What is Sales Management?
Sales management refers to the administration of the personal selling component of a company’s marketing program. It includes the planning, implementation, and control of sales programs, as well as recruiting, training, motivating, and evaluating members of the sales force.
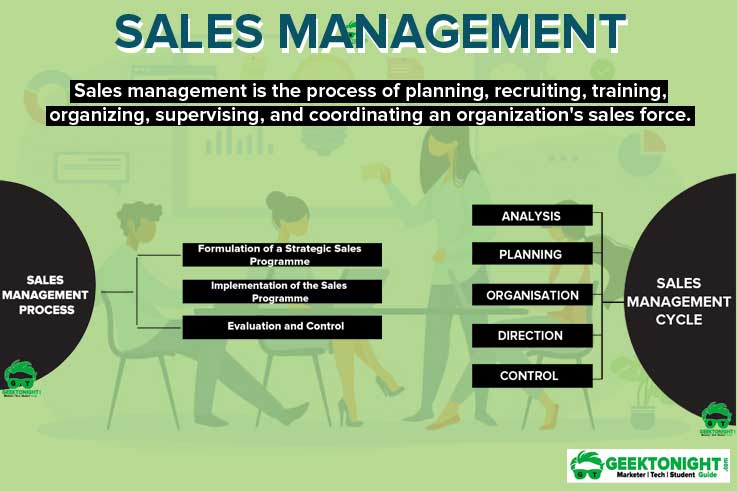
Table of Content
Sales management, apart, from the management of personal selling, encompasses marketing activities like advertising, sales promotion, marketing research, physical distribution, pricing, merchandising and so on.
Three Key Aspects of Sales Management
- Sales Operations
- Sales Strategy
- Sales Analysis
Sales Management Definition
Two sales management definition are mentioned below:
American Marketing Association (AMA) define sales management as:
“The planning, direction and control of personal selling, including recruiting, selecting, equipping, assigning, routing, supervising, paying and motivating as these tasks, apply to the personal sales force“.
B.R. Canfield define Sales Management involves the direction and control of salesmen, sales planning, budgeting, policymaking, coordination of marketing research, advertising, sales promotion and merchandising and the integration in the marketing programme of all business activities that contribute to the increased sales and profits.”
Sales Management Process
Sales management programme is formulated to respond effectively to an organization’s environmental circumstances, and these must be consistent with the businesses competitive and marketing strategies.
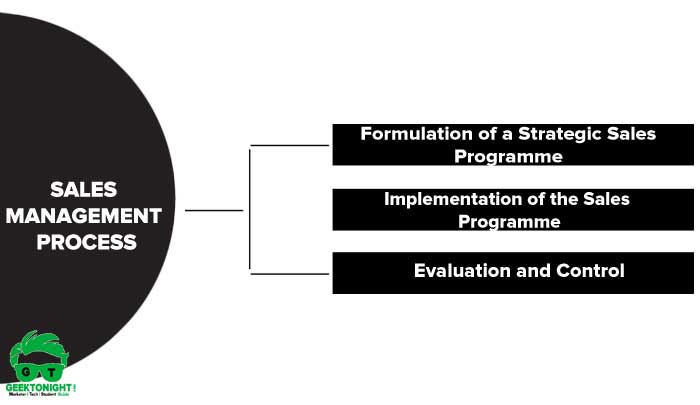
Sales management process have three stages:
- Formulation of a Strategic Sales Programme
- Implementation of the Sales Programme
- Evaluation and Control
Formulation of a Strategic Sales Programme
The strategic sales programme should consider the environmental factors faced by the firm. It should organize and plan the company’s overall personal-selling efforts and integrate these with the other elements of the firm’s marketing strategy.
Implementation of the Sales Programme
The implementation phase involves selecting appropriate sales personnel as well as designing and implementing policies and procedures that will direct their efforts towards the desired objectives.
Evaluation and Control
The evaluation phase involves developing methods for monitoring and evaluating the performance of the sales force.
Objectives of Sales Management
Sales management objectives are categorized into two types:
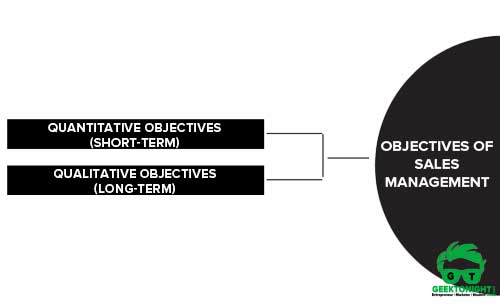
Quantitative Objectives (Short-term)
- To retain and capture market share.
- To determine sales volume in ways that contribute to profitability.
- To obtain new accounts of given types.
- To keep personal expenses within specified limits.
- To secure a targeted percentage of certain accounts of a business.
Qualitative Objectives (Long-term)
- To do the entire selling job.
- To service existing accounts, (customers).
- To search and maintain customer cooperation.
- To assist the dealer in selling the product line.
- To provide technical advice wherever necessary.
- To assist in training of middleman’s sales personnel.
- To provide advice and assist the middlemen.
- To collect and report market information of interest and use to the company management.
