Brand building process refers to enhancing a brand’s equity directly through advertising campaigns and indirectly through promotions.
A well-planned brand building process follows many sequential steps, which are contextual, and thus cannot be generalized for all brands.
Brand Building Process
A generic view of brand building process shall consist of the following bare minimum essential steps:
- Step 1: Deciding what to brand
- Step 2: Knowing the customer
- Step 3: Mission & Value proposition of offering
- Step 4: Finding the market position
- Step 5: Create the right impression
Step 1: Deciding what to brand
The first step is to answer the question as to what is being branded. Companies and practising managers usually do confuse because of the ambiguity on branding the company, product or service. This increases brand equity and creates a virtuous circle of recognition.
The alternative is to build a business full of brands: this can be very expensive, time-consuming and confusing for your customers. However, sometimes it is simply the best solution. It is advisable to create a stand-alone profit centre for each brand under such circumstances.
Step 2: Knowing the customer
Research is key to building a successful brand. Once the true customers of the product or service offering have been identified, it is easy for the company to target them cost-effectively with little or no waste. Understanding their needs, wants and desires provides a platform to build on the process of brand building.
Step 3: Mission & Value proposition of offering
Once it has been understood as to who are the customers, the next step is to structure the effort in terms of the visions, mission and the value proposition being offered through the product or service offering.
Step 4: Finding the market position
The process of finding a place to build your brand in your market and in minds of customers is called Positioning. Positioning is the precise job of differentiating your offering, then slotting it into a free spot in the market to fulfil an unfilled need. Having completed your market research, you should know who your customers are, but more importantly, you should know who is most likely to want what you’re selling.
You should know their needs and desires, where they are, how to target them, what kind of messages will motivate them to buy from you, and what kind of customer experience will make them loyal to your brand.
The next step is to frame an effective marketing communication strategy. Designing a marketing and communications strategy requires the big-picture insight that guides the marketing activity and makes sure all activities add up to success. A good core strategy gives a special kind of high-level direction.
Step 5: Create the right impression
The average consumer faces numerous promotional messages every day. They only tune into messages that appeal to their wants and needs. They ignore messages for offerings they already buy from a trusted supplier. Unless, the offering presented is unique, attractive, different and better.
To grab their attention – and win their custom – you need to be all of these things. This has been associated with a fundamental psychological error of stereotyping. When brands of competing products appear to be similar, it creates clutter in the mind of the consumer.
The brad requires a face and voice that is a unique, simple and strong representation of the business. It should reflect your brand character and embody the promise made to customers. It must be consistent in image and tone across all marketing communications. It must be targeted in message and powerful enough to grab the customer’s attention – and win their custom.
Brand Building Factors
Several factors are crucial in building successful brands, as illustrated below:
- Quality
- Positioning
- Repositioning
- Communications
- First Mover advantage
- Long term perspective
- Internal marketing
Quality
Quality is a vital ingredient of a good brand. Remember the “core benefits” – the things consumers expect. These must be delivered well, consistently. The branded washing machine that leaks, or the training shoe that often falls apart when wet will never develop brand equity.
Positioning
Positioning is about the position a brand occupies in a market in the minds of consumers. Strong brands have a clear, often unique position in the target market. Positioning can be achieved through several means, including brand name, image, service standards, product guarantees, packaging and the way in which it is delivered.
Repositioning
Repositioning occurs when a brand tries to change its market position to reflect a change in consumer’s tastes. This is often required when a brand has become tired, perhaps because its original market has matured or has gone into decline.
Communications
Communications also play a key role in building a successful brand. We suggested that brand positioning is essentially about customer perceptions – with the objective to build a clearly defined position in the minds of the target audience.
First Mover advantage
Business strategists often talk about first-mover advantage. In terms of brand development, by “first-mover” they mean that it is possible for the first successful brand in a market to create a clear positioning in the minds of target customers before the competition enters the market. There is plenty of evidence to support this.
Long term perspective
This leads to another important factor in brand-building: the need to invest in the brand over the long-term. Building customer awareness, communicating the brand’s message and creating customer loyalty takes time. This means that management must “invest” in a brand, perhaps at the expense of short-term profitability.
Internal marketing
Finally, management should ensure that the brand is marketed “internally” as well as externally. By this, we mean that the whole business should understand the brand values and position. This is particularly important in service businesses where a critical part of the brand value is the type and quality of service that a customer receives.
Reference
- V. S. Ramaswamy, S. Namakumari; 2009; Marketing Management; MacMillan Publishers Pvt Ltd.
- Kotler, Keller, Koshy, Jha; 2009; 13th Edition; Marketing Management: A South Asian Perspective.
Marketing Management Topics
Go On, Share & Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something in Marketing Management Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Brand Building Process in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
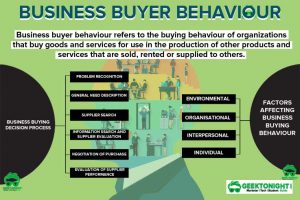
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management