Types of Contract in Business Law
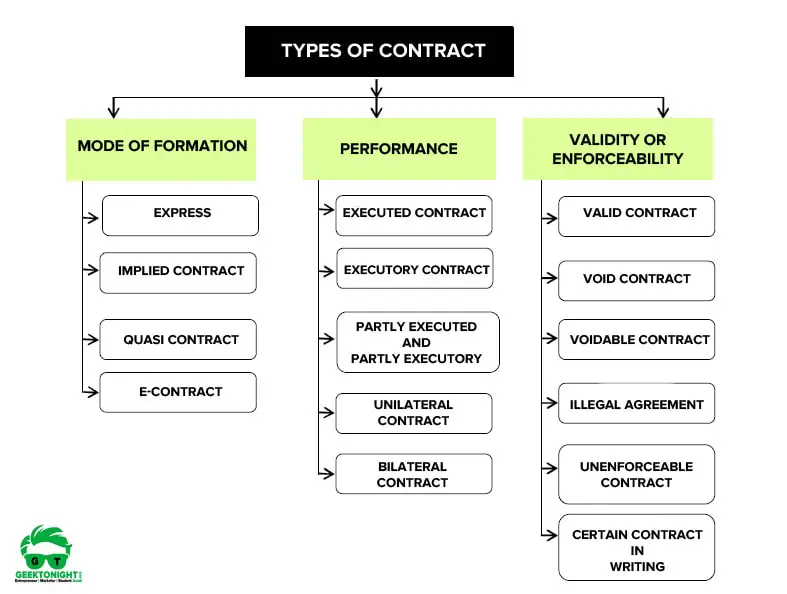
Broadly, types of contract are divided into 3 types:
- On the Basis of the Mode of Formation
- On the Basis of Performance
- On the Basis of validity or Enforceability
Table of Content
- 1 Types of Contract in Business Law
- 1.1 Express Contracts
- 1.2 Implied Contract
- 1.3 Quasi-contract
- 1.4 E-contract
- 1.5 Executed contract
- 1.6 Executory contract
- 1.7 Partly Executed and partly executory contract
- 1.8 Unilateral Contract
- 1.9 Bilateral contract
- 1.10 Valid contract
- 1.11 Void contract
- 1.12 Voidable contract
- 1.13 Illegal contract
- 1.14 Unenforceable contract
- 2 Difference Between Void and Voidable Contract
- 3 Key Points
- 4 Business Law Notes
- 5 Business Law Book References
Types of Contract
14 Types of Contract are:
- Express Contracts
- Implied Contract
- Quasi-contract
- E-contract
- Executed contract
- Executory contract
- Partly Executed and partly executory contract
- Unilateral Contract
- Bilateral contract
- Valid contract
- Void contract
- Voidable contract
- Illegal contract
- Unenforceable contract
Now let us discuss various types of contracts:
Express Contracts
A contract made by word spoken or written.
Section 9 of the Indian Contract Act 1872 provides that if a proposal or acceptance of any promise is made in words the promise is said to be express.
Example: A says to B ‘will you purchase my bike for Rs.20,000?” B says to A “Yes”.
Implied Contract
A contract inferred by
• The conduct of person
• The circumstances of the case.
By implies contract means implied by law (i.e.) the law implied a contract through parties never intended.
According to sec 9 in so for as such proposed or acceptance is made otherwise than in words, the promise is said to be implied.
Example: A stops a taxi by waving his hand and takes his seat. There is an implied contract that A will pay the prescribed fare.
Quasi-contract
In such a types of contract, the rights and obligations arise not by an agreement but by operation of law.
Example: If Mr A leaves his goods at Mr B’s shop by mistake, then it is for Mr. B to return the goods or to compensate for the price.
E-contract
An e-contract is a contract made through the digital mode.
Example: Via Internet
Executed contract
In an executed contract both the parties have performed their promises under a contract.
Example: A contracts to buy a car from B by paying cash, B instantly delivers his car.
Executory contract
In a Executory contract both the parties are yet to perform their promises.
Example: A sells his car to B for Rs. 2 lakh. If A is still to deliver the car and B is yet to pay the price, it is an executory contract.
Partly Executed and partly executory contract
In a partly executed and partly executory contract, one party has already performed his promised and the other party has yet to execute his promise.
Example: Anuj sells his bike to Bibek. Though Anuj has delivered the bike, Bibek has yet to pay the price. For Anuj, it is an executed contract, whereas it is an executory contract on the part of Bibek since the price has yet to be paid.
Unilateral Contract
A unilateral contract is also known as a one-sided contract. It is a type of contract where only one party has to perform his promise.
