What is a Presentation?
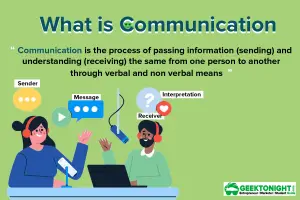
A presentation communicates a message, an idea or information to a group. It is similar to a report, but with a key difference–the human element. A presentation conveys the speaker’s personality and enables immediate interaction among all participants.
Table of Content
Objectives of Presentation
The main objectives of a presentation are:
To Inform
A presentation is created to convey some information to a group of people. For example, a presentation may display an organisation’s quarterly performance.
To Train
Most training programmes in organisations are done through the presentation mode. Such instructional presentations convey a lot of information and are created with instructional design principles to keep the audience engaged for a long period.
To Persuade
Some presentations are used to convince a group of people to accept a particular idea and/or make a certain choice.
To Motivate
The growing popularity of TED Talks indicates how a presentation can be a powerful motivation tool. These presentations trigger emotions and inspire people to act.
To Entertain
Presentations can also be used to celebrate an event. For example, a farewell presentation of a colleague can be used to narrate the story of his/her overall tenure, experiences and achievement in the organisation.
Main Elements of Presentation
A presentation is said to be effective if it has three main elements, which are as follows:
- Specific content: This refers to the information that a presentation will comprise. The information must be conveyed effectively so that it is absorbed by the audience in one sitting. It should be relevant and meaningful to them.
- Audience: A presentation should be targeted for a specific group of audience who share the same purpose and have a similar level of pre-knowledge.
- Presenter: The presenter should act as the advocate of the information. If his/her conviction and passion in the message are clearly articulated, the audience will also pay attention to the subject.
Important Presentation Skills
In today’s business environment, presentation skills are requisite in almost every professional arena. Employees are often required to give presentations on the targets achieved by them. A presentation can be effective if it is carefully planned and prepared.
However, delivering presentations is not always easy for every individual. Some people take presenting as a probable opportunity to showcase skills, while others find it a challenging task. To provide an effective presentation, a presenter must possess some abilities.
Some of them are explained as follows:
- Analytical ability
- Effective communication ability
- Creative ability
- Good interpersonal skill
- Sound time management
- Problem-solving ability
- A sense of humour
Analytical ability
It refers to a calibre which empowers an individual to collect, organise, visualise and comprehend data. Such skills enable a person to look at related patterns, draw conclusions and find solutions to problems. In addition, sound analytical skills also enable an individual to forecast future trends using various techniques such as brainstorming, forecasting, data mining and metrics interpretation.
Effective communication ability
Communication entails much more than mere talking to the audience. To communicate effectively during a presentation, one ought to showcase information lucidly. During a presentation, a person should not just have a good set of slides together; rather he needs to engage and strike a chord with the audience to transmit the intended message.
Creative ability
It refers to the ability to present things in a creative way that have not been explored earlier. Creative skills in presentation enable an individual to invent or develop something path-breaking, such as a new concept, unique way out from a problem, a method, a work of art or new machinery, etc.
Good interpersonal skill
It encompasses how an individual portrays or presents himself to the audience and builds a rapport with the audience. During a presentation, sound interpersonal skills empower a speaker to interact, communicate and collaborate with the audience effectively.
Interpersonal skills are prevalent across all personal and professional interactions between people. Interpersonal skills entail empathy, active listening and emotional intelligence.
Sound time management
While delivering a presentation, a person should manage time effectively, set a presentation schedule and end a presentation within a stipulated time. If a presentation is long, there are chances the audience may lose interest and the message may not be delivered.
A speaker cannot expect audience to actively listen to the presentation for hours. At the start of presentation, a speaker should aim to grab audience’s attention and allocate time for questions and answers at the end.
Problem-solving ability
Problem-solving is a requisite skill for a presentation. During a presentation, the audience may ask the speaker any kind of questions. On the other hand, it is important for the speaker to provide an appropriate answer to the audience to make the presentation successful.
A sense of humour
A sense of humour is crucial to deliver a quality presentation to make the environment light and engaging. Appropriate usage of light jokes relieves stress and holds the attention of an audience, which makes the presentation a memorable experience for both the speaker and the audience.
Evaluation Wheel
Evaluation wheel is a creative and effective tool that accumulates information on outcomes in a simple and accessible manner. A presenter can opt for the evaluation wheel tool to show the outcomes of the research or reports. This tool is used to provide various types of information and journeys of change within the organisation.
It offers a visual representation of progression and results in the form of a spider diagram. The evaluation wheel measures the exact outcomes for a programme at the start and end. It also helps educators, designers to comprehend information systematically. Figure shows an example of evaluation wheel:
Figure states the scale questionnaire in a circle form wherein respondents will analyse the instances from their discretion and experience and give rating on a scale of 1 to 5.
