What is Selection?
Selection is the process of evaluating job applicants to determine which candidates are most suitable for a particular job, based on their qualifications, experience, and other relevant factors.
It is basically a matching process, that is finding “FIT” between person and job.
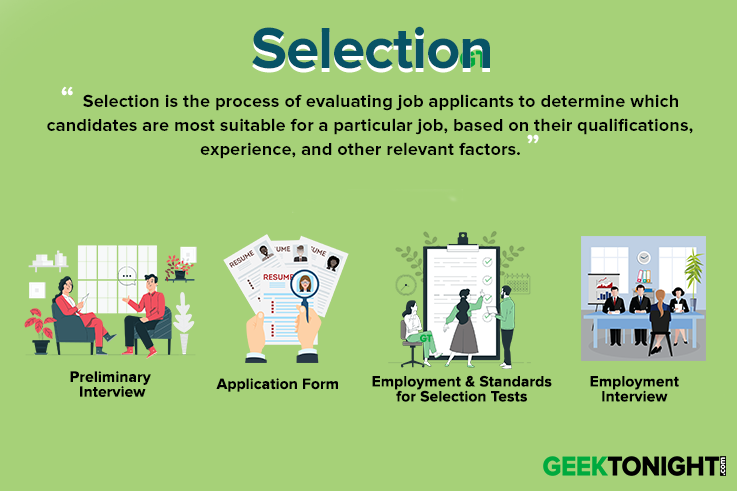
Table of Content
Selection Definition
Selection is defined as the process of choosing the best-fit candidate from a pool of qualified applicants, based on the candidate’s knowledge, skills, abilities, and other relevant characteristics. – Gatewood, Feild, and Barrick (2015)
The Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) defines selection as the process of screening job candidates to ensure that the most qualified individuals are hired.
Milkovich and Newman (2017) describe selection as the process of gathering information about job candidates and using that information to make hiring decisions that best meet the needs of the organization.
Selection Process
Steps in Selection Process are:
- Preliminary Interview
- Application Form
- Employment Test
- Standards for Selection Tests
- Employment Interview
Preliminary Interview
When a large number of applicants are available, the preliminary interview is desirable for both the company and the applicant. The main objective of such an interview is to screen out undesirable unqualified candidates at the very outset.
Care should be taken to ensure that the “weeding out” process does not lead to the elimination of desirable workers. Six items have been suggested as knock-out factors in the preliminary screening program of sales executives.
They include:
- Instability of Residence
- Failure in Business Within Two Years
- Divorce or Separation Within Two Years
- Excessive Personal Indebtedness
- Too High a Standard of Living
- Unexplained Gap in the Employment Record
Application Form
It is traditional & widely accepted for serving information from the prospective candidate. Many companies formulate their own style of application form depending upon the requirement of information based on the size of the company, nature of the business activity, type & level of the job. They also formulate different application forms for different jobs at the level. It includes the following items:
- Biographical Data: It includes name, present and permanent address, gender, date of birth, marital status, nationality, height, weight and number of dependents.
They provide information regarding the applicant’s socioeconomic background, family status & its impact on employee’s behaviour. This information can be used by the management to know the suitability of the candidate. - Educational Attainments: Education (subjects offered and grades secured) training acquired in special fields & knowledge gained from professional/technical institute or evening classes or through correspondence courses.
- Work Experience: Previous experience, number of the job held, nature of duties & responsibilities, duration of various assignments, the reason for leaving the previous employer.
- Salary: Demanded & other benefits expected.
- Personal Items: Association membership, personal likes & dislikes, hobbies.
- References: Name & address of previous employer & references.
Employment Test
They are used to get information about the candidate, which is not available from application blank or interview. They help in matching the characteristics of individuals with a vacant job so as to employ the right type of personnel.
Following the type of test are used:
- Intelligence Tests: It is a mental ability test. They measure learning ability, ability to understand instructions and make judgments. They measure several abilities such as memory, vocabulary, verbal fluency, numerical ability, perception.
- Achievement Tests: Achievement tests are designed to measure what the applicant can do on the job currently.
For example, Typing test shows typing proficiency, a shorthand test measures the person’s ability to take dictation. They are also known as work sampling tests, wherein a job applicant’s ability to do a small portion of the job is tested.
