What is Brand Equity?
Brand loyalty is defined as a consumer’s preference to buy a specific brand in a product category. It is a result of consumer’s belief that the particular brand offers better product features, price and quality than other brands which make him or her purchase repeatedly from the brand. Brand loyalty develops over time, due to the trust and appreciation a consumer feels after purchasing and using a particular brand out of a set of such brands.
Brand loyalty is a consequence of the actual usage of a product or service of a company by a customer and deriving satisfaction from it. Consumer loyalty is achieved by offering free gifts, coupons, extended warranties, incentive programs, loyalty programmes, etc. to gratify customers and motivate them to make repeat purchases from them.
Table of Content
The concept of brand equity emerged in the early 1990s. It was not defined precisely, but in practical terms, it meant that brands are financial assets and should be recognised as such by top management and the financial markets.
Brand Equity Definition
Financial accountants define brand equity as the total value of a brand as a separable asset and often called brand valuation or brand value.
Marketer defines brand equity as measuring the consumers level of attachment to a brand can be called brand strength.
In another way, the description of the associations and beliefs the consumer has about the brand called brand image.
Two general motivations for studying brand equity
- Financially based motivation to estimate the value of a brand more precisely for accounting purposes in terms of asset valuation for the balance sheet or for merger, acquisition or divestiture purposes.
- Strategy based motivation to improve marketing productivity.
Components of Brand Equity
Brand equity consists of five different components:
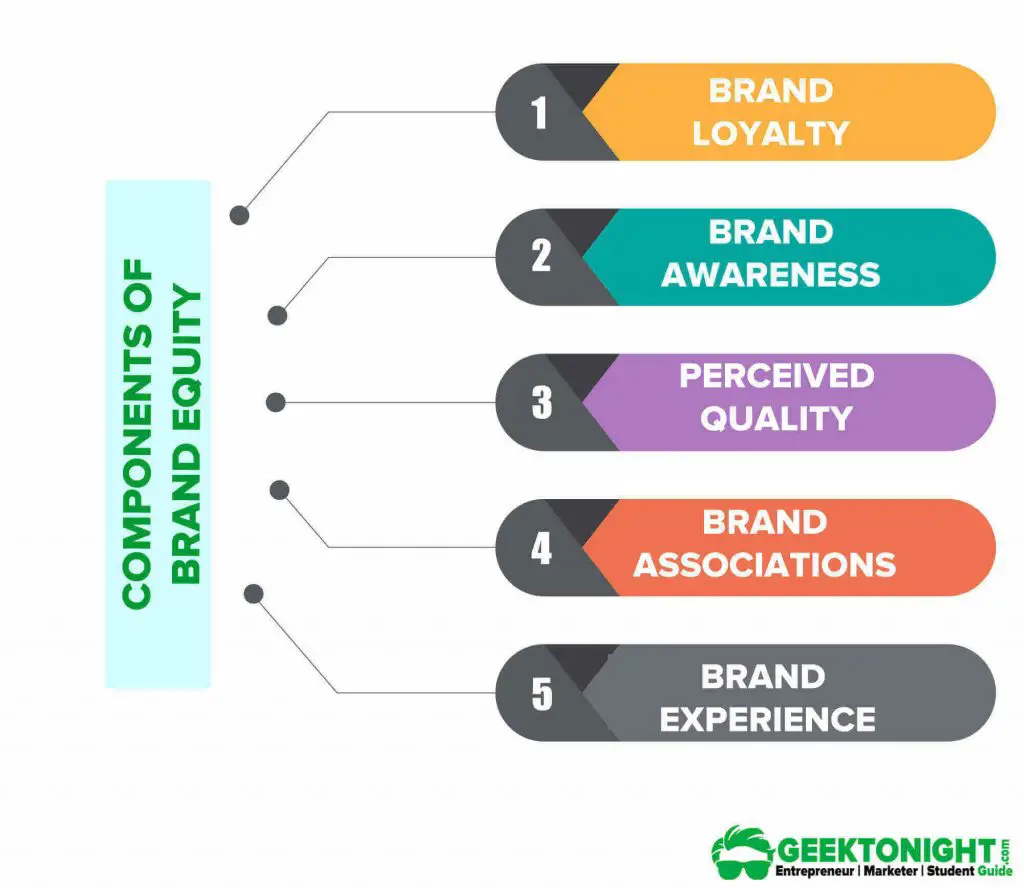
Brand Loyalty
Brand loyalty represents a favourable attitude toward a brand resulting in the consistent purchase of the brand over time prompted by a strong internal disposition. It represents a future revenue stream.
