What is Johari Window?
The Johari Window is a model used to help people understand their communication with others and themselves.
Johari Window is a psychological tool invented in 1955 by Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham. It is a simple technique for demonstrating and improving self-awareness and mutual understanding between individuals within a group.
This technique also aids in enhancing communication and teamwork and understanding group dynamics. The relationship between an individual and the group depends upon two factors, i.e., what an individual knows about himself or herself and what other people in the group know about the individual.
Table of Content
Johari Window Model
It is also called the model of personality development, self-awareness, group development and understanding interpersonal relationship. As per this model, there are four quadrants that can help in analysing self or personal awareness. Figure shows the model of the Johari Window:
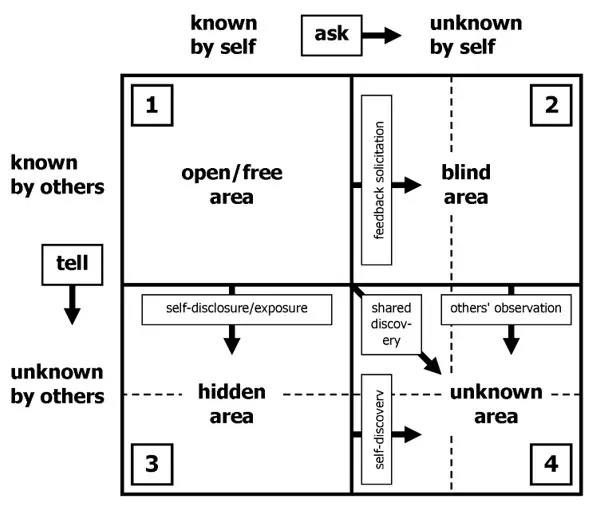
Let us discuss these four quadrants in detail:
Open Area
It defines all the aspects that an individual is willing to share with others about himself in order to build trust. The goal is to increase the open area of the window by asking for feedback from people or having meaningful interactions with other people.
Blind Area
Anything that is not acknowledged by an individual, but is noticed by others within the group comes under blind area. Blind area decreases if feedback is gained from others. The more feedback sought from others, the more one knows about his/her shortcomings, and therefore the blind spot diminishes.
It can help an individual become aware of his/her positive and negative traits as perceived by others. By working with others, one can discover and become aware about himself/herself that he/she never knew and appreciated before.
There are traits which one does not want others to know, but is aware of those aspects. For instance, an employee does not want to show his dissatisfaction with the job to others. This would certainly reduce the open area and increase the hid- den area.
Unknown Area
There are various aspects that are unknown to both parties, i.e., to the individual and the group. When areas are unknown, there are opportunities for discovery. For instance, an employee has good artistic and creative skills but he is unaware of his hidden talent and his company is also not aware of his drawing skills. The company has hired someone to design a logo. In this case, both parties are unaware of the potential existing inside the company.
Johari window reflects how individuals understand their relationship with themselves and others. Organisations also use this model to learn about the interpersonal behaviour of its employees. It can be applied to all types of communication and work settings.
The aim of the Johari window is to expand the ‘Open Area’ without stating anything too personal. People with large ‘Open Area’ communicate more openly and honestly. They get along with group easily. Therefore, the ‘Open Area’ is an important quadrant as the more you understand people in work settings, the more productive, effective and cooperative you will be when working together.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
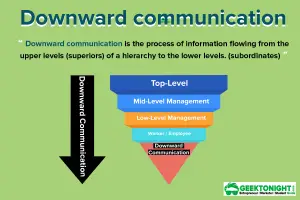
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
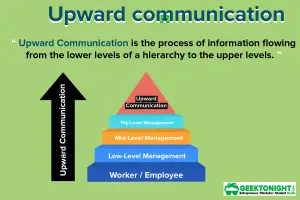
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?