For instance, service users are appropriately involved. In this case, if the respondent strongly agrees, he/she will give 5 rating and if he/she does not agree, he/she will give 1 rating. The centre of the circle is for 1 and as the respondent agrees, they reach out to edge for 5 rating.
Ps of Presentation
Even the most powerful presentation may fail if the presenter comes unprepared. A presentation is both a mental and a physical effort. There are Ps of presentation that provide a checklist to the presenter for ensuring that the presentation is well-constructed and clear so that the audience gets the message. These four Ps are explained as follows:
Prepare
A thoroughly prepared presentation captivates the interests of the audience. The topic or content of the presentation must be thoroughly researched. No one would develop interest in a vague or equivocal presentation. A speaker can make use of stories or relatable examples and quote references to give more depth to the presentation and make it intriguing.
Apart from that, it should be ensured that only important points are highlighted in bullets or using other graphical elements. Providing too much of theory or full sentences can create boredom for the audience.
While preparing for a presentation, the presenter should include the following sections:
- Introduction: This section includes the name of the topic and the purpose of the presentation.
- Body: This section contains the main content of the presentation; thus, it must be prepared in a well-organised manner.
- Summary: It provides a recap of the content of the presentation. It outlines the most important points of the presentation to ensure the key message is retained by the audience.
Practice
Practice will make a man perfect is an adage that is appropriate across all spheres of life. It helps a speaker become familiar with his/her own voice, words and phrases and adjust accordingly. By practising thoroughly, a speaker can explore how to fit different pieces of information together and practise transition.
Also, a speaker should make notes wherever required as a part of presentation support. Using an index card is a common form of note-taking that provides a quick glimpse of important points.
Present
While delivering a presentation, the speaker needs to demonstrate confidence in front of the audience. The speaker must be polite, but not apologetic in situations, such as if the session is running overtime or the microphone has stopped working.
Instead he/she should expect and ask for discipline and attention. It is important for a speaker to engage with the audience during the presentation in order to assure them that he/she is genuinely interested in talking to them. 4. Pace, pitch and pause: A presenter should deliver the presentation in an easy-to-follow pace and try changing the pace to enliven the presentation.
For example, pauses can be taken intentionally between main points to reinforce them. Along with pace, pitch is equally important. Just as pace varies in normal conversations, it should be used effectively during presentations too. For example, when asking a question, the presenter can raise the pitch and can lower it down when explaining a point.
Four Cornerstones of Making Memorable Presentations
The most crucial aspect of delivering an effective presentation is that the speaker should appear confident and the speech should look effortless. Presentations are a source of anxiety for many individuals. However, getting well-prepared before delivering a presentation can reduce this feeling considerably and ease apprehension.
There are a number of ways to overcome feelings of anxiety, stress and stage fright before the presentation in order to appear confident in front of the audience. The four cornerstones of making a memorable presentation are provided in the upcoming sections.
Know Yourself
A presenter should acknowledge his/her strengths and weaknesses. Accordingly, he/she should decide the style of delivering a presentation. For instance, if a presenter has a great sense of humour and can use it comfortably in the speech, he/she can make the presentation more engaging and interesting.
On the other hand, if the speaker who is an introvert and prefers to talk or engage less, he/she can add visuals in the presentation. Therefore, the trick is whosoever is delivering the presentation should feel comfortable.
Know Your Material
Knowing the topic thoroughly is the most important step in preparing and delivering a presentation. A presenter with well-versed knowledge of the topic is bound to feel more confident. One should perform extensive research of the topic using credible websites and surveys.
A presenter with minimal information about the topic will not be able to deliver a memorable presentation; rather, it would create a negative image in front of the audience. A good presentation is one that is centred around the main theme, presents relevant information and stimulates thought.
Know Your Purpose
It is crucial to know the purpose of the presentation. A presenter should be aware of whether the purpose is to create awareness or to build new skills or to change attitudes. For instance, professional firms or businesses use presentations for various purposes such as to create awareness, educate, motivate and persuade internal and external audiences.
Therefore, to prepare a presentation, identify its objective/purpose, determine the method of delivery, formulate a structure, include visual aids and rehearse.
Know Your Audience
One should know the type of audience and what is their purpose of attending the presentation. For instance, whether they are there for gaining knowledge or learning new skills, etc. The age, culture and knowledge base of the audience help a presenter in designing and delivering his/her presentation effectively and in a manner in which audience can easily understand and relate to.
A well-designed presentation uses visual aids effectively to reinforce the main points and enhance the audience’s level of understanding.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
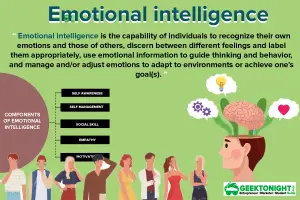
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?