Lean Techniques for Process Optimisation
Six Sigma projects add value to business processes and generate value for customers. In each stage of a Six Sigma project, the objective is to reduce process defects. Processes are the driving force in Six Sigma projects. Along with processes, comes into the picture the concept of value addition and defects. A defect, in simple terms, means a deviation from specified requirements. Hence, any entity which is in non-conformance with processes results in defects.
Since a Six Sigma project aims to reduce defects, processes must be continuously optimized to produce a lesser number of defects at different stages of project execution. Therefore, the concept of lean techniques is used for optimizing the flow of value generation.
Table of Content
An example of value flow is the people who wait in a queue to be serviced at a restaurant or a service utility such as Metro Rail. In these examples, optimizing value flow means finding ways to bring value addition for the people standing in a queue or waiting at restaurant tables to be served a meal that is to be delivered via a queue-based system.
In these cases, processes that are not adding any value for customers require a relook. For example, the customer may be served light snacks and is waiting for the main course meal. This process of serving light snacks may be lean as it is not adding value for the customer, as he may be consuming food (snacks) that he has not ordered or the cost of serving snacks turns out to be too high in terms of the long waiting or serving time for the main course food.
The process of optimizing flow aims at preventing and eliminating stoppages and unnecessary wastages from the value chain. The process to provide a product or service to a customer begins to flow once the customer places an order and ends when the customer receives his complete order.
During the intermediary stages, value additions are taken into consideration and the requirements stated by the customer are addressed in as specific a manner as possible. This shifts the focus to the process of reducing defects.
Mechanisms of Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
Some mechanisms which are adopted for optimizing flow are as follows:
- 5S Tool
- Constraint Management
- Level Loading Mechanism Implementation
- Pull System Mechanism
- Implementation of Flexible Processes
- Reducing the Lot Size Mechanism
5S Tool
This is the most important tool which is deployed to eliminate process wastage. The 5S stands for:
Sort
Sort: This technique deals with the process of ensuring that only what is necessary is being executed. In other words, this means eliminating unnecessary steps in a process.
Set in Order
This technique involves ensuring that things that are required during the process execution are placed earlier in order so that they can be retrieved easily. Medical stores serve as a good example of the use of this technique. Medical stores keep in front those medicines that are commonly demanded. Also, they are put in sorted order.
Shine
This technique is designed to optimize the value-addition process. In essence, this technique involves maintaining neatness and cleanliness at the workplace to improve efficiency. Clean working conditions aid in the improvement of productivity by removing the clutter from the workplace.
Standardized Clean–up
This involves the process of determining, implementing, and maintaining a clean environment that works. In other words, a process may have a clean environment but if it does not work then it will not add value to the process.
Sustain
This involves the formulation of habits that ensure that the workplace remains neat, tidy, and clean to improve the efficiency and productivity of the processes and the workforce.
Constraint Management
A constraint is a limitation or a hindrance in the process execution phase. Every process operates under certain constraints. Also, every constraint consumes or requires some resources to remove the bottlenecks which arise from the constraint. Thus, constraint management itself becomes an activity that needs to be accounted for. The following are the points of consideration for constraint management:
- Each constraint must have the necessary resources to keep running.
- Every unit or resource provided to the constraint is of acceptable quality level.
- Every unit or resource produced by the constraint is of acceptable quality level.
- Constraint is operated in the most efficient manner possible.
Level Loading Mechanism Implementation
It involves a process of generating a stable, smooth schedule that is responsive to market dynamics. The goal of the level-loading mechanism is to make the same quantity of an item every day. In this way, process optimization is achieved to some extent. Level loading is done by using Takt time which is calculated as:
To create a level-loaded schedule, list part name, part number, daily quantity needed, and Takt time for each part. After this, sort the list by the quantity needed and Takt Time. This results in a level-loaded schedule.
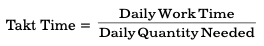
Pull System Mechanism
In this type of production mechanism, items are produced when needed. The production process is required to deliver the product fast. This is in sharp contrast to the push system of production wherein the focus is to develop the product and then hope that the buyer may buy it.
Through the pull system mechanism, the producer can deliver the product as per customer requirements and thus able to eliminate the non–value addition activities in the supply chain management process. An example of the pull systems mechanism is the weekly vegetable market wherein the fresh stock of vegetables attracts buyers.
Implementation of Flexible Processes
Flexible processes involve the use of lightweight & maneuverable tools, and fixtures and equipment. They help in improving safety, quality, productivity, and ergonomics. Flexible processes can be compared to a hybrid combination of pull and level loading mechanisms. An example of flexible processes includes bakery shops which can quickly make any bakery items such as cakes as per customer requirements.
Reducing the Lot Size Mechanism
By reducing the lot size, the producer can control the excessive quantity produced by a process, which is not required by customers. In addition, larger lot sizes pose other problems such as feedback delays, excessive inventory, obsolete inventory, etc.
Business Ethics
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Lean Six Sigma
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
Research Methodology
Management
Operations Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain



