What is Learning?
Learning can be defined as a relatively permanent change in behaviour or potential behaviour as a result of direct or indirect experience. Learning is thus a change in behaviour as a result of experience.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Learning?
- 2 Learning Definition
- 3 Meaning of Learning
- 4 Nature of Learning
- 5 Elements of Learning
- 6 Types of Learners
- 7 Characteristics of Learning
- 8 Learning Process
- 9 Principles for Learning
- 10 Factors Affecting Learning
- 11 Application of Learning
- 12 Theories of Learning
- 13 Measures of Consumer Learning
- 14 Difference between Training, Education, Learning & Development
Learning Definition
Learning is any relatively permanent change in behaviour that occurs as a result of experience.
Stephen P. Robbins
Learning is the process of having one’s behaviour modified, more or less permanently, by what he does and the consequences of his action, or by what he observes.
Munn N.L.
Learning can be defined as relatively permanent change in behaviour potentially that results from reinforced practice or experience.
Steers and Porter
Meaning of Learning
There are two primary elements in meaning of learning:
- Change must be relatively permanent: This means that after “learning” our behavior must be different, either better or worse as compared to our behaviour prior to this learning experience.
For example, you “learn” to drive a car or have learned how to use a computer. - This change must occur due to some kind of experience or practice. This learning is not caused by biological maturation.
For example, a child does not learn to walk, it is a natural biological phenomenon. We do not learn to eat or drink.
Nature of Learning
Learning is a relatively permanent change in knowledge or behavior that results from practice or experience. There are several key points in this definition.
- Learning comes change
- Change in knowledge or behavior has to be relatively permanent or long-lasting
- Learning takes place as a result of practice or through experience
Learning comes change
For example, when you learn a second language, your knowledge about how to communicate evolves, and your behavior changes when communicating with native speakers of the language.
Change in knowledge or behavior has to be relatively permanent or long-lasting
For example, If you attempt to communicate with someone in another language by looking up words in a dictionary that you quickly forget once the interaction is complete, learning did not take place because there was no permanent change in your knowledge of the second language.
Learning takes place as a result of practice or through experience
For example, Learning a second language requires much practice in pronunciation, word usage, and grammar.
Read: Motivation Definition | Types of Motivation | Importance of Motivation
Elements of Learning
Elements of learning are:
Motivation
Motivation is based on need and goals. Motivation acts as a spur to learning, with needs and goals serving as stimuli. Uncovering consumer motives is one of the prime task of marketers. Marketers educate motivated consumer segments why their product will best fulfill their needs.
Marketers use motivation research to unearth consumer motives and use it in developing marketing program.
Cues
Cues are the stimuli that give direction to those motives. In the market, marketing mix (place, price, packaging, styling, advertising and displays) serve as cues to help consumers fulfill their needs in product specific ways.
Cues serve to direct consumer drives when they are consistent with consumer expectations. Marketers must be careful to provide cues that do not upset those expectations.
For example, consumer expects high fashion stores to carry designer clothing at high prices thus; a high fashion designer should distribute his or her clothing only through exclusive stores and advertise only in quality fashion magazines..
Response
How an individual reacts to a drive or cue constitutes his or her response. Learning can occur even if responses are not overt. The carpet manufacturer who provides consistent cues to a consumer may not always succeed in stimulating a purchase, even if that individual is motivated to buy.
Instead, the manufacturer may succeed only in forming a favorable image of the carpet in the consumer’s mind i.e. evoking a tendency to respond by buying.
Reinforcement
Reinforcement increases the likelihood that a specific response will occur in the future as the result of particular cues or stimuli. Many marketers instinctively find that reinforcement serves to teach their customers a desired behavior. For example, telephone companies that give cash discounts to customers who pay their bill promptly are acting to ensure prompt payment in the future.
Types of Learners
There are following types of learners:
Visual Learners
- Visual learners learn primarily through the written word.
- They tend to be readers who diligently take down every word.
Auditory Learners
- Auditory learners learn primarily through listening.
- They focus their ears and attention on your words, listening carefully to everything you say.
- They like to talk rather than write and relish the opportunity to discuss what they’ve heard.
Kinesthetic Learners
- Kinesthetic learners learn better by doing
- This group learns best when they can practice what they’re learning
- They want to have their hands on the keyboard, the hammer, or the test tube because they think in terms of physical action.
