The structure of an organisation should provide for communication in three distinct directions: downward, upward, and horizontal. These three directions establish the framework within which communication in an organisation takes place.
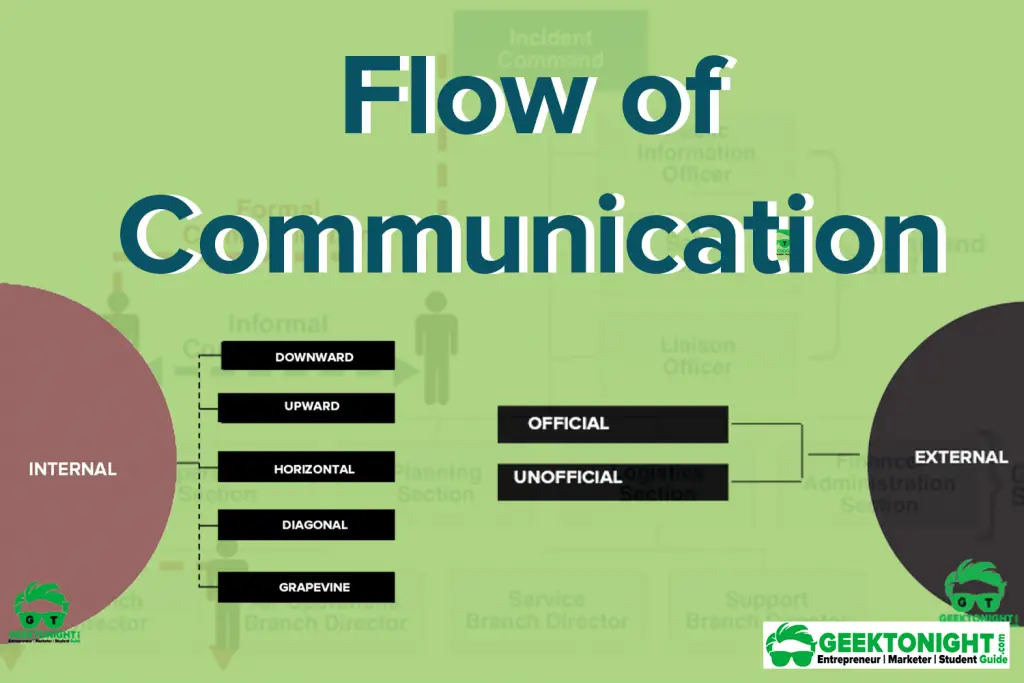
Type of Communication Flows
Flow of Communication can be of two type:
- Internal
- External
Examining each one briefly will enable us to better appreciate the barriers to effective organisational communication and the means to overcome them.
Table of Content
Internal
In understanding the forms of communication within organisations, one of the critical conceptions is directionality. Internal flow of communication in an organisation comprises the following:
Downward Communication
Communication which flows from a top level to a low level in an organisation is known as downward communication. This flow of communication is used by the managers to convey work-related information to the employees at lower levels.
Upward Communication
Flow of Communication which flows to a higher level in a company is known as upward communication. It gives feedback on how well the company is working. The subordinates use upward communication to express their performances and problems to their superiors.
The subordinates also use upward communication to tell how well they have understood the downward communication. It can also be used by the employees to share their ideas and opinions and also to take part in the process of decision-making
Horizontal Communication
In an organisation, the communication which occurs at same levels of hierarchy is known as lateral communication, that is, communication between managers, between peers at same levels or between any horizontally equivalent organisational members.
Diagonal Communication
The diagonal flow of communication concerns to communication between managers and employees situated at diverse functional divisions. In other words, it takes place when communication occurs among employees in a diverse unit of the organisation and where one of the employees involved is on a higher level in the organisation.
Grapevine Communication
Grapevine communication is a form of informal communications in business that develops within an organisation. Large organisations, where there are many people who are working closely, create certain unofficial or informal communication channels. These channels exist with or without authorised patronage.
External
The external flow of communication takes place between a manager and external groups such as suppliers, vendors, banks, financial institutes, etc. For instance, to raise capital the Managing director would interact with the Bank Manager.
2 Type of External communication are:
Official
- Press releases, conferences
- Speeches
- Advertising, marketing
- Letters, email
- Meetings with the community, stakeholders
- Blogs
Unofficial
- Whistle-blowers, media leaks
- External grapevine
- Insider trading
- Industrial espionage/intellectual property theft
- Blogs, complaints/‘flaming’ websites
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?