What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is the set of decisions and actions resulting in the formulation and implementation of plans designed to achieve a company’s objectives.
It involves formulating and implementing strategies that will help in aligning the organisation and its environment to achieve organisational goals.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Strategic Management?
- 2 Introduction to Strategic Management
- 3 Strategic Management Definition
- 4 Nature of Strategic Management
- 5 Components of Strategic Management
- 6 Characteristics of Strategic Management
- 7 Need for Strategic Management
- 8 Benefits of Strategic Management
- 9 Risks of Strategic Management
- 10 FAQ
Introduction to Strategic Management
What is Strategic Management is exciting and challenging. It makes fundamental decisions about the future direction of a firm – its purpose, its resources and how it interacts with the environment in which it operates.
Every aspect of the organisation plays a role in strategy – its people, its finances, its production methods, its customers and so on.
- Strategic Management can be described as the identification of the purpose of the organisation and the plans and actions to achieve that purpose.
- It is that set of managerial decisions and actions that determine the long-term performance of a business enterprise.
- It involves formulating and implementing strategies that will help in aligning the organisation and its environment to achieve organisational goals.
- Strategic management does not replace the traditional management
Strategic Management Definition
Different authors have given different definition but the essence is the same. Below are the strategic management definition by authors.
Taken together, these definitions capture three main elements that go to the heart of strategic management.
The three on-going processes are strategic analysis, strategic formulation and strategic implementation. These three components parallel the processes of analysis, decisions and actions.
That is, strategic management is basically concerned with:
1. Analysis of strategic goals (vision, mission and objectives) along with the analysis of the external and internal environment of the organisation.
2. Decisions about two basic questions:
(a) What businesses should we compete in?
(b) How should we compete in those businesses to implement strategies?
3. Actions to implement strategies: This requires leaders to allocate the necessary resources and to design the organisation to bring the intended strategies to reality. This also involves evaluation and control to ensure that the strategies are effectively implemented.
Nature of Strategic Management
Strategic Management can be defined as the art & science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating, cross-functional decisions that enable an organisation to achieve its objectives.
Strategic management nature is different from other aspects of management. An individual manager is most often required to deal with problems of operational nature. He generally focuses on day-to-day problems such as the efficient production of goods, the management of a sales force, the monitoring of financial performance or the design of some new system that will improve the level of customer service.
Strategic management involves elements geared toward a firm’s long term survival and achievement of management goals.
Components of Strategic Management
In its broadest sense, strategic management is about taking “strategic decisions.” A number of definitions given by various eminent authors are already being given at the beginning of the chapter. In practice, a thorough strategic management process has three main components.
Strategic Analysis
This is all about the analysing the strength of businesses’ position and understanding the important external factors that may influence that position. The process of strategic analysis can be assisted by a number of tools, including:
- PEST Analysis: A technique for understanding the “environment” in which a business operates.
- Scenario Planning: A technique that builds various plausible views of possible futures for a business.
- Five Forces Analysis: A technique for identifying the forces which affect the level of competition in an industry.
- Market Segmentation: A technique which seeks to identify similarities and differences between groups of customers or users.
- Directional Policy Matrix: A technique which summarises the competitive strength of businesses operations in specific markets.
- Competitor Analysis: A wide range of techniques and analysis that seeks to summarise a businesses’ overall competitive position.
- Critical Success Factor Analysis: A technique to identify those areas in which a business must outperform the competition in order to succeed.
- SWOT Analysis: A useful summary technique for summarising the key issues arising from an assessment of a businesses “internal” position and “external” environmental influences.
Strategic Choice
This process involves understanding the nature of stakeholder expectations (the “ground rules”), identifying strategic options, and then evaluating and selecting strategic options.
Strategy Implementation
Often the hardest part, when a strategy has been analysed and selected, the task is then to translate it into organisational action.
