What is Inventory Control?
Inventory control is concerned with the acquisition, storage, handling and use of inventories so as to ensure the availability of inventory whenever needed, providing adequate provision for contingencies, deriving maximum economy and minimizing wastage and losses.
Hence Inventory control refers to a system, which ensures the supply of required quantity and quality of inventory at the required time and at the same time prevent unnecessary investment in inventories. It is one of the most vital phase of material management.
Reducing inventories without impairing operating efficiency frees working capital that can be effectively employed elsewhere.
Table of Content
Inventory Control Techniques
Following Inventory Control techniques can be used:
- ABC Analysis
- VED Analysis
- Just-in-Time
ABC Analysis
ABC Analysis is one of the important techniques which is based on the grading of inventory according to the importance. This method is popularly known as Always Better Control.
The ABC grouping items according to annual issue value, (in terms of money), in an attempt to identify the small number of items that will account for most of the issue value and that are the most important ones to control for effective inventory management. The emphasis is on putting effort where it will have the most effect.
ABC classifications allow the inventory manager to assign priorities for inventory control. Strict control needs to be kept on A and B items, with preferably low safety stock level. Taking a lenient view, the C class items can be maintained with looser control and with high safety stock level.
The ABC concept puts emphasis on the fact that every item of inventory is critical and has the potential of affecting, adversely, production, or sales to a customer or operations. The categorization helps in better control on A and B items.
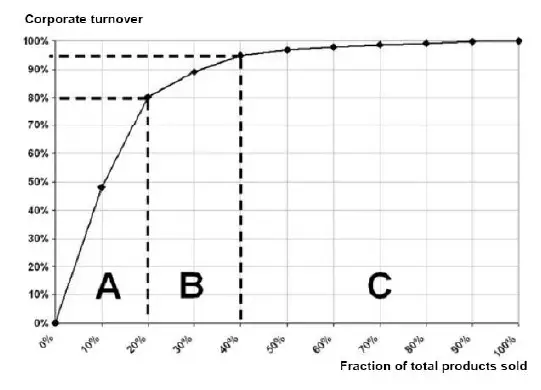
A category (High Value Materials)
A category items are goods which annual consumption value is the highest. The top 70-80% of the annual consumption value of the company typically accounts for only 10-20% of total inventory items.
B Category (Medium Value Materials)
B category items are the interclass items, with a medium consumption value of 15-25% of annual consumption value typically accounts for 30% of total inventory items.
C Category (Low Value Materials)
C category items are, on the contrary, items with the lowest consumption value. The lower 5% of the annual consumption value typically accounts for 50% of total inventory items.
Advantages of ABC Analysis
- Close and strict control is facilitated on the most important items which help in overall inventory valuation or overall material consumption.
- Proper regulation of investment in inventory which will ensure optimum utilization of available funds.
- Helps in maintaining a high inventory turnover rates.
VED Analysis
This analysis attempts to classify items into three categories depending upon the consequences of material stock out when demanded. As stated earlier, the cost of shortage may vary depending upon the seriousness of such a situation.
VED Analysis is very useful to categorize items of spare parts and components. In fact, in the inventory control of spare parts and components it is advisable, for the organization to use a combination of ABC and VED Analysis.
Such control system would be found to be more effective and meaningful.
- Vital: Vital category items are those items without which the production activities or any other activity of the company, would come to a halt, or at least be drastically affected.
- Essential: Essential items are those items whose stock – out cost is very high for the company.
- Desirable: Desirable items are those items whose stock-out or shortage causes only a minor disruption for a short duration in the production schedule. The cost incurred is very nominal
Just-in- Time (JIT)
Just-in-time also known as JIT inventory is a inventory management strategy that is aimed at monitoring the inventory process in such a manner as to minimize the costs associated with inventory control and maintenance. To a great degree, a just-in-time inventory process relies on the efficient monitoring of the usage of materials in the production of goods and ordering replacement goods that arrive shortly before they are needed.
This simple strategy helps to prevent incurring the costs associated with carrying large inventories of raw materials at any given point in time. Many purchasing departments employ a JIT inventory for such key items as raw materials and machine parts.
This means that records are kept that make it possible to place a new order for a given component when the number of units on hand decreases to a pre-determined point.
In times past, this type of inventory control often was accomplished by maintaining a flip card inventory, such as the old Kardex system. Today, this same type of component usage is often managed with purchasing and inventory control software.
Financial Accounting
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Posting In Accounting?
- What is Trial Balance?
- What is Accounting Errors?
- What is Depreciation In Accounting?
- What is Financial Statements?
- What is Departmental Accounts?
- What is Branch Accounting?
- Accounting for Dependent Branches
- Independent Branch Accounting
- Accounting for Foreign Branches
Corporate Finance
Management Accounting




