What is Advertising?
Advertising is a paid form of communication in which the sponsor or the brand owner has made payments to the media to carry the message through their set of media vehicles.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Advertising?
- 2 Advertising Definition
- 3 Objectives of Advertising
- 4 Media of Advertising
- 5 Features of Advertising
- 6 Types of Advertising
- 6.1 Brand Advertising
- 6.2 National Advertising
- 6.3 Local Advertising
- 6.4 Retail Advertising
- 6.5 Nation and Destination Advertising
- 6.6 Political Advertising
- 6.7 Social Advertising
- 6.8 Directory Advertising
- 6.9 Direct Response Advertising
- 6.10 Business to business Advertising
- 6.11 Institutional Advertising
- 6.12 Public Services Advertising
- 6.13 Interactive Advertising
- 6.14 Outdoor Advertising
- 6.15 Electronic Advertising
- 6.16 Film Advertising
- 6.17 Unconventional Media
- 7 Advertising Management Process
- 8 Importance of Advertisement
- 9 Ethics in Advertising
- 9.1 Does Not Make Fake or False Claims
- 9.2 Directly Related to the Purpose and Nature of Advertising
- 9.3 Ethics also Depend on what we Believe
- 9.4 Advertising is Often Criticized for being Offensive and in the Bad Taste
- 9.5 Pharmaceutical Advertising
- 9.6 Alcohol
- 9.7 Cigarettes and Tobacco
- 9.8 Ads for Social Causes
- 9.9 Children
- 10 Reference
- 11 Marketing Management Topics
Advertising Definition
Any paid down non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods or services by business firms identified in the advertising message intended to lead to a sale immediately or eventually. – American Marketing Association
William J. Stanton, “Advertising consists of all the activities involved in presenting to a group, a non-personal oral or visual, openly sponsored message regarding a product or service or idea, this message is called an advertisement, is disseminated through one or more media and is paid for by the identified sponsor“.
Richard Buskirk, “Advertising is a paid form of non-person presentation of ideas, goods or services by an identified sponsor“.
Wheeler, “Advertising is a paid form of non-person‘s presentation of ideas, goods or services by an identified sponsor“.
According to Jermy Bullmore, Chairman of J. Walter Thompson, “Advertising is any paid form of communication intended to inform and/or influence one or more people“.
Objectives of Advertising
Objectives of advertising are:
To inform
- Telling the market about a new product.
- Suggesting new uses for a product.
- Informing the market for a price change.
- Explaining how the product works.
- Describing available services.
- Correcting false impressions reducing consumers fears.
- Building the company image to persuade.
To persuade
- Building brand preference
- Encouraging switching to your brand
- Changing customers perception of the product attributes
- Persuading customers to purchase now
- Persuading customers to receive a sales call
To remind
- Reminding consumers that the product may be needed in the near future
- Reminding them where to buy it
- Keeping it in their minds during off-seasons
- Maintaining its top of mind awareness
Media of Advertising
Media of advertisement means any object or any device, which is used to communicate the message, either written or oral, to the potential consumers.
For the convenience of study, means of advertisement may broadly be divided into four parts:
Press Advertising
Press is considered the most popular media of advertisement these days. It is also considered the cheapest and the best media because of its wide circulation.
Press advertising may be divided in two forms;
- Newspapers advertisement: All the advertisements made through newspapers are called Newspapers advertisements. A newspaper may be of national level, state level or district level. It may be daily, weekly or fortnightly and in any language.
- Magazines or journals advertisements: When an advertisement is published in a magazine or a journal, it is called magazine or journal advertisement.
Outdoor or Mural Advertising
Outdoor advertisements are the advertisements, which attract the customers when they are out of their home. These advertisements are displayed on roads or otherwise.
Direct Mail Advertising
Direct mail advertising means the form of advertising, in which the advertiser sends personal message in writing through post to some selected persons.
Salient features of direct mail advertising:
- The advertisement messages are prepared in writing.
- These messages are addressed directly to some selected persons.
- The message may be different for different persons
Other Media of Advertising
Some other forms of advertising may be explained as under:
- Fairs and exhibitions: In India, various fairs and exhibition are organised in different parts at different times. By taking part in this fairs and exhibitions, businessmen and manufacturers can display their goods.
- Cinema: Cinema is considered the cheapest and the most popular medium of entertainment these days. Advertisers get their cinema slides prepared and these slides are played in the beginning and during interval.
- Radio and television: Radio and television have become very common these days. Advertisement through radio and television is becoming more and more popular these days.
- Loudspeakers: Under this form of advertising, a rickshaw or a Tonga or a car, etc. is hired. A loudspeaker is placed on it and the message is announced in different localities of the city.
- Free samples: Under this method, some samples packing are prepared and distributed among consumers. These samples provide an opportunity to the consumers to use these samples and then adopt these products.