Brand Loyalty has two dimensions:
- Behavioural approach: have defined loyalty by the sequence of purchases and/or the proportion of purchases.
- Cognitive approach: underlines that behaviour alone does not reflect brand loyalty.
Customer loyalty is of strategic importance to the firm. It is an asset. Brand loyalty is the core of brand equity. It shows how likely a customer will switch to another brand, especially when that brand undergoes a change, be it in price or in product features
Brand Awareness
Brand awareness is the ability of a potential buyer to recognise or recall that a brand is a member of a certain product category.
Brand Awareness has two dimensions:
- Brand recognition: when a consumer is able to confirm prior exposure when given the brand as a cue.
Example: when they go to the store, will they be able to recognize the brand as one to which they have already been exposed? - Brand recall: consumers ability to retrieve the brand when given the product category, the needs fulfilled by the category, or some other type of probe as a cue.
Example: recall of Kellogg’s Corn Flakes will depend on their ability to retrieve the brand when they think of the cereal category.
Brand awareness is a crucial determinant of its participation in the consideration or evoked set. Generally, when a brand is not able to get a recall, it is not included in the consideration set. A recall is essential for finding membership in the evoked set. The mind share (top-of-the-mind recall) often leads to market share.
Perceived Quality
Perceived quality can be defined as the customer’s perception of the overall quality or superiority of a product or service relative to alternatives. Perceived quality is customer based.
Perceived quality has two dimensions:
- Objective quality: means the actual superiority of product or service.
- Perceived quality: perception of superiority of a product or service with respect to its intended function.
Benefits of perceived quality of a brand equity
- Firstly, perceived quality gives a powerful reason for the customer to consider and buy a specific brand.
- Second, perceived quality allows a brand to acquire a position or differentiation.
Brands with higher quality perception can afford to charge price premiums. The premium can be further deployed in brand-building efforts.
Brands with higher perceived quality find greater acceptance from trade partners and they are willing to carry such brands. Finally, it can be the basis to leverage brands into launching extensions.
Brand Associations
A brand association is any mental linkage to the brand. An association can affect the processing and recall of information, provide a point of differentiation, provide a reason to buy, create positive attitudes and feelings and serve as the basis of extensions.
Brand Association has three dimensions:
- Attributes: those descriptive features that characterise a product or service.
- Benefits: are the Personal value and meaning that consumers attach to the product or service.
- Attitudes: are defined in terms of consumers’ overall evaluations of a brand.
Benefits of brand association of a brand equity
- Firstly, Brands are bought for what is associated with them.
- Secondly, associations create value, is by becoming the basis of differentiation.
- Finally, associations provide a basis for extending the brand into new product categories
Brand Experience
Brand Experience is a type of experiential marketing strategy that includes a holistic set of conditions created by a company which is used to influence the feeling of the consumer towards its brand.
Read: Customer Based Brand Equity | Keller’s brand equity model
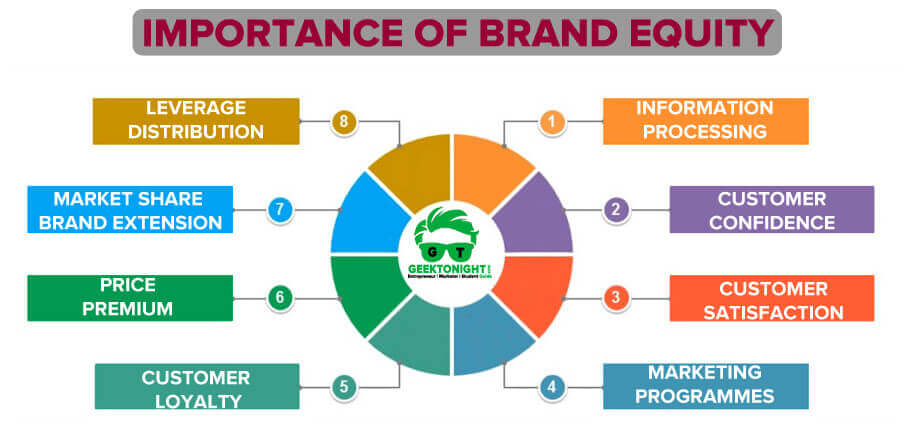
Importance of Brand Equity
Importance of Brand Equity is not only to capture market share but it also provides value to the customer, as well as to the firm. The resulting customer value becomes a basis for providing value to the firm.
