What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
Human resource management (HRM) is the process of acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees, and of attending to their labor relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
- 2 HRM Definition
- 3 Nature of HRM
- 4 Scope of HRM
- 5 Objectives of HRM
- 6 Functions of HRM
- 7 Importance of HRM
- 8 Skills and Proficiency of HR Managers
- 9 Human Resource Manager Competency
- 10 Why is Human Resource Management Important to all Managers?
- 11 HR Technology
- 12 HR Certification
HRM Definition
According to M L Cuming, “Human Resource Management is concerned with obtaining the best possible staff for an organization and having got them looking after them so that they want to stay and give their best to their jobs.”
Dale Yoder defines Human Resource Management as that part of the phase of management dealing effectively with control and use of manpower as distinguished from other sources of power.
According to F. E. L. Brech, Human Resource Management is that part of management progress which is primarily concerned with the human constituents of an organization.
Edison defines Human Resource Management as the science of human engineering.
According to Leon C. Megginson, the term human resource can be thought of as, “the total knowledge, skill, creative abilities, talents and aptitudes of an Organization’s workforce, as well as the values, attitudes and beliefs of the individuals involved.”
Nature of HRM
What is HRM Nature? Human resource management aims at fulfilling the goal of each individual and the organization on a whole.
Nature of HRM are:
- Pervasive Force
- People Oriented
- Action-Oriented
- Future-Oriented
- Development Oriented
- Enhance Employee Relations
- Interdisciplinary Function
Nature of human resource management are:
Pervasive Force
Human Resource Management is an inherent part of an organization. It is pervasive in nature and present in all enterprises at all levels of management. It is the responsibility of each manager to select the right candidate under him and pay attention to the development and satisfaction of each sub-ordinate.
People Oriented
Human Resource Management focuses on and values people at work both as individuals and groups. It encourages people to develop their full potential and in return give the best to the organization.
Action-Oriented
Human Resource Management does follow rules, records, and policies but it stresses the action. The focus is on providing an effective and timely solution to employees for any problems, tensions, or controversies faced by them.
Future-Oriented
To sustain and grow in this competitive environment organizations follow long term strategic planning. Effective Human Resource Management prepares people for current as well as future challenges, especially working in an environment characterized by dramatic changes.
Development Oriented
HRM continuously works towards the development of employees. There are various tools used to make the employees reach their maximum potential. Training programs are held to help employees enhance their skills and knowledge. Monetary and non-monetary reward structures are tuned to motivate the employees.
Enhance Employee Relations
HRM helps to build a healthy relationship between the employees at various levels. It encourages mentoring and counseling to help employees in times of need. It aims at creating a culture in the organization that is conducive to learning and growth.
Interdisciplinary Function
The knowledge that has influenced Human Resource Management is interdisciplinary in nature. It drives knowledge from five major bodies: education, system theory, economics, psychology, and organizational behaviour.
Jump Section: | What is HRM? | HRM Definition | Importance of HRM |
| Nature of HRM | Scope of HRM | Functions of HRM | Objectives of HRM
Scope of HRM
What is HRM Scope? Human Resource management has a very wide scope, Every department and activity in an organization needs human resources, even if it is about running machinery.
The scope of human resource management can be broadly divided into three:
HRM in Personnel Management
The objective here is to ensure the individual growth of each employee which indirectly contributes to the overall growth of the entire organization.
HRM in Employee Welfare
This aspect of HRM is concerned with the working condition and the amenities at the workplace. It makes the environment worth working by eliminating workplace hazards, providing job safety, medical and health services etc.
HRM in Industrial Relation
The main aim of this aspect is to maintain peace and harmony in the organization. It requires effective interaction with the labour or employee unions, sensitively addressing their grievances and settling their disputes.
Objectives of HRM
The primary objective of HRM is to place a competent and willing workforce in the right position and at the right time.
Further, it aims to obtain maximum individual development, desirable working conditions and at the same time, it focuses on contributing to the realization of the organizational goals.