- Competition: Some producers announce a competition in it, consumers are required to reply to some questions and to give a slogan about the product. They are also required to send some wrappers or cartoons or cash memo that may prove that they have purchased the product. It increases the sales of the product.
Features of Advertising
Looking into the meaning and definition of advertising we can sum up the following features of advertising.
- Non-personal Presentation of Message: In advertising there is no face-to-face or direct contact with the customers. It is directed to the prospective buyers in general.
- Paid Form of Communication: In advertising the manufacturer communicates with prospective customers through different media like newspapers, hoardings, magazines, radio, television, etc. He has to pay certain amount for using some space or time in these media.
- Promotion of Product, Service or an Idea: Advertisement contains any message regarding any particular product, service or even an idea. It makes people aware of the product and induces them to buy it.
- Sponsor is Always Identified: The identity of the manufacturer, the trader or the service provider who issues an advertisement is always disclosed.
- Communicated through Some Media: Advertisements are always communicated through use of certain media. It is not necessary that there will be just one medium. All the media may also be used like print or electronic media.
Types of Advertising
Since advertising is one of the popular mediums of brand communication, it is used in many forms and for many purposes. It is possible to classify types of advertising into various forms as mentioned below.
Types of Advertising are:
- Brand Advertising
- National Advertising
- Local Advertising
- Retail Advertising
- Nation and Destination Advertising
- Political Advertising
- Social Advertising
- Directory Advertising
- Direct Response Advertising
- Business to business Advertising
- Institutional Advertising
- Public Services Advertising
- Interactive Advertising
- Outdoor Advertising
- Electronic Advertising
- Film Advertising
- Unconventional Media
Brand Advertising
This is the most popular form of advertising as all possible media including television is flooded with brand advertising. Brands like Surf Excel, Pepsi, and Coke in India are shown more frequently on Indian televisions. These kinds of advertisements are done to build brands and develop a unique brand identity for the firm.
National Advertising
These advertisements are uniform across the nation and are released through national media covering the nation.
Local Advertising
These advertisements are carried out in local and vernacular media to promote the product in a local region.
Retail Advertising
These advertisements are brought to promote retail outlets and dealer points.
Nation and Destination Advertising
These advertisements are brought out to promote a nation as a tourism destination. These are also used for promoting states, cities and tourist attractions.
Political Advertising
These are done for political parties, politicians and individual candidates during elections and referendums.
These advertisements are brought out for a social cause like against AIDS, sexual exploitation, women trafficking, child labour and other critical issues in a society.
Directory Advertising
These are the advertisements done in directories and yellow pages and followed by people while collecting a telephone number or a home address. People normally refer to these directories to buy products and services.
Direct Response Advertising
These advertisements are used in any medium, which tries to stimulate sales directly. The consumer can respond by mail, telephone or Internet.
Business to business Advertising
These kinds of advertisements are carried out targeting business and organisational marketers. These messages are directed towards retailers, wholesalers and distributors. These advertisements are placed in professional journals and trade association publications.
Institutional Advertising
Institutions like colleges, universities, missionary of charities and large corporates bring out these advertisements. When these are brought out by large corporates we call them corporate advertising.
The purpose of such advertising is to create positive goodwill, which will ultimately contribute towards achieving the overall marketing and brand-building goal of the organisation. Many companies use such advertisements to build a positive image in the eyes of the consumers and general audience at large.
Public Services Advertising
Government and government sponsored institutions bring such advertisements for the benefit of general public. They communicate a message on behalf of some good cause. Advertising professionals create these advertisements for public relations department of large corporates, highlighting a social cause.
Interactive Advertising
These are typical Internet-based advertisement, which is delivered to individual consumers who have access to the World Wide Web. Advertisers use web pages, banner ads, spots; pop-ups and email programs to reach the target audience.
Outdoor Advertising
These are forms of advertising in which the marketer uses out of the home media like wall paintings, hoardings, bulletins, kiosks and mobile vans for communicating with audience.
Electronic Advertising
These forms of advertising use electronic media like television, radio, video and audiocassettes, electronic display boards, CDROMs for promotion of products and services.
Film Advertising
These are new forms of advertising in which brands are placed inside the film and actors are shown using these products during the movie for increasing its usage among the audience.
Unconventional Media
These forms of advertising are of recent origin and use traditional art forms like jatraa, puppet dance and other local dance forms to communicate about products and services to the audience.
Advertising Management Process
As an advertising manager one needs to know how to decide on and design an effective advertising campaign.