Sales Management Functions
Sales management is viewed as having a systematic relationship with each other. All functions and activities are considered as a dynamic process, composed of numerous interrelated parts, aiming to achieve the organizational sales objectives.
Different sales management functions are:
Managerial functions
Planning
- Forecasting demand
- Sales territory planning
- Personal selling
- Promotional efforts.
Organizing
- Structure
- Resource allocation
- Responsibility assignment
- Delegation of authority
Direction
- Leadership
- Motivation
- Communication
- Promotional steps including personal selling
Control
- Delegation
- Quota fixing
- Performance evaluation
- Incentives
- Budgets
Co-ordination
- Liaison
- Integration of various elements internally
- Public Relations
- Creating goodwill
Staff functions
- Recruitment and selection.
- Deployment and evaluation of performance
- Training and development.
- Career development.
- Compensation and incentives.
- Motivation and empowerment.
Advisory functions
- Product attributes/quality aspects.
- Pricing policies.
- Promotional steps
- Personal selling aspects.
- Distribution policies and channel selection criteria.
- Advertisement policies such as media selection and target audience.
- Transportation and warehousing aspects.
Liaison Functions
- Production department.
- Finance department.
- Marketing department.
- R & D department
- Distribution network
- After Sales Service department
Sales Management Cycle
A sales manager looks after and manages a firm’s personal selling functions.
Sales Management Cycle is shown below:
Analysis
This involves probing into the sales records of the company, analysing the reports of salespeople, investigation of marketing trends and other environmental factors.
Planning
It involves setting objectives of the firm’s sales efforts, formulation of sales strategies and policies in order to achieve those objectives.
Organisation
It involves the determination of the structure of the sales force and delegation of authority which is supposed to be necessary to achieve the organisation’s objectives.
Direction
It involves proper supervision and implementation of the plans with the help of proper communication, motivation and leadership.
Control
It involves a comparison of the actual with the desired results, finding out reasons for the deviation and taking corrective actions accordingly.
Importance of Sales Management
The importance of sales management are:
Society
To the Society: If jobs are to be made available for all those, who want and expect them, the economy must continuously expand its production of goods and services.
Equally important here is the fact, that an economy needs individuals, to sell what is produced. Through their persistent efforts to create and stimulate demand, salespeople could be said to be the life and blood of a productive economic system.
Consumers
To the Consumers: Professional people know their product or service, its major uses, limitations and benefits; which helps them to serve their customers, quite effectively.
For example, an insurance agent can analyze the hazards and risks that confront a client’s business or home-situation, examine existing coverage and offer helpful advice, in order to eliminate the gaps or overlaps in coverage, in addition to saving the client’s money.
The sales-engineers are qualified to analyze technical-problems, which may be confronting a particular organization and they can give the right recommendations for developing efficient operations.
Business Firms
To Business Firms: A business firm can be profitable only if its revenues exceed its costs. The prime responsibility of the salespersons is to sell the goods, produced by the organization, at a profit. Companies, salespeople and customers are different levels in the marketing chain; and these stand to benefit by sales activities.
The salesperson becomes an important source of field-intelligence by providing important (and sometimes very crucial) information, about the nature of competitive-activities, and also about the changing needs of customers.
The financial results of a firm depend on the performance of the sales department. Many salespeople are among the best-paid people in the business. It is one of the fastest and surest routes to enter into the top management bracket.
Difference Between Sales and Marketing
| COMPARISON | SALES | MARKETING |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Sales refers to the process of selling, whereby product is offered for sale to the customer at a certain price and at a given period of time. | Marketing is understanding the requirements of the customers in such a way that whenever any new product is introduced, it sells itself. |
| Orientation | Product-oriented | Customer-oriented |
| Approach | Fragmented approach | Integrated approach |
| Focus | Company needs | Market needs |
| Related to | Related to flow of goods to customers. | Related to all the activities which facilitates flow of goods to customers. |
| Duration | Short-term | Long-term |
| Relationship | One-to-One | One-to-Many |
| Aims at | Profit maximization through sales maximization. | Profit maximization through increased consumer satisfaction and market share. |
Responsibilities of a Sales Manager
Sales management involves a number of responsibilities. It is the income-producing division of a business.
The sales manager is responsible for:
- Providing profit contribution.
- Creating a proper image for the company and its products/services.
- Achieving the sales targets of the organisation.
- Satisfying customers and participating in marketing activities.
- He is responsible to the customer and society for the continuing growth of the organisation.
FAQ
Sales management refers to the administration of the personal selling component of a company’s marketing program.
Read Complete: What is Sales Management?
Different sales management functions are: 1. Managerial functions 2. Staff functions 3. Advisory functions 4. Liaison Functions
Read Complete: Sales Management Functions
Importance of Sales Management
The importance of sales management are:
1. Society 2. Consumers 3. Business Firms
Read Complete: Importance of Sales Management
Sales management process has three stages:
1. Formulation of a Strategic Sales Programme 2. Implementation of the Sales Programme 3. Evaluation and Control
Read Complete: Sales Management Process
Reference
- “Sales Management” By V.Das, Gupta 3.
- “Marketing Management” By Philip Kotler
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on What is Sales Management in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Sales Management
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO)?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?




I’m reading your idea and writing.I think your best author.