What is Business Law?
Business Law is also known as Commercial law or corporate law, is the body of law that applies to the rights, relations, and conduct of persons and businesses engaged in commerce, merchandising, trade, and sales.
It is often considered to be a branch of civil law and deals with issues of both private law and public law.
Table of Content
Meaning of Law
The word ‘Law’ has been derived from the Teutonic word ‘Lag, which means ‘definite’.
On this basis Law can be defined as a definite rule of conduct and human relations. It also means a uniform rule of conduct which is applicable equally to all the people of the State. Law prescribes and regulates general conditions of human activity in the state.
“A law is a rule of conduct imposed and enforced by the sovereign.” – Austin
“La“Law is the body of principles recognised and applied by the state in the administration of justice.” – Salmond
Introduction to Business Law
Business law encompasses all of the laws that dictate how to form and run a business. This includes all of the laws that govern how to start, buy, manage and close or sell any type of business. Business laws establish the rules that all businesses should follow.
A savvy businessperson will be generally familiar with business laws and know when to seek the advice of a licensed attorney.
Business law includes state and federal laws, as well as administrative regulations.
Business Law Definition
Business law defines as a branch of law that “regulates relations that originate from conducting economic activities or that are in a close subject or functional relation with such activities.“
Business Law Meaning
Business Law originated in the common law system, particularly the one in the United States of America. By its content, it is a counterpart of the term “commercial law”.
The reasons to adopt the term “business law” are the following:
- In our area, commerce is understood as the exchange of goods for money rather than as an equivalent of all economic activities;
- the term “economic law” is not common in market economies as it reminds of an enforced legal administrative framework of conducting economic activities;
- “social property” as a proprietary basis of “economic law” has disappeared.
Business Law of India
Prior to the enactment of the various Acts constituting Business Law, business transactions were regulated by the personal laws of the parties to the suit.
The rights of Hindus and Muslims were governed by their respective laws and usages. Where both parties were Hindus, they were regulated by the Hindu Law and where both parties were Muslims, the Mohammadan Law was applied.
Gradually, the need for the enactment of a uniform law regulating the contracts was realised and this gave birth to the Indian Contract Act 1872
The sources of business law in India are generally the English laws which, in turn, have their roots in the following:
English Mercantile Law
The English Mercantile Law constitutes the foundation on which the super-structure of the Indian Business Law has been built.
The Statute Law
When a Bill is passed by the parliament and signed by the President, it becomes an ‘Act’ or a ‘statute’. The bulk of Indian Business Law is Statute Law.
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872;
- The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1981;
- The Sale of Goods Act, 1930;
- The Indian Partnership Act, 1932;
- The Companies Act, 1956 are instances of statute Law.
Judicial Decisions
Judicial decisions or case law are usually referred to as precedents and are binding on all courts having jurisdiction lower to that of the court which gave the judgement.
They are also generally followed even by those of equal jurisdiction in deciding similar points of law. Whenever an Act is silent on a point or there is ambiguity, the judge has to decide the case according to the principles of justice, equity and good conscience.
Customs and Usages
Custom or usage of a particular trade also guides the courts in deciding disputes arising out of mercantile transactions, but such a custom or usage must be widely known, certain any reasonable, and must not be opposed to any legislative enactment.
Summary
Business law encompasses all of the laws that dictate how to form and run a business. This includes all of the laws that govern how to start, buy, manage and close or sell any type of business.
The word ‘Law’ has been derived from the Teutonic word ‘Lag, which means ‘definite’. On this basis, Law can be defined as a definite rule of conduct and human relations. It also means a uniform rule of conduct which is applicable equally to all the people of the State.
There are various branches of law like International law, constitutional law, criminal law, civil law, business law or mercantile law.
The main sources of business law in India are English law, Judicial decisions, Customs and Usages and Indian statutes.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
Business Law Book Reference
- Goel, P. K. (2006). “Business Law for Managers” Wiley
- Sheth, T. (2017). “Business Law” (2ed.) Pearson.
- Kuchhal. M.C. & Prakash. “Business Legislation for Management” (2ed.) Vikas Publishing.
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Law Note? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on What is Business Law? Definition, Meaning, Books in the comments section.
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
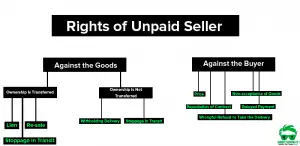
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
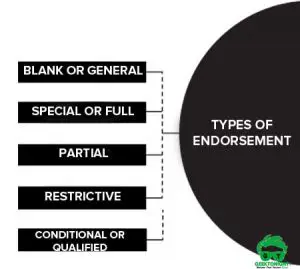
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
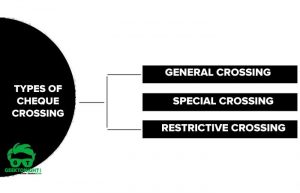
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Business Law Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India