The main objectives of HRM are:
- To help the organization achieve its goals: HRM is the means to assist the organization to achieve its goals. It ensures effective utilization of Human Resources which in turn results in the efficient utilization of all the other organizational resources.
- To employ a skilled workforce and focus on their training and development: HRM aims at employing the skills and abilities of the workforce efficiently. It generates maximum development of Human Resources within the organization by offering opportunities for growth to employees through training and development.
- To ensure employee job satisfaction and maintain a quality of work-life: HRM focuses on fulfilling the personal objectives of the employees which helps in enhancing their contribution to the organization. Their objective is to ensure respect for human beings by providing various services and welfare facilities to the personnel.
- Societal Objective: HRM must ensure that there is compliance with the legal and ethical standards of the society at each level and function of the organization. It implies that organizations manage human resources in an ethical and socially responsible manner.
Functions of HRM
Functions of HRM are:
- HR Planning
- Job Analysis and Design
- Recruitment and Selection
- Orientation and Placement
- Training and Development
HR Planning
Human Resource Planning is a process that identifies current and future human resource needs for an organization to achieve its goals.
Job Analysis and Design
Job Analysis is the determination of the precise characteristics of a job through an in-depth and detailed examination of the activities to be performed.
Job design allows job analysis. It involves designing the content of a job, it combines the tasks into a job to be assigned to an individual and further fixes the duties and responsibilities to do the job.
Recruitment and Selection
Recruitment is the process of searching the best-qualified candidate from within or outside the organization in a cost-effective manner.
Orientation and Placement
Orientation is the process in which the new employees are introduced and made familiar to their jobs, complex processes, coworkers, and organizations. Placement includes assigning tasks to new employees and the promotion or transfer of present employees.
Training and Development
Training is the process of enhancing the knowledge and skill of an employee required for a particular job.
Development is an ongoing and continuous process that aims at improving the personality and attitude of employees.
Importance of HRM
The Importance of human resource management can be discussed at three levels:
Instrument for growth to an organization
The survival and growth of the organization depend largely on the competence and its effective management. Human resource management makes workers efficient and motivated through training, supervision, and inspiring leadership.
Liaison between the employee and employer
It tries to maintain the balance between the available jobs and the job seekers according to their needs and organizational requirement.
Its significance can also be determined by the elimination of wastages and providing a healthy and conducive environment for employee growth.
Professional field
Human Resource Management has moved to a specialist function. The realization of employee goals is the sole responsibility, as a specialist function.
Its focus has moved from employee management to employee development. The skills development and individual capacity utilization are the challenges faced by human resource managers in the current scenario.
Jump Section: | What is HRM? | HRM Definition | Importance of HRM |
| Nature of HRM | Scope of HRM | Functions of HRM | Objectives of HRM
Skills and Proficiency of HR Managers
Job of an HR manager is the most challenging one as there is no factor of production as complex as people. HR managers need to integrate processes, people and technology in an efficient and effective manner that should enable the organization to achieve its goals.
While doing all this they need to assess, develop, reward and retain a wide variety of people. Discussed below are the skill sets that an efficient HR manager should possess
Multi- knowledgeable
HR managers should possess knowledge of all the diverse fields that collectively run a business. Since HR management is required in all the departments and at all levels, it is important that HR managers should be competent in all the diverse areas of finance, sales, marketing, operations etc
Personal attributes
HR managers should possess the mental ability to communicate, articulate and handle people and situations with intelligence He should have the learning skills as he needs to continuously upgrade himself to stay abreast with the outside world.
Coaching and teaching is a continuous process that an HR professional undertakes to develop the employee’s skills and personality.
HR managers should have both leadership and executive skills. They should be able to lead a large group of people towards a course of action that is in the best interest of the individual as well as the organization. They should also accurately and quickly execute the management’s decision regarding personal issues.
Professional attitude
HR manager’s job is getting professionalized. He should be organized as there is no margin of error when dealing with the lives and careers of people. He should have a comprehensive understanding of HR policies, principles, programs, practices and laws.
