What is Demand Forecasting?
Demand forecasting is an attempt to estimate the future level of demand on the basis of past as well as present knowledge and experience, to avoid both under production and overproduction.
It may be based on estimates of demand potential of the entire industry. The demand forecasting serves as the reference point for all marketing control efforts. It is indispensable in modern business.
Table of Content
What is Forecasting?
Forecasting is an attempt to predict the future by examining the past. Business firms can estimate and minimise future risk and uncertainty through forecasting and forward planning. Without forecasting, forward planning will be directionless and meaningless.
Demand Forecasting Definition
Demand forecasting is an estimate of sales during a specified future period based on proposed marketing plan and a set of particular uncontrollable and competitive forces.
– Cundiff and Still
Demand forecasting may be defined as the process of finding values for demand in future time periods
Evan J. Douglas
Steps in Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a scientific exercise. It has to go through a number of steps. At each step, critical considerations are required to be made.
Steps in demand forecasting are:
- Identification of Objective
- Nature of Product and Market
- Determinants of Demand
- Analysis of Factors
- Choice of Method
- Testing Accuracy

Identification of Objective
Economist first should be clear about the uses of forecast data and how it is related to forward planning by the firm. Depending upon the scenario, the economist has to choose the type of forecast: short-run, active or passive, conditional or non-conditional, etc.
Nature of Product and Market
Nature of the product or service is an important consideration for which we are attempting a demand forecast. Forecasting of demand must examine carefully whether the product is a consumer good or producer good, perishable or durable.
It should also consider the stage at which the product is i.e. introduction, growth, maturity and saturation, or obsolescence and decline.
Finally, the nature of competition in the market (perfect or imperfect) should not be overlooked.
Determinants of Demand
Different determinants will assume a different degree of importance in different demand functions, depending on the nature of product and nature of forecasts, In addition, it is important to consider socio-psychological determinants; especially demographic, sociological and psychological factors affecting the demand.
Analysis of Factors
In an analysis of statistical demand function, it is customary to classify the explanatory factors into
- Trend factors
- Cyclical factors
- Seasonal factors
- Random factors
An analysis of factors is especially important depending upon whether it is the aggregate demand in the economy or the industry’s demand or the company’s demand or the consumer’s demand which is being predicted.
Choice of Method
The economist has to choose a particular technique from among various techniques of demand forecasting, depending upon the nature of the product.
Testing Accuracy
There are various methods for testing statistical accuracy in a given forecast. Some of them are simple and inexpensive; others are quite complex and difficult.
This testing is needed to avoid/reduce the margin of forecasting error and thereby to improve the decision-making.
Read: Consumer Behaviour – Classification, Importance, Stages
Features of Demand Forecasting
Eight major features of demand forecasting method can be identified with forecasting methods (techniques) to identify key characteristics of a good demand forecasting method.
- Time Horizon
- Level of Detail
- Stability
- Pattern of Data
- Type of Model
- Cost
- Accuracy
- Ease of Application
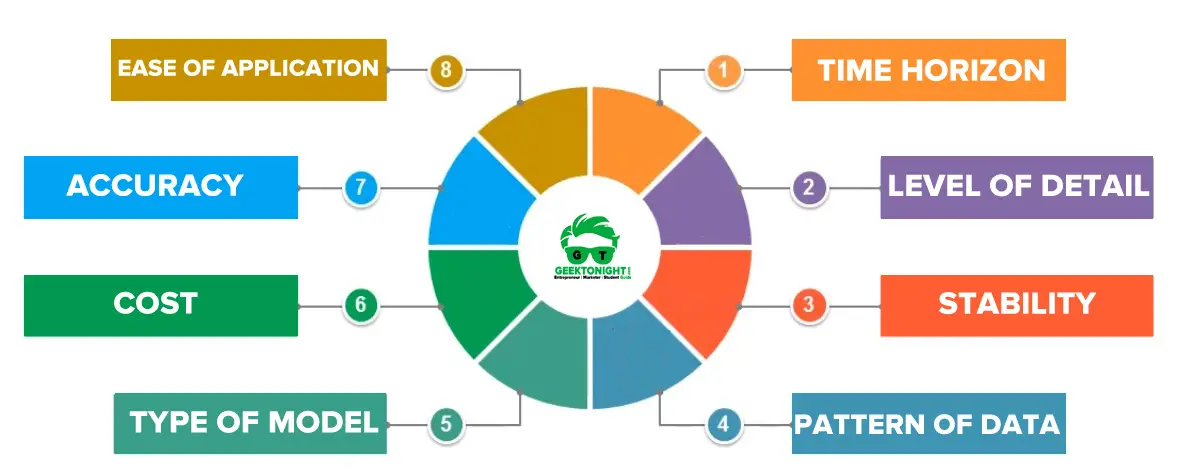
Time Horizon
The length of time over which a decision is being made has a bearing on the appropriate technique to use. The probability of forecasting error generally decreases with an increase in the length of the time horizon.