Go To Section: What is Strategic Management? | Introduction to Strategic Management | Risks of Strategic Management |
Characteristics of Strategic Management
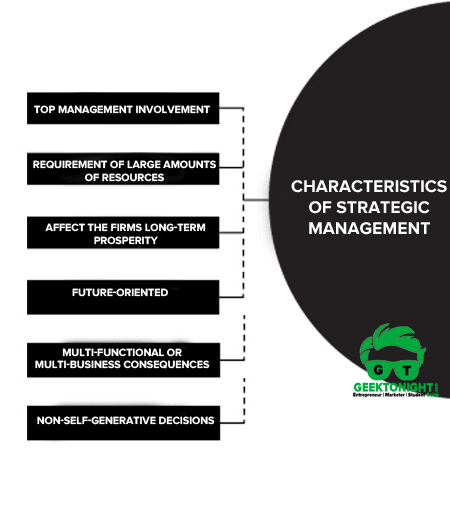
The Characteristics of Strategic Management are as follows:
- Top management involvement
- Requirement of large amounts of resources
- Affect the firms long-term prosperity
- Future-oriented
- Multi-functional or multi-business consequences
- Non-self-generative decisions
Top management involvement
Strategic management relates to several areas of a firm’s operations. So, it requires top management’s involvement.
Generally, only the top management has the perspective needed to understand the broad implications of its decisions and the power to authorise the necessary resource allocations.
Requirement of large amounts of resources
Strategic management requires the commitment of the firm to actions over an extended period of time. So, they require substantial resources, such as physical assets, 20 manpower etc.
Example: Decisions to expand geographically would have significant financial implications in terms of the need to build and support a new customer base.
Affect the firms long-term prosperity
Once a firm has committed itself to a particular strategy, its image and competitive advantage are tied to that strategy; its prosperity is dependent upon such a strategy for a long time.
Future-oriented
Strategic management encompasses forecasts, what is anticipated by the managers. In such decisions, the emphasis is on the development of projections that will enable the firm to select the most promising strategic options.
In the turbulent environment, a firm will succeed only if it takes a proactive stance towards change.
Multi-functional or multi-business consequences
Strategic management has complex implications for most areas of the firm. They impact various strategic business units especially in areas relating to customer-mix, competitive focus, organisational structure etc.
All these areas will be affected by allocations or reallocations of responsibilities and resources that result from these decisions.
Non-self-generative decisionsti-business consequences
While strategic management may involve making decisions relatively infrequently, the organisation must have the preparedness to make strategic decisions at any point of time. That is why Ansoff calls them “non-self-generative decisions.
Read: What is Strategic Management Process?
Need for Strategic Management
Strategic management provides the route map for the firm. It makes it possible for the firm to take decisions concerning the future with a greater awareness of their implications. It provides direction to the company; it indicates how growth could be achieved.
Firms are using strategic management for the following needs:
- It helps the firm to be more proactive than reactive.
- It provides the roadmap for the firm.
- It allows the firm to anticipate change and be prepared to manage it.
- It helps the firm to respond to environmental changes in a better way.
- It minimizes the chances of mistakes and unpleasant surprises.
- It provides clear objectives and direction for employees.
Benefits of Strategic Management
Today’s enterprises need strategic management to reap the benefits of business opportunities, overcome the threats and stay ahead in the race.
The benefits of strategic management is to exploit and create new and different opportunities for tomorrow; while long-term planning, in contrast, tries to optimize for tomorrow the trends of today.
Strategic management has thus both financial and non-financial benefits:
1. Financial Benefits: Research indicates that organisations that engage in strategic management are more profitable and successful than those that do not.
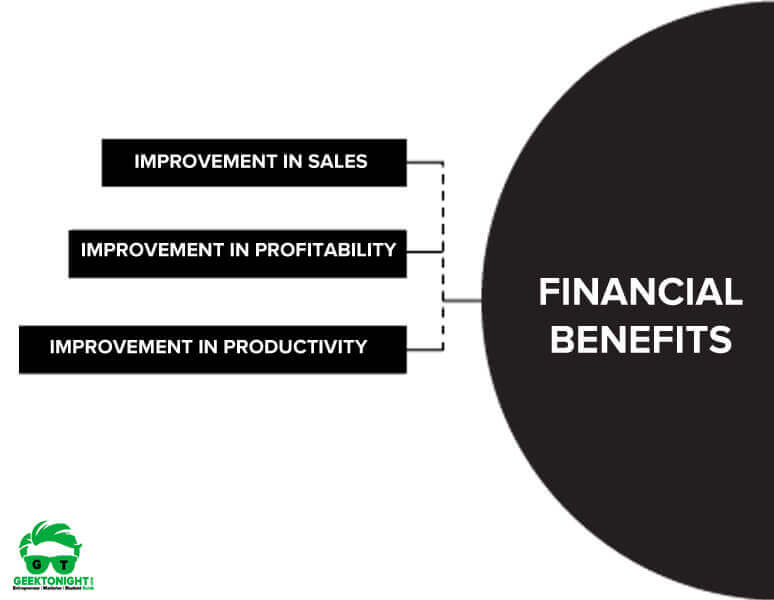
Businesses that followed strategic management concepts have shown significant improvements in sales, profitability and productivity compared to firms without systematic planning activities.
