What is Resume and Covering Letter?
Resume or a Curriculum vitae (CV) is a document that highlights the educational background, working experience and skills of a candidate. It is sent along with the application letter for a position. It enables the hiring manager to skim through the candidate’s profile and establish whether the candidate is a good fit for the position.
Table of Content
The purpose of a CV/resume is to get you an interview.
An effective resume/CV should have the following characteristics:
- It should clearly convey the details of academic and professional experiences.
- All details should be listed chronologically (most recent first).
Nowadays, however, a resume alone is not sufficient. Recruiters prefer to read a short bio or a resume summary to quickly scan the applicability of a candidate before reading the entire resume. A bio is a small, crisp biographical profile of an individual on a professional networking site such as LinkedIn. It crisply narrates the individual’s expertise and experience.
A resume summary is a short paragraph career summary that appears at the top of a resume. It highlights the individual’s skills, experience, achievements and certifications. It is usually customised according to the job being applied.
A Curriculum Vitae (CV) or resume is your personal sales brochure. It highlights your Unique Selling Points (USPs) and helps prospective employers to determine whether you are the best fit for a position.
Elements of CV/Resume
Elements of CV/resume are as follows:
- Personal information
- Educational qualifications
- Projects/internships undertaken
- Achievements/awards
- Professional experience
- Publications, conferences attended
- Areas of interest
- Languages known
Personal information
An applicant should provide the details of his/her name, address, phone numbers and e-mail address. Details of the date of birth, marital status or other information are optional.
Educational qualifications
An applicant should add details about all his/her educational qualifications starting with the most recent or expected degree. It should include names of degrees, majors, institutions and dates of completion (or expected date) in reverse chronological order (most recent first).
Projects/internships undertaken
An applicant should provide the title and a brief description of his/her projects, the theoretical framework and conclusions, area of research, etc.
Achievements/awards
The achievements and awards received by the applicant should be listed in detail.
Professional experience
This part of the CV is often divided into various categories such as “Research Experience,” “Consulting,” “Fieldwork,” “Work Experience,” or “Postdoctoral Work,” as well as many others, depending on the area of work.
Publications, conferences attended
This part of the CV should accurately reflect the professional work that an applicant has produced in his/her discipline. These should be arranged in reverse chronological order and may be subdivided into sections. Work in progress should also be included.
Areas of interest
List the courses you are preparing to teach and topics that indicate your present and future research directions. If your background allows you to teach in several fields, you may include a list of graduate courses taken.
Languages known
List all languages you read and speak and note those in which you are fluent.
The current trends in the market show that a resume alone does not suffice the purpose of getting the desired job. This is where the concept of cover letters finds relevance. The cover letter is a tool to help introduce a job seeker in an impressive and personalised manner while applying for a job.
A well-crafted cover letter gives information over and above the individual’s resume as it guides the employer through the journey of some of the most important career and life achievements of the applicant. When writing a cover letter, it is best to organise the content of the letter based on the requirements of the job one is applying for.
Objectives of Cover Letter
Before beginning the cover letter, it is best to become aware of the objective of the same so that it meets the requirements and achieves the purpose of complementing the application along with the applicant’s resume.
A well-written cover letter achieves several goals, which are as follows:
- Introduces the applicant and his/her credentials to the potential employer
- Brings out the reasons for one’s interest in the organisation and the position
- Acts as a sales letter specifying why one qualifies for that specific job
- Establishes a personal connect with a potential employer which goes above a simple resume
- Highlights an individual’s unique personality and proves his/her suitability
- Catches the attention of the potential employer in setting up a personal interview
Guidelines to Write a Cover Letter
Before you read the guidelines, remember you need to do your best in drafting the best cover letter you can. This is your first introduction to the organisation, hence it should make them want to meet you. Remember you want them more than they want you.
The following are some guidelines to write an impressive cover letter:
- Stick to the accepted format for a cover letter.
- Format the cover letter on one page, typed, and single-spaced.
- Proofread the letter before sending it across to avoid grammatical, technical, factual or spelling errors.
- Address the letter to a specific person, rather than keeping it general.
- Avoid guessing the gender of the addressee. Instead, use the individual’s full name, for example, ‘Dear Kelly Jones’.
- Be creative. Refer to samples but do not copy the content as such.
- Write the beginning paragraph in a way that interests the employer to read further.
- Gain the attention of the reader by showing interest in the organisation and the job profile.
- Highlight points that show what you can do and how you can contribute to the organisation.
- Exhibit enthusiasm and self-confidence but with modesty.
- Be patient, polite and persistent while following up with the organisation.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
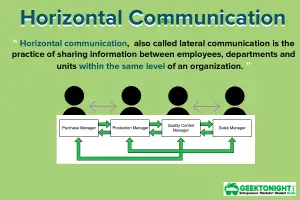
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
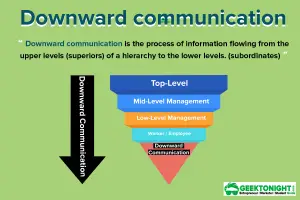
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?