Read: Perception Definition | Importance of Perception | Perception Bias
Characteristics of Learning
Characteristics of learning are:
- Learning is Purposeful
- Learning is a Result of Experience
- Learning is Multifaceted
- Learning is an Active Process
Learning is Purposeful
Each student sees a learning situation from a different viewpoint. Each student is a unique individual whose past experiences affect readiness to learn and understanding of the requirements involved.
Learning is a Result of Experience
Since learning is an individual process, the instructor cannot do it for the student. The student can learn only from personal experiences; therefore, learning and knowledge cannot exist apart from a person.
Learning is Multifaceted
Learning is multifaceted in still another way. While learning the subject at hand, students may be learning other things as well. They may be developing attitudes about aviation-good or bad-depending on what they experience.
Learning is an Active Process
Students do not soak up knowledge like a sponge absorbs water. The instructor cannot assume that students remember something just because they were in the classroom, shop, or airplane when the instructor presented the material.
Learning Process
The learning process has the following steps:
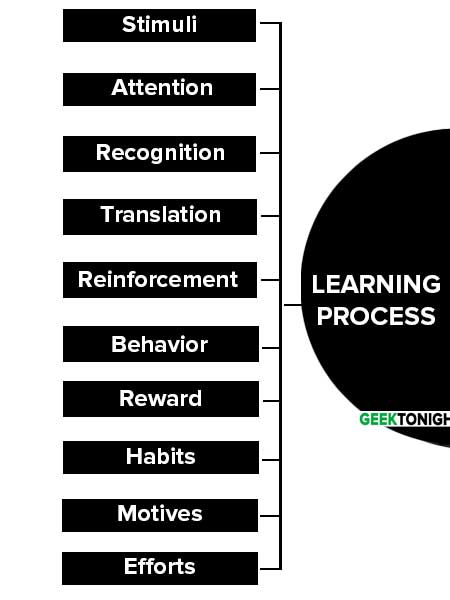
Stimuli
Stimuli are any objects and language which draw the attention of people. Employees get stimuli from the actions of their superiors. Superiors tell and advice employees who pay attention to these stimuli. All the stimuli may not be fully attended to.
Attention
The degree of attention depends upon the nature of stimuli. All stimuli are not paid attention to. Technical and interesting stimuli are highly attended. Career-oriented stimuli are generally accepted by employees. The personality levels of employees influence their desires to learn, motives for need fulfilment and tension reduction.
Recognition
Attention-paid stimuli are recognised as acceptable factors of improvement and new life styles. Employees paying attention to stimuli are recognising the stimuli for learning purposes. The levels of recognition depend upon the levels of values, preferences, needs and desires of the employees.
Translation
The translation and evaluation process is a crucial point for implementing the stimuli in behaviour through reinforcement. Employees behave properly through attitude changes, objectivity, mental and physical development. It is observed in better performances.
Reinforcement
Reinforced perception is learning. The perception process includes stimuli, attention, recognition, translation and behaviour. Perception leads to learning, but perception itself is not learning unless it is reinforced.
Repeated action is reinforcement. Reinforcement may be positive, negative, punishment and extinction. Learners learn as per their perception levels. Generally positive reinforcement is more effective for making permanent changes in behaviour.
Behavior
Learning changes behaviour through reinforcement of perceived knowledge. It makes permanent changes in behaviour. A temporary change in behaviour is not learning. Positive behaviour gives rewards to employees.
Reward
Employees expect rewards for learning. If the translated behaviour provides a reward, it is accepted, otherwise it is not accepted. Employees develop their behaviour into habits. Rewards may be monetary or non-monetary.
Habits
A permanent change in behaviour becomes a habit which helps continuous improvement in behaviour and performance. Employees develop the habit of selfappraisal and development. It helps to instil creativity and confidence in employees who are encouraged to behave properly again and again.
Motives
Motives depend on the level of satisfaction. Employees getting more satisfaction through learning develop high motives. Less satisfied learners have low motives. Learning is complete only when motives are fully realised and translated into efforts.
Efforts
Habits help achieve good efforts and performance. This is a continuous process. Efforts are the automatic outcome of good habits which are acquired through the learning process. Self-development is possible through self-effort. Employees willing to develop themselves are self-motivated and effort-oriented.
Read: Personality Definition | Determinants of Personality | Personality Characteristics
Principles for Learning
Over the years, educational psychologists have identities several principles which seem generally applicable to the learning process. They provide additional insight into what makes people learn most effectively.