- Improvement in sales
- Improvement in profitability
- Improvement in productivity
2. Non-financial benefits: Besides financial benefits, strategic management offers other intangible benefits to a firm.
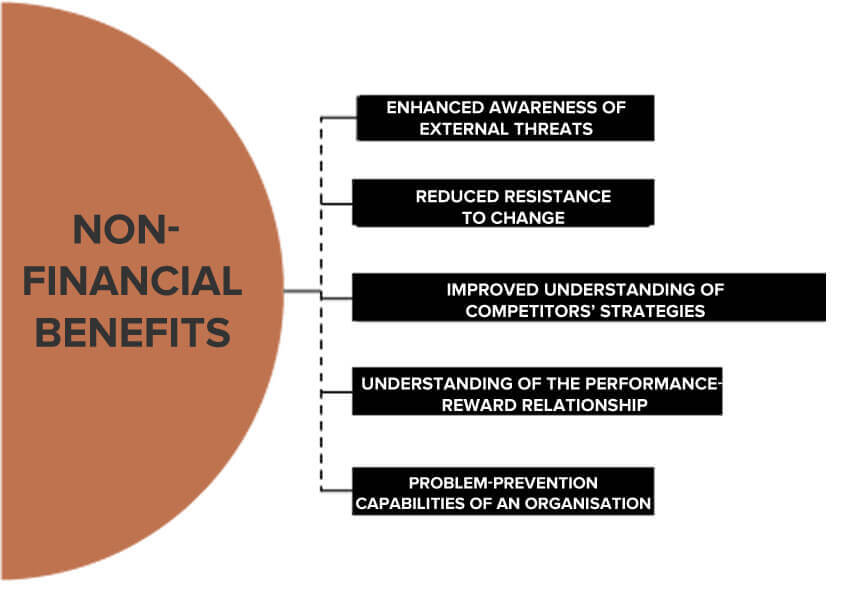
They are;
- Enhanced awareness of external threats
- Improved understanding of competitors’ strategies
- Reduced resistance to change
- A clearer understanding of the performance-reward relationship
- Enhanced problem-prevention capabilities of an organisation
- Increased interaction among managers at all divisional and functional levels
- Increased order and discipline
Read: What is Value Chain Analysis?
Risks of Strategic Management
Strategic management is an intricate and complex process that takes an organisation into unchartered territory. It does not provide a ready-to-use prescription for success. Instead, it takes the organisation through a journey and offers a framework for addressing questions and solving problems.
Strategic management is not, therefore, a guarantee for success; it can be dysfunctional if conducted haphazardly.