Level of Detail
The level of detail needed should match the focus of the decision-making unit in the forecast.
For example, production planning must make its decision at the individual product level, whereas the corporate planning department is likely to be happy with aggregate demand forecasts by product categories.
Stability
Forecasting in situations that are relatively stable over time requires less attention than those that are in constant flux. In stable situations, the existing pattern is assumed to continue in the future and past patterns can be easily extrapolated in future.
Pattern of Data
Data required to use the underlying-relationships should be available on a timely basis. Each forecasting method is based on an underlying assumption about the data.
As different forecasting methods vary in their ability to identify different patterns, it is useful to make the pattern in the data fit with the method that suits it the most.
Type of Model
Other assumptions are also made in each forecasting technique that must fit the situation under consideration. The technique used should be easily comprehended by the management to give quick meaningful results.
Cost
Several costs are associated with adopting a forecasting procedure. The variation in costs affects the selection of the forecasting method. There is a need for an economic consideration of balancing the benefits against the extra cost of providing the improved forecasting.
Accuracy
It is measured by the degree of deviations between past forecasts and current actual performance or present forecasts and future performance. If the likely state comes close to the actual state, it means that the forecast is dependable.
Ease of Application
Models must be chosen within the abilities of the users to understand them and within the time allowed for using them. This will enable management to properly interpret the results. The simplicity of handling the method matters in the selection of the method.
Read: 4Ps of Marketing Mix
Methods & Techniques of Demand Forecasting
The choice of choosing techniques of demand forecasting is complicated because each situation might require a different method. Management should be aware of the factors favouring one method over another in a given demand-forecasting situation.
Some of the methods of demand forecasting are discussed below:
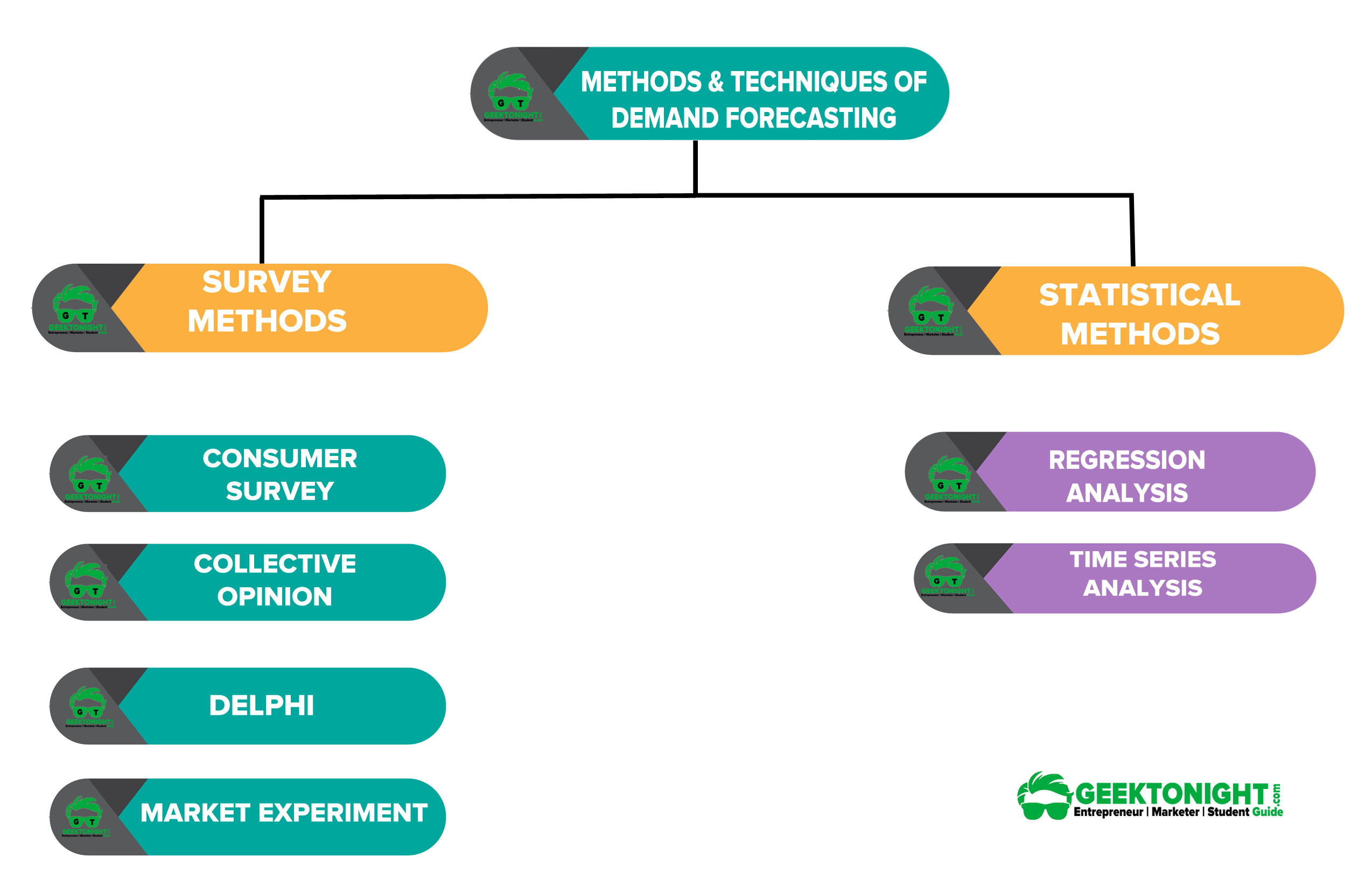
Survey Methods