- Overall Promotional Goal
- Setting Advertising Objective
- Communication Objective
- Sales Objective
- Setting up Advertising Budget
- Develop Advertising Campaign
- Evaluate Campaign and Provide Feedback
The advertising management process is shown in Figure
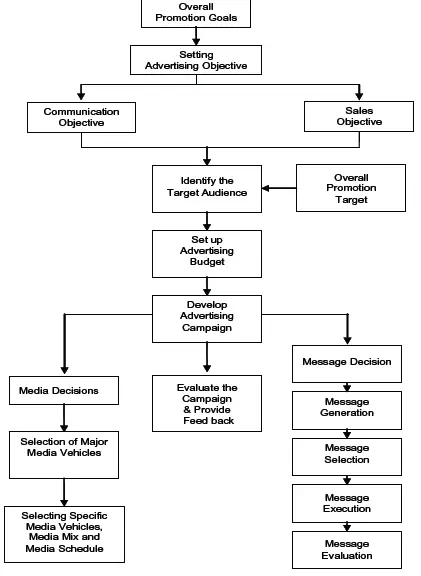
Overall Promotional Goal
The most obvious objective marketers have for promotional activities is to convince customers to make a decision that benefits the marketer.
Setting Advertising Objective
Promotion or brand manager should set objectives for an advertising campaign and also for each ad in each medium used.
Communication Objective
Marketers strive to influence how prospective customers think. To do that, they need to understand how and when to guide them.
- First, they must be aware of to whom they are offering the solutions.
- Then they want to hook customers and engage them as they become interested.
- Next, they need to build understanding and become a credible source of information.
- Finally, should entice customers to take action and purchase the products and services.
Sales Objective
A critical decision is to define the target market for the product or service. This would involve finding and precisely defining those variables that indicate who and where the best prospects are
Consumer research may be needed to find out:
- Who buys the product?
- What do they really buy?
- When do they buy?
- How do they use the product?
Setting up Advertising Budget
The objectives determine what is expected of advertising to accomplish in a defined period of time. The budget controls all proposed expenditures by fixing a limit.
- Affordable method: Promotion budget is set at the level management thinks the company can afford.
- Percentage-of-sales method: Promotion budget is set as a specified percentage of either past or forecasted sales.
- Fixed-sum-per-unit method: Promotion budget is set as a predetermined dollar amount for each unit sold or produced.
- Meeting competition method: Promotion budget is set to match a competitor’s promotion outlays on either an absolute or relative basis.
- Task-objective method: Once marketers determine their specific promotion objectives, the amount (and type) of promotional spending needed to achieve them
Develop Advertising Campaign
Media Decisions: Media planning is quite complex because of the nature of different kind of media. Media plan determines the best way to reach the audience with the advertiser’s message.
Message Decisions: An excellent advertising message is estimated to be ten times or more effective than an average message in influencing consumer attitudes, preferences and purchase decision for the product.
Evaluate Campaign and Provide Feedback
Post-testing is done to evaluate the final results of the campaign. These results are concerned with measuring the effectiveness of the ad.
Post-testing is done at the end of the campaign to determine to what extent the advertising campaign objectives have been accomplished and then to make any appropriate changes. It provides feedback to promotion managers and helps future planning.
Importance of Advertisement
Advertising broadens the knowledge of the consumers. With the aid of advertising, consumers find and buy necessary products without much waste of time. The main benefits of advertising may be narrated as follows:
- Benefits to Manufacturers
- Benefits to Wholesalers and Retailers
- Benefits to Consumers
- Benefits to Salesmen
- Benefits to Community or Society
Benefits to Manufacturers
Advertising helps in creating and sustaining demand for existing and new products. It builds brand image and goodwill of the firm.
- It increases sales volume by creating attraction towards the product.
- Retail price, maintenance is also possible by advertising where price appeal is the promotional strategy.
- It helps to establish a direct contact between manufacturers and consumers.
- It leads to smoothen the demand of the product. It saves the product from seasonal fluctuations by discovering new usage of the product.
- It creates a highly responsive market and thereby quickens the turnover that results in lower inventory.
- Selling cost per unit is reduced because of increased sale volume. Consequently, product overheads are also reduced due to mass production and sale.
- It helps easy introduction of new products into the markets by the same manufacturer.
- It helps to create an image and reputation not only of the products but also of the producer or advertiser. In this way, it creates goodwill for the manufacturer.
- Advertising gives the employees a feeling of pride in their jobs and to be in the service of such a concern of repute. It thus inspires the executives and workers to improve their efficiency.
- Advertising is necessary to meet the competition in the market and to survive.
Benefits to Wholesalers and Retailers
- Easy sale of the products is possible since consumers are aware of the product and its quality.
- It increases the rate of the turnover of the stock because demand is already created by advertisement.
- It ensures more economical selling because selling overheads are reduced.
- It enables them to have product information.
- It supplements the selling activities.
- The reputation created is shared by the wholesalers and retailers alike because they need not spend anything for the advertising of a well advertised product.
