Psychologist Abraham Maslow proposed Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory in psychology in 1940. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is one of the earliest and best-known of motivation theories.
Maslow wanted to understand what motivates people. He believed that individuals possess a set of motivation systems unrelated to rewards or unconscious desires.
Maslow (1943) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. When one need/goal is fulfilled then a person seeks to fulfil the next one, and so on.
Table of Content
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
The Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory assumes that people are motivated to satisfy 5 levels of needs those are a psychological need, security need, social need, esteem and self-actualization needs.
Maslow categorized the five needs into higher and lower orders.
Lower-order: Physiological and safety.
Higher-order needs Social, esteem, and self-actualization.
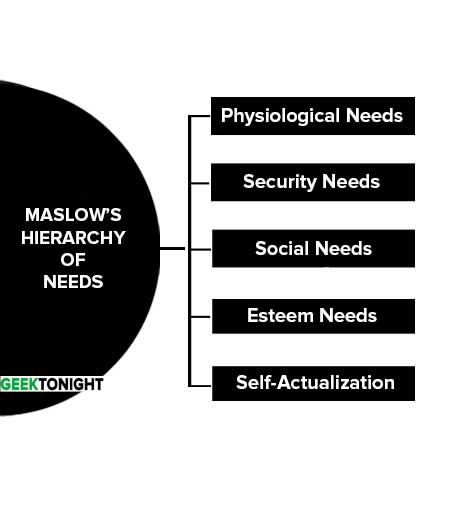
Maslow suggests that five levels of needs are arranged in accordance with the importance. Starting from the bottom of the hierarchy, an individual is motivated first and foremost to psychological need.
When the need are satisfied then he is motivated and moves up the hierarchy to satisfy security need. This moving up and process continue till the end-user reaches the self-actualization
Physiological Needs
Definition: Physiological needs are considered the most important because they are a most immediate need and hence are also known as basic needs.
- These are also needed our body to stay functional.
- It is the bottom and most important needs.
Example:
1. It includes food, clothes, shelter, air, water, sexual activities etc.
2. Basic pay, workspace in the context of organization behaviour.
Security Needs
Definition: Security or safety needs are referred to as a requirement for a secure physical and emotional environment.
- The need is free from worry about money and job security and desire for safe working condition.
- Security needs are satisfied for people in the workplace by job continuity.
- A grievance resolving system and an adequate insurance and sentiment benefit package.
Example:
1. Financial security, Heath and wellness, a desire for adequate housing.
2. Job security, adequate medical benefits, and safe working conditions in the context of organization behaviour.
Definition: Social needs are needs related to a special aspect of human life. They include the needed for love and affection and the need is affected by one’s peers.
- For most people, these needs are satisfied by a combination of family and community relationship and friendship on the job.
- Manager can help the ensure the satisfaction of these important needs by allowing social interaction and making employees feel like a part of a team or workgroup.
Example:
1. Social acceptance, need to belong, to relate to others.
2. Good co-workers and supervisors, participating in social functions in the context of organization behaviour.
Esteem Needs
Definition: The Esteem needs are concerned with self-respect, self-confidence, feeling of personal worth.
- A feeling of being unique and recognition satisfaction. It is the image of the self in the eye of others.
- A person with high esteem thinks that people think highly of him. It is our esteem that gives us a recognition of our skill.
Example:
1. when someone says that he is funny, entertaining and amiable. He must have heard other saying the most of think about him.
2. Promotions and being recognized at work in the context of organization behaviour.
Self-Actualization
Definition: Self-actualization is the realizing of oneself. Many people reach a stage in their life where they start wondering what is expected out of them in their life.
- It is the final need on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
- They hear a voice that tells them to fulfil their destiny. Such people to figure out the meaning of their lives and faces of an existential question.
Example:
1. Obtaining our full potential, becoming confident, eager to express our beliefs, and willing to reach out to others to help them.
2. Challenging projects, opportunity for innovation and creativity in the context of organization behaviour.
Read: What is Organizational Behavior?
Deficiency Needs vs Growth Needs
Physiological, security, social, and esteem needs arose due to deprivation are termed as deficiency needs. In order to avoid unpleasant feelings or consequences, we must satisfy these lower-level needs.
Growth needs don’t stem from a lack of something, but rather from a desire to grow as a better individual. It is termed as the highest level of the pyramid.
Advantages of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Simple to understand
- It takes into account human nature
- Relevant in all field
Read: Motivation Theories
Disadvantages of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Needs do not necessarily follow a hierarchy
- The theory is difficult to test/measure
Read: Vroom’s Expectancy Theory of Motivation
Reference
- Robbins, Stephen P. 2010. Organizational Behaviour. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall.
Management Topics
- What is Management?
- Who Is a Manager?
- Marketing CIs Management an Art or Science
- Classical Management Approach
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- Organising in Management
- What is Organisation Structure?
- What is Departmentation?
- What is Span of Control?
- What is Authority?
- What is Staffing?
- What is Human Resource Planning?
- What is Job Analysis?
- What is Recruitment?
- Modern and Others Schools of Management Thought
- What is Selection?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Controlling?
- What is Leadership?
- What is Organisational Change?
- Motivation in Management
- Motivation Theories
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Herzberg Two Factor Theory
- Mcclelland’s Needs Theory of Motivation
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Organizational Behavior Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs | Organisational Behavior in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)