Under this approach, surveys are conducted about the intentions of consumers (individuals, firms or industries), opinion of experts or of markets.
When taking sample surveys, a selected subset is surveyed and through study, inferences are drawn. These methods are usually suitable for short-term forecasts due to the nature of consumers’ intentions.
A few important survey methods:
Consumer Survey Method
A firm can ask consumers, what and how much they are planning to buy at various prices of the product for the forthcoming time period, usually a year.
Collective Opinion Method
Also called sales-force polling), salesmen or experts are required to estimate expected future demand of the product in their respective territories and sections.
Delphi Method
It is also known as Reasoned Opinion. A variant of opinion poll and survey method is a Delphi method, developed by Rand Corporation of USA in the late 1940s for predicting technical changes.
Market Experiment Method
Under this method, the main determinants of the demand of a product like price, advertising, product design, packaging, quality, etc., are identified.
These factors are then varied separately over different markets or over different time periods, holding other factors constant. The effect of the experiment on consumer behaviour is studied under actual or controlled market conditions, which is used for overall forecasting purpose.
Statistical Methods
These methods make use of historical data (time series or cross-section) as a basis for extrapolating quantitative relationships to arrive at the future demand patterns and trends. The data may also be analysed through econometric models.
These are useful for long-term forecasting, for old products and for larger levels of aggregation. They are based on scientific ways of estimation, which are logical, unbiased and proved to be useful. However, the biggest disadvantage is that it is difficult to apply these methods.
Time Series Analysis
It is an arrangement of statistical data in chronological order, i.e., in accordance with its time of occurrence. It reflects the dynamic pace of steady movements of a phenomenon, over a period of time.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is perhaps the most popular method of forecasting among economists. It is a mathematical analysis of the average relation between two or more variables, in terms of the original units of the data.
Read: What is Marketing Environment?