Benefits to Consumers
- Advertising helps in eliminating the middlemen by establishing direct contacts between producers and consumers. It results in cheaper goods.
- It helps them to know where and when the products are available. This reduces their shopping time.
- Advertising stresses on quality and very often prices. This forms an indirect guarantee to the consumers of the quality and price. Further large scale production assumed by advertising enables the seller to sell a product at a lower cost.
- It provides an opportunity to the customers to compare the merits and demerits of various substitute products.
- This is perhaps the only medium through which consumers could know the varied and new uses of the product.
- Modern advertisements are highly informative.
Benefits to Salesmen
- Introducing the product becomes quite easy and convenient because the manufacturer has already advertised the goods informing the consumers about the product and its quality.
- Advertising prepares necessary ground for a salesman to begin his work effectively. Hence sales efforts are reduced.
- The contact established with the customer by a salesman is made permanent through effective advertising because a customer is assured of the quality and price of the product.
- The salesman can weigh the effectiveness of advertising when he makes direct contact with the consumers.
Benefits to Community or Society
- It helps artists by making available more job opportunities. It also supports the Press.
- Advertising leads to a large-scale production creating more employment opportunities to the public in various jobs directly or indirectly.
- It initiates a process of creating more wants and their satisfaction results in higher standard of living. For example, advertising has made more popular and universal the uses of such inventions as the automobiles, radios, and various household appliances.
- Newspapers would not have become so popular and so cheap if there had been no advertisements. The cheap production of newspapers is possible only through the publication of advertisements in them. It sustains the Press.
- It assures employment opportunities for the professional personnel and artists.
- Advertising does provide a glimpse of a country’s way of life. It is, in fact, a running commentary on the way of living and the behaviour of the people and is also an indicator of some of the future in this regard.
Ethics in Advertising
Ethics is the most important feature of the advertising industry. Though there are many benefits of advertising but then there are some points which do not match the ethical norms of advertising.
- Does Not Make Fake or False Claims
- Directly Related to the Purpose and Nature of Advertising
- Ethics also Depend on what we Believe
- Advertising is Often Criticized for being Offensive and in the Bad Taste
- Pharmaceutical Advertising
- Alcohol
- Cigarettes and Tobacco
- Ads for Social Causes
- Children
Does Not Make Fake or False Claims
An ethical ad is the one which does not lie, does not make fake or false claims and is in the limit of decency. The main area of interest for advertisers is to increase their sales, gain more and more customers, and increase the demand for the product by presenting a well decorated, puffed and colourful ad.
They claim that their product is the best, having unique qualities than the competitors, more cost-effective, and more beneficial. But most of these ads are found to be false, misleading customers and unethical.
Ethics in advertising is directly related to the purpose of advertising and the nature of advertising. Sometimes exaggerating the ad becomes necessary to prove the benefit of the product.
For example a sanitary napkin ad which shows that when the napkin was dropped in a river by some girls, the napkin soaked water of the entire river.
Ethics also Depend on what we Believe
If the advertisers make the ads on the belief that the customers will understand, persuade them to think, and then act on their ads, then this will lead to positive results and the ad may not be called unethical.
Advertising is Often Criticized for being Offensive and in the Bad Taste
There are several grounds for criticism. For example, TV ad of unpleasant products (haemorrhoid treatment, diarrhoea products) or sexual explicitness.
Pharmaceutical Advertising
Such ads help in creating awareness, but one catchy point here is that the advertisers show what the medicine can cure but never talk about the side effects of that same thing or the risks involved in the intake of it.
Alcohol
Till today, there has not come any liquor ad which shows anyone drinking the original liquor. They use mineral water and sodas in their advertisements with their brand name. These types of ads are called surrogate ads.
These types of ads are totally unethical when liquor ads are totally banned. Even if there are no advertisements for alcohol, people will continue drinking.
Cigarettes and Tobacco
These products should never be advertised as consumption of these things is directly responsible for cancer and other severe health issues. Such ads are banned in countries like India, Norway, Thailand, Finland and Singapore.
These types of ads are ethical and are accepted by the people. But ads like condoms and contraceptive pills should be limited, as these are sometimes unethical, and are more likely to loose morality and decency at places where there is no educational knowledge about all these products.
Children
Children are the major sellers of the ads and the product. They have the power to convince the buyers. But when advertisers are using children in their ad, they should remember not to show them alone doing work on their own like brushing teeth, playing with toys.
Reference
- V. S. Ramaswamy, S. Namakumari; 2009; Marketing Management; MacMillan Publishers Pvt Ltd.
- Kotler, Keller, Koshy, Jha; 2009; 13th Edition; Marketing Management: A South Asian Perspective.
Marketing Management Topics
Go On, Share & Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something in Marketing Management Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Advertising in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management