They involve:- Motor-involving physical manipulation of things
- Verbal
- Aptitude Test: Measures an individual’s potential to learn certain skills-clerical, mechanical, mathematical. These tests indicate whether an individual has the ability to learn a given job quickly and efficiently.
- Personality Test: Personality tests measure an individual’s personality factors and the relationship between personality factors and actual job criteria. The personality aspects which are evaluated are as follows – motivation, emotional balance, self-confidence, interpersonal behavior.
- Assessment Centre: Assessment center is an extended work sample. It uses groups and individual exercises. A batch of applicants is assessed by a team of 6 to 8 trained assessors.
Techniques are:- In baskets
- Group Discussions
- Business games
- Individual Presentation
- Structured Interview
- Graphology Tests: Analysis of lines, loops, hooks, strokes, curves in a person’s handwriting to assess the person’s personality and emotional makeup.
- Polygraph Tests: Also known as lie diction test, records physical changes in the body such respiration, blood pressure and perspiration on a moving roll of paper while answering a series of questions. Suitable for government agencies for filling security, police, fire and health positions.
- Issues: Is it possible to prove that the responses recorded by the polygraph occur only because a lie has been told? What about those situations in which a person lies without guilt (pathological liar) or lies believing the response to be true.
- Integrity Tests: To measure an employee’s honesty to predict those who are more likely to steal from an employer.
Such questions are generally asked:- Do you carry office stationery back to your home for occasional use?
- Do you mark attendance for your colleagues also?
- Have you ever told a lie?
Standards for Selection Tests
- Reliability: Test scores should not vary widely under repeated conditions.
- Test-retest reliability: techniques giving same results when repeated on the same person.
- Inner-rater reliability: giving same results, when used by two or more different rates.
- Intra rater reliability: technique which gives the same results, when repeatedly used by the same rater to rate the same behavior or attitudes at different times.
- Validity: is the extent to which an instrument measures what it intends to measure. Example typing speed.
- Content validity: is the degree to which the content of the test represent the actual work situation. Example, Typing test has high content validity for typist.
- Construct validity: is the degree to which specific trait is related to successful job performance. Example, Honesty would be important for bank cashier.
- Qualified people
- Preparation
- Suitability
Employment Interview
It is the oral examination of candidates for employment. In this step, the interviewer matches the information obtained about the candidate through various means to the job requirements and to the information obtained through his own observations during the interview.
It gives an opportunity to a recruiter to:
- To ask questions that are not covered in the tests.
- To make judgments on the candidates enthusiasm and intelligence.
- To assess facial expressions, appearance, nervousness.
- To give the facts to the candidate regarding the company policies, programs and promote goodwill of the company.
The coverage of the interview may include:
- Experience and education
- Previous employment
- Gaps in employment history
- Information on health, financial & domestic matters
- Marital status
- Likes & dislikes
- Expected level of achievement
- Extracurricular activities.
Difference Between Recruitment and Selection
- Recruitment means searching for sources of labor and stimulating people to apply for jobs, whereas selection means selecting of right kind of people for various jobs.
- Recruitment is a positive process whereas selection is a negative process.
- Recruitment creates a large pool of applicants whereas selection leads to the screening of unsuitable candidates.
- Recruitment is a simple process, it involves contracting the various sources of labour whereas selection is a complex and time-consuming process. The candidate has to clear a number of hurdles before they are selected for a job.
Types of Interview
Types of interview are:
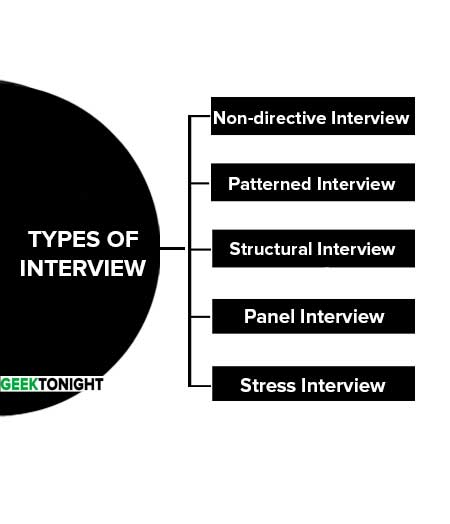
Non-directive Interview
In this, the recruiter ask questions as they come to mind. There is no specific format. The question can take any direction.