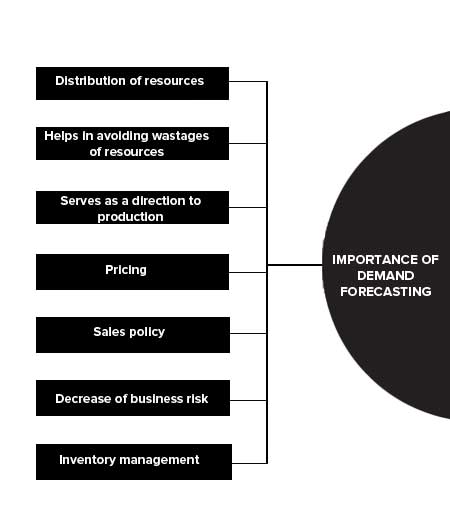
Importance of Demand Forecasting
Importance of demand forecasting are given below:
- Distribution of resources
- Helps in avoiding wastages of resources
- Serves as a direction to production
- Pricing
- Sales policy
- Decrease of business risk
- Inventory management
Distribution of resources
We know that inputs are processed to result into output. These inputs include resources like materials, machinery and of course human resources.
The business firm also has to make decisions regarding capital arrangement, manpower planning and so on. In short, the estimation of demand enables the firm to undertake critical business decisions.
Helps in avoiding wastages of resources
Demand forecasting is not an option but compulsion in today’s competitive environment. In order to avoid wastages, it is always beneficial to have a sense of future demand for products and services.
Serves as a direction to production
If there is a proper prediction of the demand, then it serves as a handy tool for the businesses to undertake future production activities. According to the demand in the market, the company can control their production.
Pricing
The decision regarding the pricing of goods and services is perhaps one of the most critical business decisions. If there are sincere predictions about the future sales of the firm’s product then it could serve as a good aid to devise pricing strategies.
Sales policy
Production is followed by sales. The business firms can plan their sales policy effectively on the backdrop of demand forecasting.
This also implies that the distribution of goods and services can be done appropriately depending upon the predictions of the demand for the product.
Decrease of business risk
Where there is a business there is a risk. Demand forecasting though does not completely remove the business uncertainties, helps in reducing the risks and uncertainties to a certain extent.
Inventory management
Inventories is one of those aspects which is closely associated with demand. This is because inventories are kept by the producers to meet the demand in the coming times.
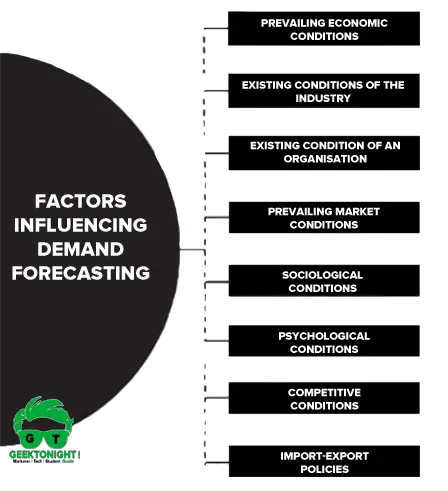
Factors Affecting Demand Forecasting
- Prevailing economic conditions
- Existing conditions of the industry
- Existing condition of an organisation
- Prevailing market conditions
- Sociological conditions
- Psychological conditions
- Competitive conditions
- Import-export policies
FAQ
Demand forecasting is an attempt to estimate the future level of demand on the basis of past as well as present knowledge and experience, to avoid both under production and overproduction.
Methods & Techniques of Demand Forecasting
Methods of Demand Forecasting
1. Survey Methods
Consumer Survey Method
Collective Opinion Method
Delphi Method
Market Experiment Method
2. Statistical Methods
Time Series Analysis
Regression Analysis
Read Complete Article: Methods of Demand Forecasting
Techniques of Demand Forecasting
1. Qualitative Techniques
Survey Methods
Opinion Polls
2. Quantitative Techniques
Time Series Analysis
Smoothing Techniques
Barometric Methods
Econometric Methods
Marketing Management Topics
Go On, Share & Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something in Marketing Management Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Demand Forecasting in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management