Importance of Brand Equity are:
- Information processing
- Customer confidence
- Customer satisfaction
- Marketing programmes
- Customer Loyalty
- Price Premium
- Market Share and Brand Extension
- Leverage distribution channels
Value to Customers
Information processing
It helps customers in information processing. A brand is
useful in aiding customers in interpreting, processing, and storing information
about products and brands. It simplifies this process.
Customer confidence
A brand’s assets enhance customer confidence in the purchase
decision. One feels more confident in purchasing a brand. A brand’s assets in
the purchase decision.
Customer satisfaction
The final value to the customer comes in the form of usage satisfaction.
Value to Marketer
Marketing programmes
The effectiveness and efficiency of marketing programmes are increased by brand equity assets. The expenditure associated with a brand to achieve a goal generally tends to be less than an unbranded product aiming to achieve the same goal.
Customer Loyalty
Brand equity dimensions allow a firm to have greater customer loyalty. The customers can exhibit preference and commitment to a brand only.
Brand equity allows a firm to charge a premium. That is, a customer may willingly support a brand in spite of greater sacrifice that needs to be made.
Brand equity provides great opportunities for growth. In fact, most firms now rely on brand extensions to achieve growth rather than launch new brands.
Leverage distribution channels
Brand equity is a good source of achieving leverage in distribution channels. It is easier to get access to the distribution chain when the brand has equity.
Examples of Brand Equity
Starbucks Brand Equity
Starbucks is a US-based company has been operating in the coffee shop industry since 1971 and have a global reach of 28,000 outlets. Starbucks distinguished itself from competitors based on the coffee taste and ambience.
Porsche Brand Equity
Porsche has strong brand equity in the automobile industry due to its reliability image through the use of high quality, unique material. It is viewed as a luxury brand and owner pay not only for the product but for a great experience.
Apple Brand Equity
Apple is known among the consumer for its strong brand equity in the mobile industry. The design of the Apple brand is associated with culturally and economically technology power and has been implemented Total quality management.
Read: What is Strategic Management?
Brand equity measurement
Understanding of brand equity is an important task for an organization, without it they will struggle to set metrics for improvement.
Brand equity measurement is certainly complex and involves many variables, but it’s wholly possible.
Different ways to brand equity measurement
Brand Awareness
Customer knowledge about the product is an important part of brand equity. “conversion share” is a leading indicator for consumer awareness about your company product.
Measuring brand awareness for brand equity among target customers can take many forms:
- Surveys and focus groups
- Web traffic
- Search volume for your brand and products
- Social mentions and reviews
Local Marketer Perception Metrics
Local outlets are directly responsible for the way your customers experience the brand. By monitoring local marketers’ sentiment, we can understand whether your brand equity is increasing or decreasing and improve the quality of your support to local representatives.
Measuring Local Marketer Perception for brand equity among target customers can take many forms:
- Surveys
- Focus groups
- Software adoption rates
- Campaign deployment rates
What is Positive Brand Equity?
Positive brand equity means if consumer perception of and experiences with the brand is good and lead to purchase of product then it has positive brand equity.
Benefits of Positive brand equity helps in the following ways:
- A company can charge a premium price
- Brand Line extension
- It can help boost a company’s stock price.
Marketing Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What is Marketing?
- What is A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What is Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What is Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What is International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- What Is Consumer Research?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management