Example: Anuj promises to pay Rs. 1000 to anyone who finds his lost cellphone. B finds and returns it to Anuj. From the time B found the cellphone, the contract came into existence. Now Anuj has to perform his promise, i.e. the payment of Rs. 1,000.
Bilateral contract
A Bilateral contract is one where the obligation or promise is outstanding on the part of both the parties. It is also known as a two-sided contract.
Example: Aj promises to sell his car to Bj for Rs. 1 lakh and agrees to deliver the car on the receipt of the payment by the end of the week. The contract is bilateral as both the parties have exchanged a promise to be performed within a stipulated time.
Valid contract
If the contract entered into by the parties and satisfies all the elements of a valid contract as per the act, it is said to be a valid contract.
Void contract
Section 2 (j) states as follows: “A contract which ceases to be enforceable by law becomes void when it ceases to be enforceable”. Thus a void contract is one which cannot be enforced by a court of law.
Example: Mr Aj agrees to write a book with a publisher. After few days, Aj dies in an accident. Here the contract becomes void due to the impossibility of performance of the contract.
It may be added by way of clarification here that when a contract is void, it is not a contract at all but for the purpose of identifying it, it has to be called a void contract.
Voidable contract
Section 2(i) defines that an agreement which is enforceable by law at the option of one or more parties but not at the option of the other or others is a voidable contract.
This infact means where one of the parties to the agreement is in a position or is legally entitled or authorized to avoid performing his part, then the agreement is treated and becomes voidable.
Such a right might arise from the fact that the contract may have been brought about by one of the parties by coercion, undue influence, fraud or misrepresentation and hence the other party has a right to treat it as a voidable contract.
Illegal contract
Illegal contract are those that are forbidden by law. All illegal contracts are hence void also. Because of the illegality of their nature they cannot be enforced by any court of law.
In fact, even associated contracts cannot be enforced. Contracts which are opposed to public policy or immoral are illegal. Similarly contracts to commit a crime like supari contracts are illegal contracts.
Unenforceable contract
A type of contract which satisfies all the requirements of the contract but has technical defects is called an unenforceable contract.
A contract is said to have a technical defect when it does not fulfil the legal formalities required by some other act. When such legal formalities are compiled are complied with, later on, the act becomes enforceable.
Difference Between Void and Voidable Contract
| Basis | Void Contract | Voidable Contract |
| Definition | It means contract which ceases to be enforceable. | It means an agreement enforceable by law, by one or more parties. |
| Nature | Valid when made but subsequently becomes unenforceable. | It remains as voidable until cancelled by the party |
| Right or Remedy | No legal remedy is available for the void contract. | Aggrieved party has a remedy to cancel the contract. |
| Performance | Party cannot demand the performance of contract. | If aggrieved party does not cancel it within a reason-able time, performance can be demanded. |
| Reason | Contract becomes void due to change in law or circumstances. | If consent is not obtained freely then it is regarded as a voidable contract. |
| Damages | Party cannot claim damages. | Party can demand damages in certain cases. |
Key Points
- Void agreement – Agreement not enforceable by law and is without any legal effect.
- Void contract – Valid at the time of making but becomes void subsequently due to change in circumstances.
- Voidable Contract – Agreement enforceable at the option of the aggrieved party. Until the party won’t nullify, it remains valid.
- Illegal agreement – An agreement prohibited or forbidden by law.
- Express contract – Where parties orally or written defines the terms and conditions of the contract.
- Implied contract – Contract inferred from an act, conduct or from the circumstances of the case.
- Executed contract – Which has been completely performed by all the parties.
- Executory contract – One in which something remains to be done by all the parties.
- Bilateral contracts – Where the obligations on the part of both the parties are outstanding at the time of formation of the contract.
- Unilateral contract – Where only one party has to perform his duty or obligation.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Business Law Book References
- Goel, P. K. (2006). “Business Law for Managers” Wiley
- Sheth, T. (2017). “Business Law” (2ed.) Pearson.
- Kuchhal. M.C. & Prakash. “Business Legislation for Management” (2ed.) Vikas Publishing.
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Law Note? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Types of Contract | Business Law in the comments section.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
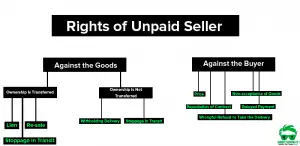
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
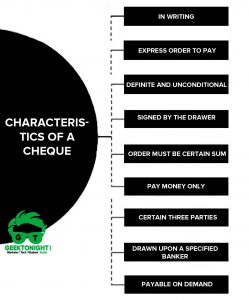
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India




Bht aacha …it helps students to acquire deep knowledge about business law
Thanks! Keep reading and provide your feedback.