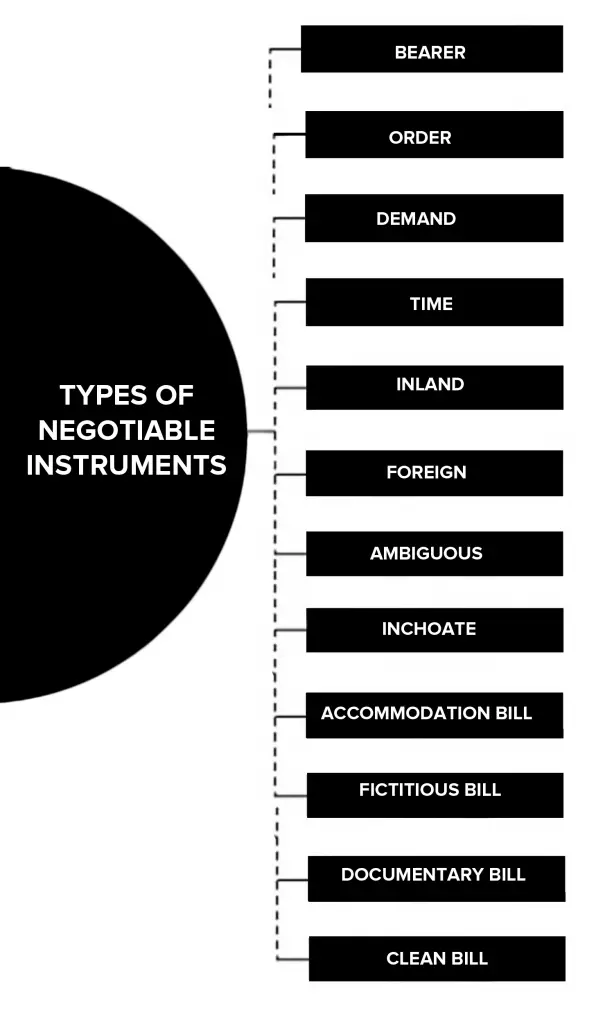
Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Bearer Instrument
- Order instrument
- Demand instrument
- Time instrument
- Inland instrument
- Foreign instrument
- Ambiguous instrument
- Inchoate Instrument
- Accommodation Bill
- Fictitious Bill
- Documentary Bill
- Clean bill
Negotiable Instruments Act
Section 13 of the Negotiable Instruments Act states that a negotiable instrument is a promissory note, bill of exchange or a cheque payable either to order or to bearer.
Table of Content
Classification of Negotiable Instruments
Broadly, Negotiable instruments are classified into 4 types.
- Based on Transfer (Bearer, Order)
- Based on payment (Demand, Time)
- Based on Location (Inland, Foreign)
- Other Instruments (Ambiguous, Inchoate)
Types of Negotiable Instruments
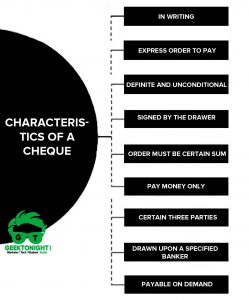
8 major types of negotiable instruments are discussed below:
- Bearer Instrument
- Order instrument
- Demand instrument
- Time instrument
- Inland instrument
- Foreign instrument
- Ambiguous instrument
- Inchoate Instrument
- Accommodation Bill
- Fictitious Bill
- Documentary Bill
- Clean bill
Based on Transfer
There are 2 types of negotiable instruments that are based on transfer:
Bearer Instrument
The negotiable instrument is payable to bearer when –
- It is expressed to be payable to bearer.
- The last endorsement is in the blank.
A promissory note cannot be payable to bearer. The bill of exchange cannot be made payable to bearer on demand.
Order instrument
The negotiable instrument is payable to order –
- Which is payable to a particular person.
- Which is payable to a particular person or his order.
- Which is payable to the order of a particular person.
Based on payment
There are 2 types of negotiable instruments that are based on payment:
Demand instrument
- The negotiable instrument, on which time for payment is not specified, is an instrument payable on demand.
- The negotiable instrument which is expressed to be payable on demand is also a demand instrument.
A cheque is always payable on demand. A demand instrument may be presented for payment at any-time. The demand instrument is not entitled to any days of grace.
Time instrument
An instrument in which the time for payment is specified is known as time instrument. The time instrument may be payable-
- On a specified day or
- After a specified period or
- Certain period after sight or
- On the happening of an event which is certain to happen.
Based on Location
There are 2 types of negotiable instruments that are based on location:
Inland instrument
A negotiable instrument is an inland instrument if it is –
- Drawn or made in India.
- Payable in India or is drawn on a person resident in India.
Example: A bill drawn in India payable in Japan, upon a person in India is an inland instrument.
Foreign instrument
The negotiable instrument which is not an inland instrument is called a foreign instrument.
The foreign instrument must be drawn outside India and made payable outside or inside India.
Other Instruments
2 other types of negotiable instruments are:
Ambiguous instrument
An ambiguous instrument means an instrument which can be constructed either as a promissory note or bill of exchange. Once the option is exercised, the instrument shall be treated accordingly.
Inchoate Instrument
Conditions for an inchoate instrument
- A person signs a negotiable instrument.
- The negotiable instrument is stamped.
- The negotiable instrument is either wholly blank or is partially blank.
- The person signing such negotiable instrument delivers it to another person.
Accommodation Bill
An accommodation bill means a bill which is drawn accepted without consideration. The person who becomes the holder of such a bill of good faith and for consideration after maturity may recover the amount from any party.
Fictitious Bill
A factitious bill is a bill in which the name of the drawer or the payee or both is fictitious.
Documentary Bill
A documentary bill means a bill to which the documents of title of the goods are attached.
Clean bill
A clean bill means a bill to which no document relating to the goods, is attached.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Business Law Book References
- Goel, P. K. (2006). “Business Law for Managers” Wiley
- Sheth, T. (2017). “Business Law” (2ed.) Pearson.
- Kuchhal. M.C. & Prakash. “Business Legislation for Management” (2ed.) Vikas Publishing.
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Law Note? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Types of Negotiable Instruments | Business Law in the comments section.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India