6 Most important principles for learning are:
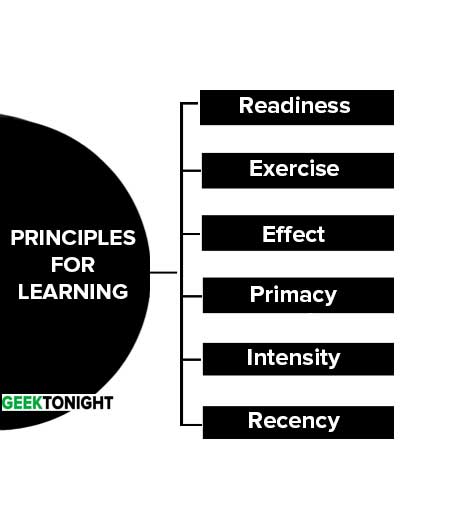
Readiness
Readiness implies a degree of single-mindedness and eagerness. When students are ready to learn, they meet the instructor at least halfway, and this simplifies the instructor’s job.
Exercise
The principle of exercise states that those things most often repeated are best remembered. It is the basis of drill and practice. The human memory is fallible. The mind can rarely retain, evaluate, and apply new concepts or practices after a single exposure.
Effect
The principle of effect is based on the emotional reaction of the student. It states that learning is strengthened when accompanied by a pleasant or satisfying feeling, and that learning is weakened when associated with an unpleasant feeling.
Primacy
Primacy, the state of being first, often creates a strong, almost unshakable, impression. For the instructor, this means that what is taught must be right the first time.
Intensity
Intensity: A vivid, dramatic, or exciting learning experience teaches more than a routine or boring experience. A student is likely to gain greater understanding of slow flight and stalls by performing them rather than merely reading about them.
Recency
The principle of recency states that things most recently learned are best remembered. Conversely, the further a student is removed time-wise from a new fact or understanding, the more difficult it is to remember.
Factors Affecting Learning
The key factors affecting learning include:
- Their resources
- Their image of learning
- The rewards associated with any learning activity
- The availability of information about learning opportunities
- The availability of appropriate learning environments, possibly virtual learning
- The climate in which learning takes place, especially that created by government and employers.
Read: What is Assessment Centre | Use of Assessment Centre | Assessment Centre Method
Application of Learning
Some of the behaviour modification techniques are given below which may be used in the organization:
- Use of Lotteries to reduce Absenteeism
- Work pay Vs sick pay
- Training and Development
- Discipline
- Self-Management
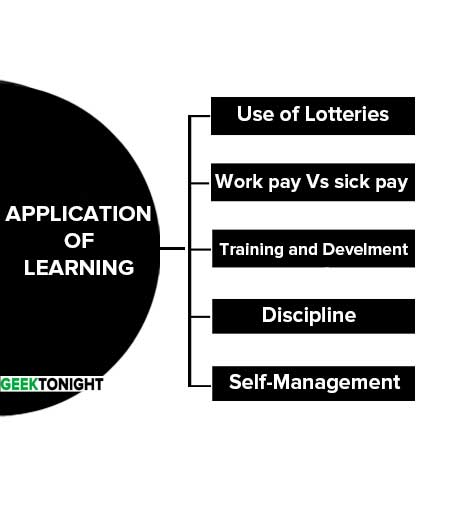
Use of Lotteries to reduce Absenteeism
Attractive prizes can be included in a lottery that can be used gainfully to achieve a reduction in absenteeism.
Work pay Vs sick pay
Organizations have to leave policy. Apart from other leave, there is a provision for a few days of sick leave in a year.
Training and Development
Training and development programmes must be run systematically and in a preplanned manner.
Discipline
Behavior modification can be achieved by laying down the minimum standard of discipline in the organization. Defence organizations are most disciplined organizations because they do not compromise on the standards, be it related to training, work, supervision, accounting or disbursement of salary and wages etc.
Self-Management
Learning concepts are meant for modifying the behaviour of others. These theories are also applicable for self-management. Individuals should lay down personal standards, objectives relating to personal growth, identify various courses of action to adopt and modify self-attitude and behaviour.
Theories of Learning
Theories of learning have been developed as models of learning which explain the learning process by which employees acquire a pattern of behavior. There are four theories of learning discussed below.
- Classical conditioning theory
- Operant conditioning theory
- Cognitive learning theory
- Social learning theory
Read Complete: Theories of Learning
Measures of Consumer Learning
For marketers, the dual goals of consumer learning are increased market share and brand-loyal consumers. These goals are interdependent.
