What is Ownership Concentration?
Ownership concentration refers to the distribution of ownership of a company’s shares among its shareholders. It is a measure of the degree to which ownership of a company is concentrated in the hands of a few large shareholders or is widely dispersed among many small shareholders.
Table of Content
Ownership Concentration
To understand the concept of ownership concentration, we have to first understand the meaning of ownership structure, of which ownership concentration is an important component. Ownership structure refers to the distribution of voting rights among different equity shareholders of an organisation.
It gives a clear indication about the identity of the owners of the organisation. The concept of ownership structure is important in corporate governance because the economic efficiency of the organisation depends on it. Ownership structure comprises two main components, namely, ownership concentration and ownership composition.
Ownership concentration occurs when the power to control the activities of an organisation lies in the hands of a few shareholders. The degree of ownership concentration determines the distribution of power among shareholders and managers in an organisation.
The control of shareholders becomes weak when ownership is dispersed, which implies that a majority of shares are distributed among numerous small shareholders. Generally, small shareholders do not have any interest in monitoring the activities of the organisation because it involves high costs and few benefits.
In countries such as the US and UK, corporate ownership is relatively discrete or dispersed. In case of dispersed ownership, the power to monitor the organisational activities lies with managers. As discussed earlier, if a small number of shareholders possess the majority of shares, then the ownership is concentrated in a few hands. In such a case, the shareholders may try to fulfil their own interests at the expense of other investors as well as minority shareholders.
The shareholders ensure that their interests are taken care of in the following ways:
- Paying special dividends to themselves
- Influencing the organisation to enter into unethical business practices
- Taking high-risk projects for their own benefits
An inverted U-shaped relationship exists between the degree of ownership concentration and profitability of an organisation as shown in Figure:
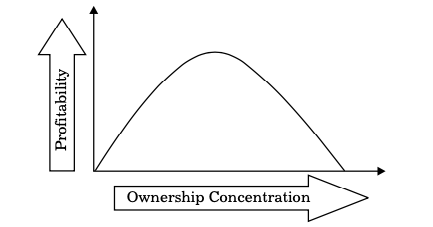
As ownership concentration increases during the initial stage, sufficient funds are raised for the growth and expansion of the organisation. As a result, profitability increases and the curve goes up (Figure).
However, as the number of shareholders increases, the profit earned by the organisation has to be distributed among them in the form of dividends. Therefore, the curve starts declining after crossing a certain limit of ownership concentration.
There are two important concepts of ownership concentration. These are managerial ownership and controlling shareholders. Let’s discuss these two concepts in the following sections.
Managerial Ownership
Managerial ownership refers to the extent to which managers have certain powers and rights to take decisions for an organisation. Ownership and management are segregated because of the agency problem, which represents a conflict of interest between decisions taken by managers and the owners (shareholders). The owners want to maximise their own profit, while managers focus on maximising organisational profit.
Managers often perform well when they have a higher share in the organisation. In 1988, Stulz studied the relationship between managerial ownership and the performance of an organisation and found out that managers try to own voting rights to minimise their probability of losing control over the organisation.
Controlling shareholders refer to a single or a group of shareholders who possess a large number of shares in an organisation. A controlling shareholder can influence the Board of Directors in order to gain control of an organisation.
Therefore, the controlling shareholder may exert both a positive and negative influence over the organisation. The Indian government has promulgated many laws to keep a check on shareholders having major holdings. The Company Law Board also helps in protecting the rights of shareholders with fewer holdings.
Business Ethics
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Lean Six Sigma
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
Research Methodology
Management
Operations Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain




