In an IT project life cycle, a business case is the first deliverable which provides a detailed analysis of the feasibility study, the cost and risk involved in the project, the benefits, and the organisational value of the project. It is not a budget plan but it provides the management with all the detailed information with the help of which, one can decide whether to fund the project or discard the project plan.
Table of Content
The main purpose of developing a business case is to find out how the IT solution can create business value. There are many benefits of developing an IT project, some of which are as follows:
- It can increase the profit margins of an organisation.
- It can provide services in an efficient manner.
- It can improve customer satisfaction by providing fast access of information at any time.
- It can improve communication within or outside the organisation.
- It can help in decision-making.
- It can improve reporting capabilities.
Instead of the abovementioned benefits of IT projects, there are many IT projects that failed to return the benefit to the organisation. Most of these IT projects failed because they started without a de tailed analysis or understanding of the costs and risks involved in the project. Thus, an IT project should be selected on the basis of the val ue that it will bring to the organisation. The business case will show how the investment in the IT project will bring business value to the organisation.
IT Value Chain
The IT value chain is developed by Michael Porter, an American aca demic. It is a high level model used to describe how an organisational goal is aligned with the organisational strategy. The ultimate goal of the IT value chain is to provide maximum value to the organisation. While the project is completed, the actual achievement of the project is compared with the Measurable Organisational Value (MOV) in or der to determine if the project is successful or not. MOV is the overall goal and measures of success in an IT project.
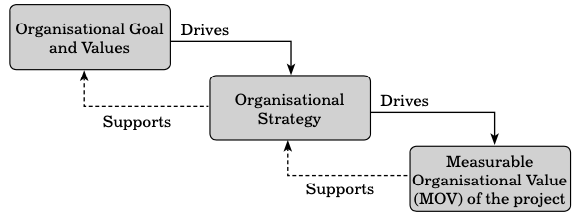
IT Value Chain
Project Goal
Apart from the organisational objective, a project has also some defi nite goals. However, the goals of the project support the overall objec tive of the organisation. The goals of the project are usually defined in terms of its scope, schedule, budget and quality as shown in Figure
As shown in Figure above, each goal is equally important for the overall success of the project.
Developing the Business Case
The business case should show how the cost involved in the IT project can lead to increase in the business value.
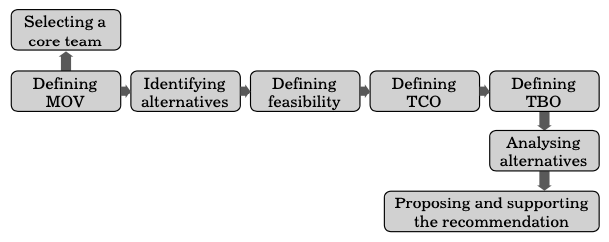
The following are the processes that should be carried out to develop a business case:
- Selecting a core team: A core team should be selected for devel oping a business case. The core team should have a manager, IT specialists, business specialists, etc. They should be well aware of the opportunities, limitations as well as risks that can be involved in IT.
- Defining Measurable Organisational Value (MOV): The main purpose of selecting a core team is to define the risks and benefits of the project and then identify the alternatives that can benefit the organisation. For this, the IT project must support the goal and objective of the organisation.
The process of managing the IT project is guided by MOV. A MOV can never be defined until the goal of the project is clearly defined or understood. MOV should be mea surable and verifiable to determine whether a project is successful or not. It provides value to the organisation as it guides in taking decisions and managing the IT projects. - Identifying alternatives: An organisational problem can be solved through various strategies. More than one strategy should be cho sen to solve a particular organisational problem so that there can be some alternatives in case the first approach fails. The alternatives should have a potential solution to the organisational problem.
- Defining feasibility and accessing the risk: Defining feasibility and accessing risk is very important. Feasibility can be viewed in many terms, such as economic feasibility, technical feasibility, organisational feasibility and other feasibility. Risk focus on deter mining the right and wrong in the project. It also determines how the organisation will avoid or minimise the risk involved in the project.
- Defining total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Total Cost of Owner ship (TCO) will include the direct and indirect cost as well as the ongoing cost. It is a list that includes the impact of cost. so, while preparing the business cases, TCO plays a very important role as it determines all sorts of cost.
- Defining total Benefits of Ownership (TBO): Total Benefits of Ownership (TBO) includes all the direct and indirect benefits as well as the ongoing benefits that are associated with the projects. TBO can be arrived at from increased high value work, improved work accuracy and efficiency, accurate decision-making, improved customer service, etc.
- Analysing alternatives: After determining the cost and benefits involved in the project, all the alternatives are compared to each other. The two most common ways to analyse the alternatives are financial models and scoring models. Financial models are based on profitability or cash flow, whereas scoring models are based on weightage score.
- Proposing and supporting the recommendation: When alterna tives are identified and analysed, it is required to choose any one of them. If the analysis was done carefully, the recommendation would be relatively easier.
Best Project Management Courses
Project management skills are in demand. If you are ready to get started, consider enrolling in the Google Project Management: Professional Certificate Learn the job-ready essentials of project management in six months or less, such as initiating projects, risk management and change management. Also we have made list of best project management courses as there are a plethora of options available, and it can be challenging to identify the best one.
Best Project Management Tool
Best for:
- Mid & Large Size Team
- Higher Plan
- Standard Feature
- Flexible Database & Stability
Best for:
- Small & Growing Team
- Smaller Plan
- Standout Feature
- Try New Feature
The ideal project management tool selection will eventually rely on the particular requirements of your team. We suggest experimenting with the free versions of various tools to gauge your team’s comfort level and then proceeding accordingly.
Project Management Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Project Management?
- Functions of Project Management
- What is Project?
- Project Managers
- What is Project Life Cycle?
- Project Feasibility Study
- What is Project Analysis?
- What is Project Planning?
- What is Project Selection?
- What is Project Schedule?
- What is Project Budget?
- What is Project Risk Management?
- What is Project Control?
- Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
- Best Project Management Tools
- What is Project Organisation?
- What is Project Contract?
- Types of Cost Estimates
- What is Project Execution Plan?
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Project Scope Management
- Project Scheduling Tools and Techniques
- Project Risk Identification
- Risk Monitoring
- Allocating Scarce Resources in IT Project
- Goldratt’s Critical Chain
- Communication in Project Management | Case Study
- Plan Monitor Control Cycle in Project Management
- Reporting in Project Management
- IT Project Quality Plan
- Project Outsourcing of Software Development
- Implementation Plan of Software Project
- What is Project Implementation?
- What is Project Closure?
- What is Project Evaluation?
- Software Project Management Challenges
- What is Project Management Office (PMO)?
- IT Project Team
- Business Case in IT Project Life Cycle
- PMP Study Guide