What is Logistics?
Logistics deals with all activities that facilitate product flow from the point of raw material acquisition to the point of final consumption as well as the information flow that set the production in motion for the purpose of providing adequate levels of customer service at a reasonable cost.
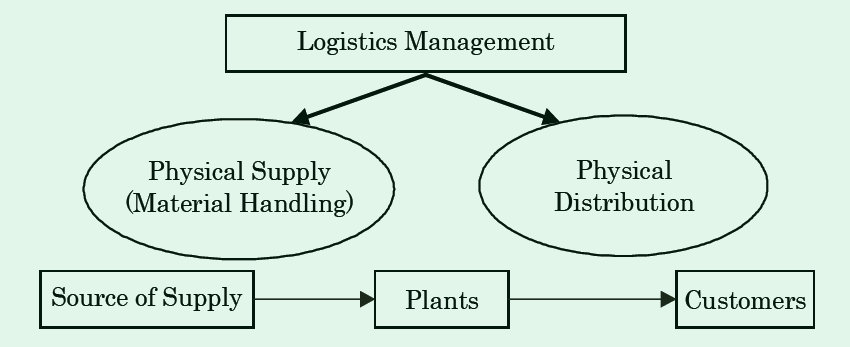
Logistics management involves two issues namely, movement of raw materials to the plant known as physical supply or material management and second, flow of finished products from the plant to the customers, known as physical distribution. Logistics management activities can be grouped as primary and secondary activities.
Table of Content
Logistics has always been a central and essential feature of all economic activities. The concept of logistics as an integrative activity in business has developed within the last twenty years.
Logistics management is a process of strategically managing the movement and storage of materials, parts and finished inventory from supplier through the firm and on to customers.
Logistics is thus concerned with the management of the physical distribution of material. It begins from sources of supply and ends at the point of consumption. It is, therefore, much wider in its reach than simply a concern with the movement of finished goods – a commonly held view of physical distribution.
Types of Logistics
There are different types of logistics systems or subsystems used in organisations.
They can be classified as:
- Supplier logistics
- Organisational or corporate logistics
- Customer logistics
Supplier logistics takes care of the flow of supplies and raw materials from a vendor to the company; the corporate logistics takes care of the flow of goods to the customer point whereas customer logistics takes care of how customers handle the product from company’s source to his consumption point.
Supplier Logistics
The key issue in supplier logistics is to buy the right things. This needs to address two critical issues i.e. supplier evaluation and ordering of the final product. The manager should be able to evaluate the quality of the supplier, prior to issuing purchase orders and he should be able to clearly describe the products to be ordered in order to make sure that the supplier knows exactly what the firm wants.
For physical distribution management, product transportation and delivery services have to be evaluated. The company may procure transportation and product storage services from the supplier. The suppliers should be evaluated on their capability to provide required services of acceptable quality level.
The marketing manager should ask the following questions while evaluating the supplier logistics system.
- Do they have sufficient and reliable equipment?
- Do they have enough resources including manpower, storage space, etc.?
- Are their resources and equipment well managed?
- Do they have the system to allocate their resources?
While placing an order with the supplier, one should make sure that he has included desired date, time and routing of the required transportation service and has mentioned about required storage conditions of the merchandise.
Production/Corporate Logistics
To cater to growing market needs, the company needs to establish a new production system for logistics as well as modified production systems to accomplish the true real-time sales’ system.
For this, a new revolutionary production project team should be formed whose sole purpose is to establish a ‘production, sales and logistics total linkage system’ that will eventually eliminate overstock and shortage problems. This kind of production system is called Market Linkage Production System (MLPS).
Components of Market Linkage Production System
The following are the components of market linkage production system. They are replenishment production system and purchase support system.
For an effective market linkage production system:
- the marketing manager should have documented procedures defining the number of processes
- he should use suitable equipment and working environment
- monitor suitable process parameters and develop systems for maintenance of equipment.
Replenishment Production System (RPS): RPS analyses the trends of all outgoing shipments from distribution centres to all dealers and of inventory movements at a factory warehouse.
It then generates ‘actual demand/from marketing information’ from which the most suitable production plan by model/line is established.
It then creates the optimal production level and decides the production order for days (2 and 3) by everyday simulation process. The production would exist just for a specified number of days.
This means that the company possesses a production plan in terms of days rather than in terms of months. It also means that the daily market changes are represented on production plans since the system relies on Actual demand marketing information’ instead of on the ‘more sales plan’.
Purchase Support System (PSS): This system consists of a single resource plan, ordering and payment system that makes it possible to work successfully.
Such standard purchase support systems can re-establish the business process that will cut down the ‘total cycle time’ from customers to vendors. This process will expedite the process responding to the customer needs, prevent shortage problems and reduce the unnecessary cost, which arises from overstock.
The firm should establish some procedures or instructions to define the proper manner of handling, transporting, storing and delivering products. Transportation equipment and storage equipment should be periodically serviced to ensure proper functioning.
The company should have three stages of inspection as mentioned under:
- Receiving, inspection and testing: It ensures that product arrives in company in good shape.
- In-process inspection and testing: It ensures that the product is handled properly during manufacturing process.
- Final inspection and testing: It usually performed before dispatching the product to the customer.
It is required that the firm should define the training needs of its employees and provide training in the areas of operation of material handling equipment and customer care so that the right product is delivered to the customers at the right time and in the right shape.
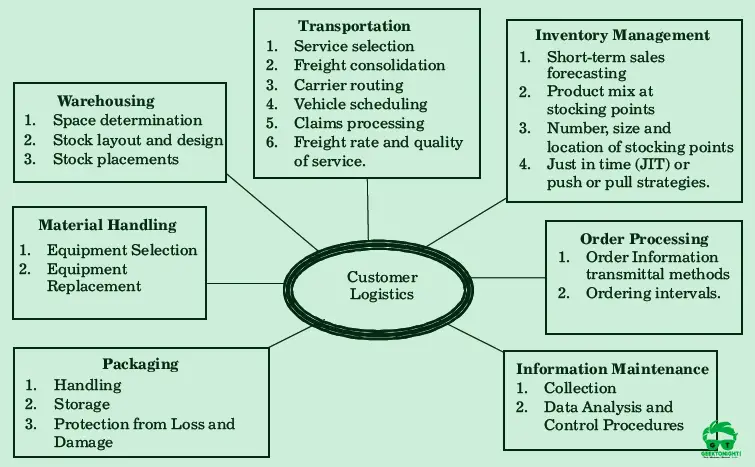
Customer Logistics
Customer logistic involves a seven ‘R’ framework namely, it should be a process of
- Right quantity of the
- Right product or service to the
- Right place in the
- Right conditions at the
- Right cost and at the
- Right time with the
- Right impression.
If these seven aspects are taken care of, customer logistics process will be able to create higher levels of customer satisfaction. It will also show that the company is concerned about the customers and their logistics requirements.
The focus of customer logistics should be on speedy and timely delivery, shorter lead time, safety of goods and users and lowering of distribution costs.
The objective of this process should be to achieve on-time delivery and realise higher customer satisfaction by implementing a flexible and swift customer logistics system.
The following diagram shows components of a customer logistics system.
Reference
- V. S. Ramaswamy, S. Namakumari; 2009; Marketing Management; MacMillan Publishers Pvt Ltd.
- Kotler, Keller, Koshy, Jha; 2009; 13th Edition; Marketing Management: A South Asian Perspective.
Marketing Management Topics
Go On, Share & Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something in Marketing Management Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Types of Logistics in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management






