
- Consideration: implies “stepping into the shoes of others”. Effective communication must take the audience into consideration.
- Clarity: implies stressing on a particular message or goal at a time, rather than trying to achieve too much at once.
- Concreteness: Concrete communication means being particular and clear rather than fuzzy and general. Concreteness strengthens confidence.
- Courtesy: in message entails the message should show the sender’s expression as well as should respect the receiver. The sender of the message should be sincerely polite, judicious, reflective and keen.
- Correctness: in communication means that there are no grammatical errors in communication.
Role of Communication in Business
According to Drucker, there are three dimensions to being an effective communicator in all spheres of management. They are as follows:
Communication With Your Directs
A manager’s success is decided by the level of output from his/her directs. The first rule of understanding is do they understand their JD (job description) and the value they provide to the organization? For if this is not determined, any communication will be hard to process and applied to work more slowly. In a worst case scenario a manager can misdirect, rather than direct if the employee does not realize their contribution.
Are there any obstructions or news they need to be aware about that impact their work? Are there upcoming changes to events that your directs will need to adapt to? What is some news that can improve their performance? Keeping your directs “in the loop” instead of expecting from them to find out news by themselves builds a level of trust and increases their skills and work production.
What is needed out of you? Listen to your team and ask questions of what is holding them back and what processes can be added or eliminated in order for them to perform. Their perception of their work environment equated to yours can be entirely different, it is your duty to catch as much as you can and optimize the environment.
Communication With Your Peers
Communicate what you are working on and what is going well and not as well. Your peers may not report to you, but they can render valued assistance and expertise. Inquire if there is anything you or your team is doing to keep them back.
If one department is doing well at the expense of others, the organization cannot improve and loses traction. With this question about feedback, your peers may also ask you what they are doing to hold you back. This criss-cross communication will assure you both have the information needed to improve yourselves and your teams.
Communication With Your Boss
Determine what communication techniques your boss finds effective. Are they a reader or a listener? Do they value verbal communication or hardcopy communication? Sending weekly reports to a boss that understands more verbally will be ineffective for the both of you, as you’ll keep writing and he’ll keep on deleting not knowing what to look for.
About any disruptions or possible complexities in a project keep your boss in the loop and communicate instantly. Without this upwards communication, your boss may assume that everything is running smoothly. Embarrassment is not making a mistake; embarrassment comes when your boss says “You knew we were at a disadvantage in this field for weeks, why did you not inform me?”
Invite feedbacks: Discover what you or your team could work on, what the priorities are and if there is any news that can affect you or your team. For without direction, you will be mistaken. Your boss will most likely ask the same question with feedback, part your insights and ask for possible answers for the future. Once there is understanding of what you and your manager need or do not require to perform on key targets, the question that follows is always: “Why didn’t we share each other’s feedback before?”
Success in an organization depends on all three spheres of communication: your directs, your peers and your boss. Drawing these spheres closer to the centre so they overlap more and more with uninterrupted communication and improvement will result not only in you being successful, but everybody around you as well.
Tools of Business Communication
In an organisation, effective communication may result in increased productivity, reduced employee turnover, and improved relationships among employees. Communication plays a vital role in conveying ideas or information be it day-to-day interpersonal conversations or mass interaction. However, in an organisation, the effectiveness of business communication largely depends on the tools used for communication. These tools are also called communication tools, mediums, or methods.
- Face-to-face communication: It is one of the most common techniques wherein one-to-one communication happens between two individuals. In an organisation, face-to-face communication is used for establishing a personal connection with various stakeholders and generating business.
The effectiveness of face-to-face communication depends on various elements, such as tone, pitch, and body language of individuals involved in communication. The major benefit of face-to-face interaction is that it offers direct access to the receiver. In this way, not only the message is delivered immediately but also the feedback is received without any delay. Face-to-face communication helps in resolving conflicts as there happens to be a minimum communication gap. - Telephonic communication: It is another significant business communication tool that helps in delivering the message directly to the recipient over the phone. Telephonic conversation needs the sender to be precise and clear in their saying as the recipient does not get a chance to see the body language of the sender.
- E-mail: It is one of the most widely used written communication tools. In an organisation, employees use e-mails for various pur- poses, such as sharing business reports or transmitting any other business concern. E-mails can be used for sending information to multiple recipients at the same time.
- Social media: It involves online communication channels that al- low individuals to share their ideas, views, and thoughts and participate in social networking. Social media provides a relatively inexpensive platform to carry out campaigns for business purposes.
Various social media tools, such as Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter have emerged as valuable business communication tools. The main advantage of social media is that it allows organisations to hold real-time communication with customers and understand their needs and expectations. - Web conferencing: It has become one of the most famous online communication tools, especially in today’s fast-paced business world. Web conferencing allows individuals to hold real-time communication with multiple users at remote locations through the Internet. It enables users to conduct business meetings and seminars, make presentations, hold product demonstrations, provide online education, and offer customer support.
Barriers To Communication
Organisational Barriers
The barriers that generate within an organisation are called organisational barriers. These barriers often put a negative impact on the flow of information. The organisational barriers can be categorised into the following types:
- Unfavourable communication environment: If communication takes place in an environment that is full of trust and confidence, it results in a positive response from the receiver. On the other hand, if communication takes place under an unfavourable environment, even well formulated and meaningful information produces a negative impact. Thus, the communication environment of an organisation puts a significant impact on the effectiveness of business communication.