Patterned Interview
The employees follow a predetermined sequence of questions. Questions regarding his technical competence, personality traits, attitudes, motivation, etc.
Structural Interview
They are fixed job-related questions presented to each applicant. They are asked for a specific job.
Panel Interview
In this type of interview, the candidate is interviewed by a group of panellists representing the various stakeholders in the hiring process. Within this format, there are several approaches to conducting the interview.
Stress Interview
It is an interview in which the applicant is made uncomfortable by a series of often rude, annoying or embarrassing questions to test the applicant’s confidence level and ability to stand erect in a difficult situation is put to test.
Steps in Interview Process
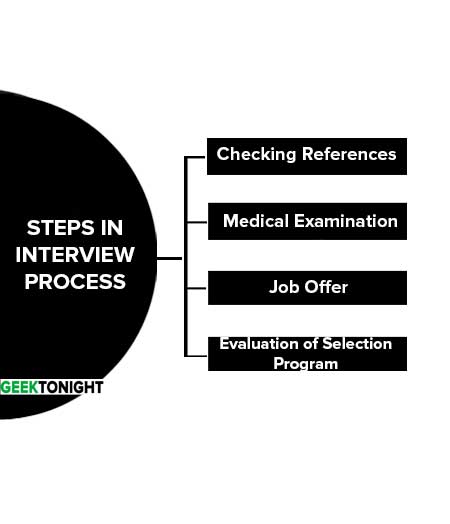
Checking References
An applicant may be asked to in the application blank to supply two types of references:
- Character references
- Experiences references
Medical Examination
A proper medical examination will ensure a higher standard of health and physical fitness of the employee and will reduce the rate of accidents, labor turnover & absenteeism.
The advantages of the medical examination are:
- It serves to ascertain the applicants physical Capabilities to meet the job requirement.
- It serves to protect the organization against the unwarranted claims under workmen compensation laws or against law suits for damages.
- It helps to prevent communicable diseases entering the organization.
Job Offer
It is made through a letter of appointment. It contains a date by which the appointee must report on duty. Decency demands that the rejected applicants be informed about their non-selection.
Evaluation of the Selection Program
Analysis of the Program
- Is the selection program consistent with the HRM theory and practice?
- Have well defined selection policies and procedures been developed?
- Are the employment policies consistent with the public policies?
How well is the program implemented?
Feedback Notes
- How many persons have rejected the company?
- What is the image created in the minds of university and institute?
Analysis of Results
- How well do those hired on job perform the job?
- What percentage of those who apply are hired?
- What portion of employee turnover can be attributed to faulty selection?
- What contribution does each of the selection tools make on the program?
Mistakes Committed by Interviewers
An interview is an act. Interviewees must be treated properly so as to leave a good impression about the company.
Here is a list of mistakes generally committed by the interviewers:
- Favor applicants who share his own attitudes.
- Not asking the right questions and not getting relevant responses.
- May be influenced by ‘cultural noise’- responses the applicant believes are socially acceptable rather than facts.
- May allow themselves to be unduly influenced by associating a particular personality trait with a person’s origin or cultural background, stereotyping.
- May allow the ratings to be influenced by his own likes or dislikes (bias).
- The poorly dressed candidate is not intelligent, attractive females are good for public dealings, etc. ‘Halo effect’- athlete make good salespeople.
- Candidate order error.
- Have been under pressure to hire at short notice.
- Have been influenced by the behaviour (his body language) his or her dress (especially in case of a female candidate) and other physical factors that are not job-related.
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)
Human Resource Planning
Management Topics
- What is Management?
- Who Is a Manager?
- Marketing CIs Management an Art or Science
- Classical Management Approach
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- Organising in Management
- What is Organisation Structure?
- What is Departmentation?
- What is Span of Control?
- What is Authority?
- What is Staffing?
- What is Human Resource Planning?
- What is Job Analysis?
- What is Recruitment?
- Modern and Others Schools of Management Thought
- What is Selection?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Controlling?
- What is Leadership?
- What is Organisational Change?
- Motivation in Management
- Motivation Theories
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Herzberg Two Factor Theory
- Mcclelland’s Needs Theory of Motivation
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Human Resource or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on What is Selection in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)