Thus, it is important for marketers to measure how effectively consumers have “learned” its message. Recognition and recall tests are conducted for measureing consumer learning.
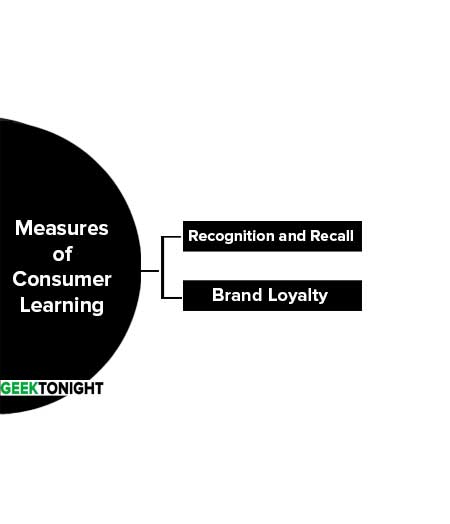
Recognition and Recall
Recognition and Recall tests are conducted to determine whether consumers remember seeing an advertisement and the extent to which they have read it or seen it and can recall its content.
Recognition tests are based on aided recall, whereas recall tests use unaided recall. In recognition tests, the consumer is shown an ad and asked whether he or she remembers seeing it and can remember any of its salient points.
In recall tests, the consumer is asked whether he or she has read a specific magazine or watched a specific television show, and if so, can he or she recall any ads or commercials seen, the product advertised, the brand and any salient points about the product.
Brand Loyalty
Brand Loyalty is the ultimate desired outcome of consumer learning. Brand loyalty consists of both attitude and actual behaviours toward a brand and that both must be measured. Attitudinal measures are concerned with the consumers’ overall feelings about the product and the brand, and their purchase intentions.
Behavioural measures are based on observable, factual behaviours regarding the brand, such as quantity purchased, purchase frequency and repeated buying.
Behavioural scientists who favour the theory of instrumental conditioning believe that brand loyalty results from an initial product trial that is reinforced through satisfaction, leading to repeat purchase.
Cognitive researchers, on the other hand, emphasize the role of mental processes in building brand loyalty. They believe that the consumers engage in extensive problem-solving behaviour involving brand and attribute comparisons, leading to a strong brand preference and repeat purchase behaviour.
Therefore, brand loyalty is the synergy among such attitudinal components as perceived product superiority, customer satisfaction, and the purchase behaviour itself.
Difference between Training, Education, Learning & Development
Training
Training is nothing but learning by doing. It is a well-planned program aimed at developing specific skills and knowledge of the manpower. It is a common concept of human resource development where an attempt is made to improve the performance, productivity and competency of the existing and potential employees through learning. The program is specially designed by the organisation to achieve definite goals.
An employee undergoing training is presumed to have had some formal education. No training program is complete without an element of education.
Education
It is theoretical learning in classrooms. The purpose of education is to teach theoretical concepts and develop a sense of reasoning and judgment. That any training and development program must contain an element of education is well understood by HR Specialists.
Any such program has resource persons to enlighten participants about theoretical knowledge of the topics proposed to discuss. In fact, organizations depute or encourage employees to do courses on a part-time basis. CEOs are known to attend refresher courses conducted by business schools.
Education is more important for managers and executives rather than low cadre workers. Anyways education is common to all employees, their grades notwithstanding.
Learning
Learning is the process of absorbing that information in order to increase skills and abilities and make use of it under a variety of contexts. Whatever the goals, the quality of the learning will rely largely on the quality of the training, and so the role of a trainer is very important as it can have a huge effect on the outcome of a course for the learner.
In essence, learning is all about equipping a person to tackle not just today’s issues, but preparing him/her to creatively come up with ways to tackle tomorrow’s issues.
Development
Development means those learning opportunities designed to help employees to grow. Development is not primarily skills-oriented. Instead, it provides the general knowledge and attitudes, which will be helpful to employers in higher positions.
Efforts towards development often depend on personal drive and ambition. Development activities such as those supplied by management development programs are generally voluntary in nature. The development provides knowledge about the business environment, management principles and techniques, human relations, specific industry analysis and the like is useful for better management of a company.
Reference
- Robbins, Stephen P. 2010. Organizational Behaviour. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall.
- Caldwell, D.F., and C.A. O’ Reilly III, “Measuring Person-Job Fit with a profile-comparison Process,” Journal of Applied Psychology, December 1990, pp.648-57.
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Organizational Behavior Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on What is Learning? | Organisational Behavior in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)