- Complexity in communication policy: Complex communication policies lead to poor communication system within an organisation. This is because many employees fail to understand the policies, which ultimately leads to communication failure. A well-designed communication policy encourages easy flow of communication among employees and departments.
- Excessive authority layers: Too many layers of authority in an organisation lead to poor flow of communication. This is because; information reaches to its final destination after passing through several hierarchical levels. This may lead to distortion of message and may also cause in communication delay.
- Lack of open-door policy: Open door policy can help in fostering communication between management and lower-level employees. The policy relates to the concept that the manager’s door is always open for communication. With this policy, employees can approach the top management without any hitch and talk about anything. Lack of such policy may decrease the level of communication among employees.
- Sexual harassment at workplace: Sexual harassment can affect working conditions and may lead to hostile working environment. It could negatively impact the working ability and performance of an employee. Many individuals often finds it difficult to handle such instances of sexual harassment and do not know when to speak up.
This badly affects the communication process within the system as the person may feel embarrassed or afraid of the repercussions. However, the major step to deal with such situation is to communicate the issues to individuals who can help resolving the same. - Glass ceiling: Glass ceiling is a phrase, introduced in the 1980s, for the artificial barriers that create obstacles in the way of women and minorities in terms of leading to higher positions in the organisation.
The United States Federal Glass Ceiling Commission defines the glass ceiling as the unseen, yet unbreachable barrier that keeps minorities and women from rising to the upper rungs of the corporate ladder, regardless of their qualifications or achievements. Glass ceiling is one of the major reasons for creating communication barrier within an organisation. It escalates the issues of gender differentiation and gender stereotyping which prevents individuals to raise their voice against the biasness and communicate effectively.
Personal barriers
Communication barriers that are created at an individual level (by sender/receiver) are called personal barriers. Some factors, such as attitude towards superiors, colleagues and other team members largely affect the flow of information. Negative attitude may lead to distortion of information, which may acts as a barrier to effective communication. Let us discuss the major types of personal barriers:
- Stereotyping: It refers to categorising people into a single class based on some trait. In stereotyping, the receiver compares the sender with some other person on the basis of a common trait. This affects the objectivity of effective communication as the receiver may misjudge the intention of the sender.
- Halo effect: It is a type of perceptive bias where a particular perception of one’s personality trait influences the perception of the entire personality of a person. For example, if you consider a person kind, you may also tend to think that he/she is intelligent, hard-working, and generous.
- Fear of high ranking: Sometimes people are not comfortable in exchanging their views and ideas with their superiors. In such a case, it would be difficult for superiors to understand what is required and take appropriate actions. This leads to a communication gap between employees and their superiors.
- Poor communication skills: Sometimes people do not have effective communication skills. This may create chaos and misinterpretation of the message by the receivers. For example, improper usage of grammar may make the information unclear.
- Psychological barriers: Some emotional or mental factors such as prejudices impact the perception of the message by its receiver. It leads to various consequences, such as pre-evaluation of information before it is actually received, selective listening, selective retention, and selective transfer of information.
Other Barriers
Apart from the aforementioned barriers there are certain other types of barriers, which are:
- Use of jargon: Jargon refers to difficult or special words, which are specific to a group or profession. For example, it would be difficult for a marketing head to understand complicated networking terminology used by the IT head in an e-mail. In such a case, the whole communication would become futile.
- Distance: The physical distance between the sender and the receiver may delay communication and affect the expectations of both the sender and the receiver.
- Dilution of the actual message: Dilution of information takes place when one person gets the information and passes it on with an addition or an omission to the other person.
- Lack of response: Lack of response or inappropriate response from the receiver discourages the sender to communicate further. This creates a communication gap between the two.
Characteristics of Non-verbal Communication in Organization
- Non-verbal communication indicates the attitude and feeling in addition to what is being expressed through words.
- Non-verbal communication relies on observation and interpretation.
- Non-verbal message may compliment or contradict.
- All body movements with exception of instrument movements are meaningful.
- Dress or language used will reveal the communicator states or education.
- Body movement and facial expressions often occurs spontaneously and can support or contradict the verbal message.
- It has been found that non-verbal communication forms the larger part of the overall communication activity.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Reference
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company.
- Business Communication: “M.K. Sehgal, Vandana Khetrapal, Excel Books.
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons.
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Business Communication | Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
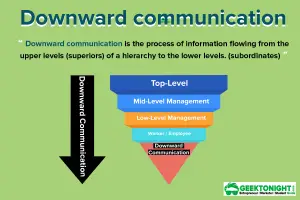
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
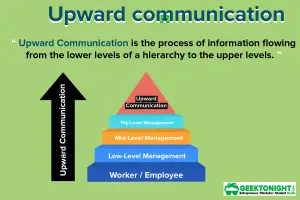
- Upward Communication
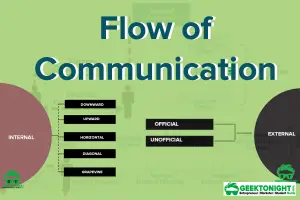
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?