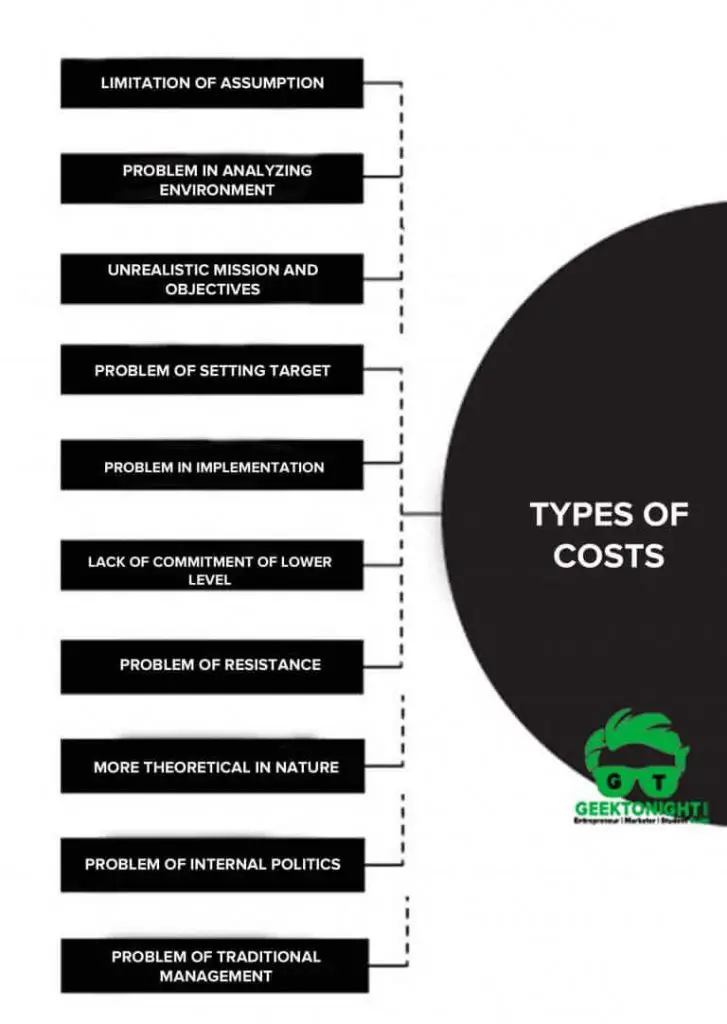
The following are the risk of strategic management:
- Limitation of Assumption
- Problem in Analyzing Environment
- Unrealistic Mission and Objectives
- Problem of Setting Target
- Lack of Commitment of Lower Level
- Problem of Resistance
- More theoretical in Nature
- Problem of Internal Politics
- Problem of Traditional Management
Limitation of Assumption
Strategic management is based on certain assumptions, if that assumption remains good then the plans will be implemented otherwise there be no use of strategic management.
Problem in Analyzing Environment
The success of strategic management depends on the correct analysis of internal as well as external environment. Here especially the external environment scanning is important to grab opportunities which many times does not proved.
Unrealistic Mission and Objectives
If the mission and objectives are not realistic then the strategic management can’t be successful.
Problem of Setting Target
Implementation of a strategy is important if it is not implemented well then there may be the problem, the strategy may not give the desired result.
Lack of Commitment of Lower Level
Generally the strategies are framed by top-level management and at the time of framing if top-level management has not consulted with lower then lower-level management may not be that much committed.
Problem of Resistance
There may be resistance on the part of employees to accept the set target of the top management.
More theoretical in Nature
As per experts opinion strategic management is more theoretical. In practice there are different so it remains unsuccessful.
Problem of Internal Politics
In organizations, there are differences among or between departments. So as there is no good relation, proper coordination, strategies became unsuccessful.
Problem of Traditional Management
Traditional management has a narrow approach towards development. Its philosophy is not progressive; they want to run their business with the same fashion. So the strategies are not fruitful in this case.
FAQ
What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management can be described as the identification of the purpose of the organisation and the plans and actions to achieve that purpose. It is that set of managerial decisions and actions that determine the long-term performance of a business enterprise.
(Read Complete Article)
Strategic Management Definition
Strategic management is concerned with the determination of the basic long-term goals and the objectives of an enterprise, and the adoption of courses of action and allocation of resources necessary for carrying out these goals. – – Alfred Chandler, 1962
Introduction to Strategic Management
Strategic Management is exciting and challenging. It makes fundamental decisions about the future direction of a firm – its purpose, its resources and how it interacts with the environment in which it operates.
Strategic Management Process
Strategic management process is a method by which managers conceive of and implement a strategy that can lead to sustainable competitive advantage. It is the process of managing, planning, and analyzing in order to reach all organizational goals.
Strategic Management Process Model
Steps:
1. Strategic Analysis
2. Environmental analysis
3. Strategic Choice
4. Strategy Implementation
5. Strategy Evaluation and Control
Strategic Brand Management Process
Strategic brand management process is important for creating and sustaining brand equity.
Strategic Brand Management Process has four main steps:
1. Identify and Establish Brand Positioning and Values
2. Designing and implementing brand marketing programs
3. Measuring and interpreting brand performance
4. Growing and sustaining brand equity
Business Ethics
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Lean Six Sigma
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
Research Methodology
Management
Operations Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain





That was an amazing article about what is strategic management, it helps me in understanding how strategic management is important.
that’s an amazing article