Models of Communication
Various models of communication are shown in Figure:
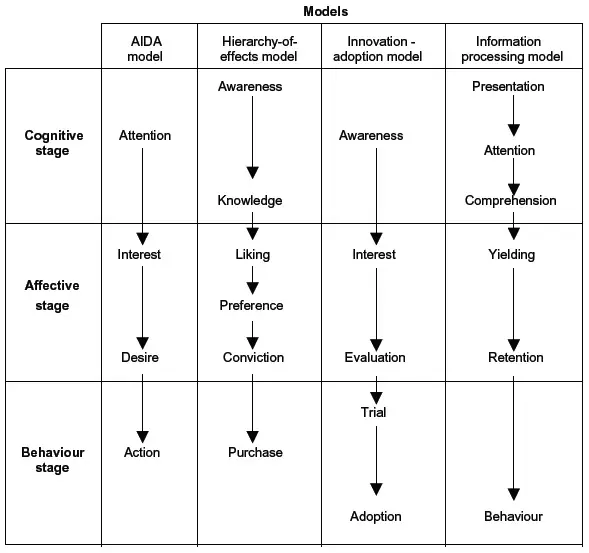
- AIDA Model
- Levidge and Steiner Model
- Hierarchy of Effects Model
- Innovation-adoption Model
- Information Processing Model
Table of Content
AIDA Model
One of the earliest model of communication and advertising effectiveness measurement revolves around what communication goals the marketers set for an advertising program. This is known as AIDA Model.
- Attention
- Interest
- Desire
- Action
It proposes that the advertising effect is the consumer response to which a potential customer is induced due to an advertising program. The hierarchy of effects can be explained as per Figure in which the customer passes through stages of attention, interest, desire and action.
AIDA Theory of model of communication highlights the importance of attracting the attention of the prospects and creating interest through the advertising messages. The desire to obtain advertised goods/services may be generated to various degrees among different prospects due to consistent exposure to advertising.
The final stage of action or buying occurs as a result of customers passing through one stage to the other. The act of purchase is influenced by many other moderating factors, like product quality, perceived brand image and distribution and logistics facilities of the company.
Levidge and Steiner Model
Levidge and Steiner’s second theory of model of communication proposed AKLPCP Model.
- Awareness
- Knowledge
- Liking
- Preference
- Conviction
- Purchase
They give higher importance to cognitive evaluations before the purchase. With an increase in competition and enhancement in discerning abilities of potential buyers and users, information is likely to play a greater role.
The persuasive power of advertising in itself is a function of the information content. This model also takes into account the prevailing degree of competition.
The competition can arise between two brands or between substitute products in two dissimilar categories.
The stage of liking (after the stage of awareness and knowledge) refers to the ability of advertising in creating a choice through its creativity and theme.
Hierarchy of Effects Model
Hierarchy of effects model of communication developed by Lavidge and Steiner is the best known. This model helps in setting advertising objectives and provides a basis for measuring results.
This model also suggests that advertising produces its effects by moving the consumer through a series of steps in a sequence from initial awareness to the ultimate purchase of a product or service.
The following are the effects of communication:
- Create awareness among 90% of target audience – Use repetitive ad in newspaper/magazines.
- Create interest in the brand among 70% of target audience – Communicate the information about the benefit of the brand such as “The cream is non-sticky and causes no harm to the skin”.
- Create positive feeling about the brand to at least 40% of the target audience and create a preference to atleast 25% of the target audience – Create favourable attitudes by supplying them samples conveying more information, carrying out promotional programme etc.
- Get trial among 20% of the target audience – Issue coupons and discounts to make trial purchase, use advertisement to achieve this.
- Continue reinforcement of advertising and more promotion to get at least 5% customers who repurchase.
Innovation-adoption Model
According to Everett M. Rogers, this model of communication evolved from work on the diffusion of innovations. The model depicts various sequential steps and stages that a consumer moves through in adopting a new product or service.
Marketers face the challenge of creating awareness and interest and the best way to persuade consumers to evaluate a brand is by inducing product trial or sometimes product-in-use demonstration. This can lead to product adoption as a result of consumer satisfaction or rejection if the consumer is not satisfied.
Information Processing Model
William McGuire developed this model of communication which assumes that advertising audience is information processors and problem solvers.
Information Processing Model include following stage:
- Presentation
- Attention
- Comprehension
- Retention
The first three stages in the model, presentation, attention, and comprehension are similar to awareness and knowledge, and yielding means the same as liking. Up to this point there is similarity with Lavidge and Steiner’s model.
The next stage, retention is unique to this model.
Retention refers to the ability of the consumer to accept and store in memory the relevant information about the product or service.
Retention of information is important because most advertising is designed to motivate and precipitate action not just immediately, and the retained information is used at a later time to make a purchase decision.
Marketing Management Topics
Go On, Share & Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something in Marketing Management Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Models of Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management