Ethical attitude
For healthy and successful running of a business, it is very important that the HR managers comply with the code of moral principles and values with respect to what is right or wrong. Employees should be coached from time to time and their ethical dilemmas should be cleared.
In case of any violation, the company should not hesitate to punish the unethical behaviour of the employees. HR professionals should communicate clearly and fairly and aim to promote equity. HR professionals are company conscience and keepers of confidential information. They should respect and maintain privacy always.
Human Resource Manager Competency
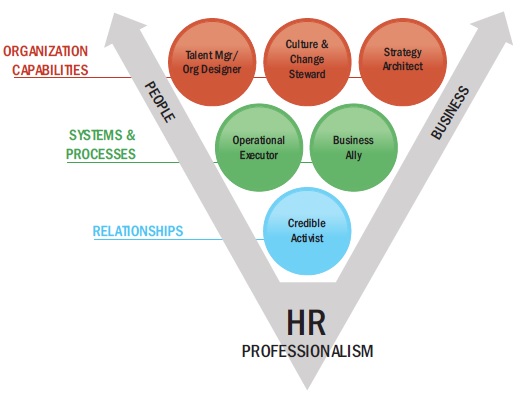
Professor Dave Ulrich and his colleagues say that today’s human resource managers need the knowledge, skills, and competencies to be:
- Talent Managers/Organization Designers, with a mastery of traditional human resource management tasks such as acquiring, training, and compensating employees.
- Culture and Change Stewards, able to create human resource practices that support the firms cultural values.
- Strategy Architects, with the skills to help establish the company s overall strategic plan, and to put in place the human resource practices required to support accomplishing that plan.
- Operational Executors, able to anticipate, draft, and implement the human resource practices (for instance in testing and appraising) the company needs to implement its strategy.
- Business Allies, competent to apply business knowledge (for instance in finance, sales, and production) that enable them to help functional and general managers to achieve their departmental goals.
- Credible Activists, with the leadership and other competencies that make them both credible (respected, admired, listened to) and active (offers a point of view, takes a position, challenges assumptions.)
Why is Human Resource Management Important to all Managers?
These concepts and techniques are important to all managers for several reasons.
- Avoid personnel mistakes: first, having a command of this knowledge will help you avoid the sorts of personnel mistakes you don’t want to make while managing.
- Improve profits and performance: similarly, effective human Resource management can help ensure that you get results through people.
HR Technology
Greater use of technology has led to organizational use of a human resource management system (HRMS), which is an integrated system providing information used by HR management in decision making. This terminology emphasizes that making HR decisions, not just building databases and using technology, is the primary reason for compiling data in an information system.
Purposes for Expanding HR Technology
The rapid expansion of HR technology serves two major purposes in organizations. One relates to administrative and operational efficiency, and the other to effectiveness.
Improve the Efficiency
The first purpose is to improve the efficiency with which data on employees and HR activities are compiled. The most basic example is the automation of payroll and benefits activities. Another common use of technology is tracking EEO/ affirmative action activities.
Beyond those basic applications, the use of Web-based information systems has allowed the HR unit in organizations to become more administratively efficient and communicate more quickly to employees.
Strategic HR Planning
The second purpose of the use of HR technology is related to strategic HR planning. Having accessible data enables HR planning and managerial decision making to be based to a greater degree on information rather than relying on managerial perceptions and intuition.
HR Certification
As the human resource manager s job becomes more demanding, human resource managers are becoming more professional. More than 115,000 HR professionals have already passed one or more of the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) HR professional certification exams. SHRM s Human Resource Certification Institute offers these exams.
Reference
- Garry Dessler, “Human Resource Management“, 13th ed., Pearson 2012.
- Aswathapa, K.(2008), Human Resource Management, 5th Ed, TMH
- J. Brattor, J. Gold, “Human Resource Management: Theory and Practice”, Machnillian Press, London, 2nd ed., 1999
- http://www.hrmguide.net/
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Human Resource Management Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on What is HRM | Definition, Nature, Scope, Objective, Function, Importance in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)







This is a monumental pieces. It is well informative, educative and Inspiring.