What is Cheque?
A cheque is a bill of exchange, drawn on a specified banker and it includes ‘the electronic image of truncated cheque’ and ‘a cheque in electronic form’.
The cheque is always payable on demand. A cheque must contain all the characteristics of a bill of exchange.
Table of Content
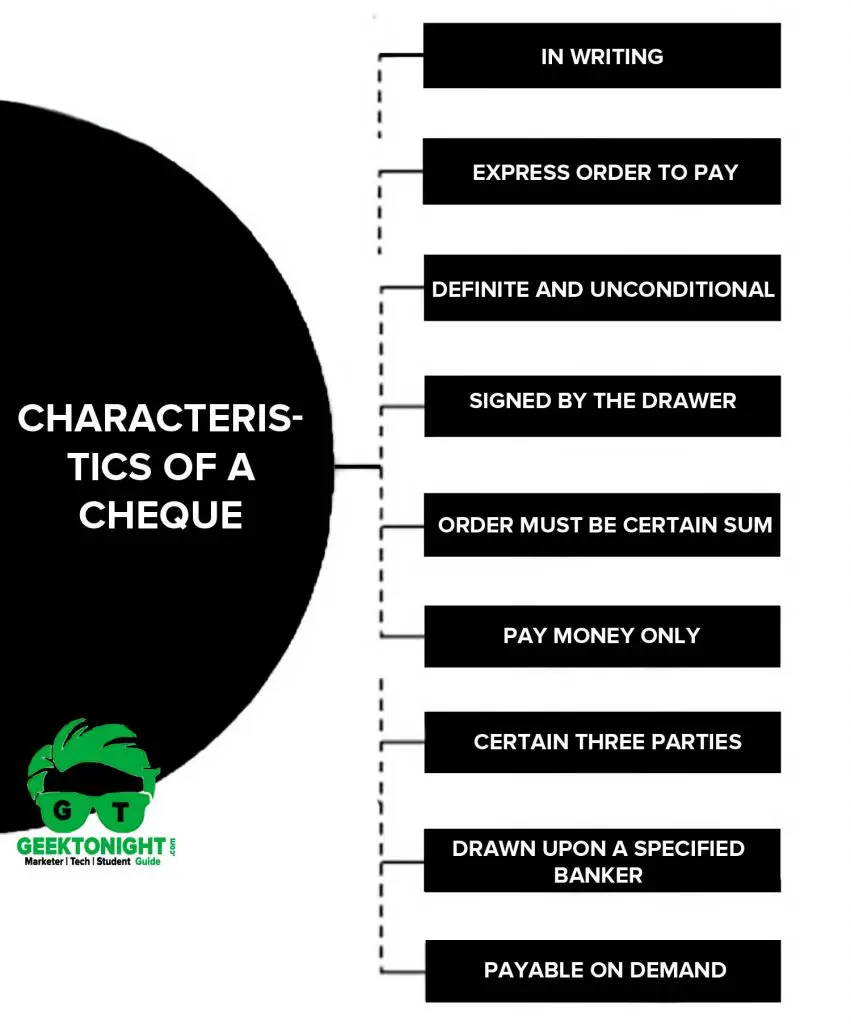
Characteristics of a Cheque
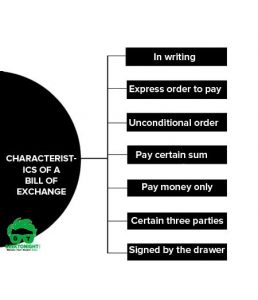
The essentials characteristics of a cheque can be summarized as under:
- It must be in writing.
- It must contain an express order to pay.
- The order to pay must be definite and unconditional.
- It must be signed by the drawer.
- The sum contained in the order must be certain sum.
- The order must be to pay money only.
- Three parties (drawer, drawee and payee) must be certain.
- It is always drawn upon a specified banker.
- It is always payable on demand.
Parties of Cheque
Basically, there are three parties to a cheque:
Drawer
Drawer is a debtor or borrower. The person who makes the promise to another to pay the debt.
Drawee
Drawee is a credit or lender. The person on whom the bill is drawn.
Payee
Payee The person to whom the money is to be paid or a person receiving payment.
Truncated Cheque
A truncated cheque means a cheque which is truncated during the course of a clearing cycle either by the clearing house or bank whether paying or receiving payment immediately on generation of an electronic image for transmission, substituting the further physical movement of the cheque in writing.
Cheque in electronic form
A cheque in electronic form means a cheque which contains the exact mirror image of paper cheque and is generated, written and signed in secure system, ensuring the minimum safety standards with the use of digital signature (with or without biometric signature) and asymmetric crypto system.
Presentment of truncated cheque
In case of and reasonable suspicion about the genuineness of the electronic image of a truncated cheque (e.g., suspicion as to fraud, forgery, tampering or destruction of the instrument), the paying banker is entitled to demand any further information regarding the truncated cheque. The payee banker can also demand the presentment of truncated cheque itself for verification.
Difference Between Bill of Exchange and Cheque
| Basis for Distinction | Bill of Exchange | Cheque |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A written document that shows the indebtedness of the debtor towards the creditor | A document used to make easy payments on demand and can be transferred through hand delivery is known as cheque |
| Defined in | Section 5 of The Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881 | Section 6 of The Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881 |
| Validity Period | Not Applicable | 3 months |
| Payable to bearer on demand | Cannot be made payable on demand as per RBI Act, 1934 | Always |
| Grace Days | 3 days of grace are allowed. | Not Applicable, as it is always payable at the time of presentment |
| Acceptance | Bill of exchange needs to be accepted | A cheque does not require acceptance |
| Stamping | Must be stamped | No such requirement |
| Crossing | No | Yes |
| Drawee | Person or Bank | Bank |
| Noting or Protesting | If a bill of exchange is dishonoured it can be noted or protested | If the cheque is dishonoured it cannot be noted or protested |
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Business Law Book References
- Goel, P. K. (2006). “Business Law for Managers” Wiley
- Sheth, T. (2017). “Business Law” (2ed.) Pearson.
- Kuchhal. M.C. & Prakash. “Business Legislation for Management” (2ed.) Vikas Publishing.
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Law Note? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Cheque | Definition, Types, Parties | Business Law in the comments section.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
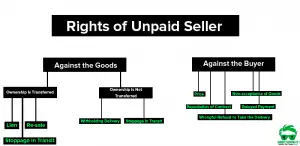
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
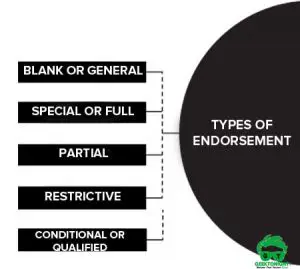
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
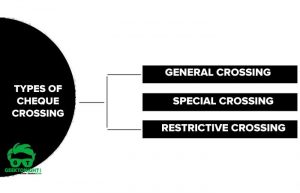
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India