The RBI plays a major role in the payment and settlement system in India. It established Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) as well as Securities Settlement System (SSS). SSS helps in electronic trading and settlement of government securities. The introduction of these systems eliminated the need for manual processing of cash and securities transactions.
Table of Content
In addition to this, the RTGS and SSS enable the centralisation of investments by market participants at the RBI’s Mumbai office. In the area of retail payments, the RBI runs and man- ages clearing houses both for paper-based and electronic transactions in four metropolitan cities—Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata and New Delhi.
The RBI is the settlement bank for retail payments in these cities in addition to 13 other big cities of India. The bank also plays a direct role in settlement and credit facilities. For this, the RBI entails participants in various payment systems to maintain accounts with the RBI. Let us discuss some of the settlement mechanisms that are used to facilitate smooth clearing of payments and other transactions.
Payment Settlement Mechanism in India
CCIL and FX-clear
Set up in April 2001, Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) supports the clearing and settlement of foreign exchange transactions in India. The prime objective of this corporation is to improve efficiency in the transaction settlement process and insulate the financial system from operations-related issues. The corporation also undertakes other related activities to broaden and deepen the money, debt and FX markets across various countries.
It started its operations on 15 February 2002 and commenced the settlement services for FX transactions from November 2002. It started services for the settlement of cross-currency deals from 6 April 2005. It also develops and manages electronic trading platforms for trading in government securities and call money. It has introduced many innovative products/tools for the clearing and settlement of foreign exchange transactions in the international market. Besides, it publishes many publications on a regular basis for the benefit of the market participants.
CCIL adopts the ‘payment-versus-payment mode of settlements’ in clearing and settling foreign exchange transactions. The key benefits associated with this model are:
- Elimination of principal/credit risks
- Maintenance of counterparty limits by members on agreed terms and conditions of the trade agreement
- Trade with counterparties
CCIL, while rendering its services, performs the following validation checks:
- Whether both the parties involved in the transaction are active members of the FX settlement segment of CCIL or not
- Duplication of message
- Correctness of conversion rate
- Valid currency
- Existence of original deal
- Provision for amendment or cancellation of deal
- Ensuring that the trade date is not greater than the current day
- Trade or settlement date is not a holiday or Saturday or Sunday.
- Settlement date is not less than the trade date or reporting date.
- No mismatch of date
- Rounding of the figure involved in the transaction
CCIL offers central counterparty (CCP) trade clearing in USD/INR. The settlement is done on Payment vs. Payment (PvP) basis and the underlying risk is mainly the principal risk in the settlement. In India, FX-Clear and Reuters Dealing System are two major trading platforms. FX-Clear is an order matching platform introduced and operated by CCIL.
Majority of forex transactions in the forex markets constitute of inter-bank transactions. FX-Clear is an inter-bank forex dealing system that allows trades in both order-matching and negotiation modes. FX-Clear also provides a platform for the settlement of funds between banks for FX transactions. The transactions done through FX-Clear are routed to CCIL which offers guaranteed settlement when done through order matching mode (where CCIL acts as counterparty). For trades done in negotiated mode (open-bid double-auction mode), the trades are manually reported to CCIL for settlement. FX-Clear is a neutral, anonymous and order-driven platform for the settlement of deals to the market participants. Through FX-Clear, orders with valid inputs are accepted for dealing.
All transactions conducted through FX-Clear are guaranteed for settlement by Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCLIL) from the point of trade, and all trades are directly sent to the Clearing Corporation. Trade cancellation options are also settled through FX-Clear to avoid invalid trades from getting included on the Order Matching mode of the FX-Clear platform.
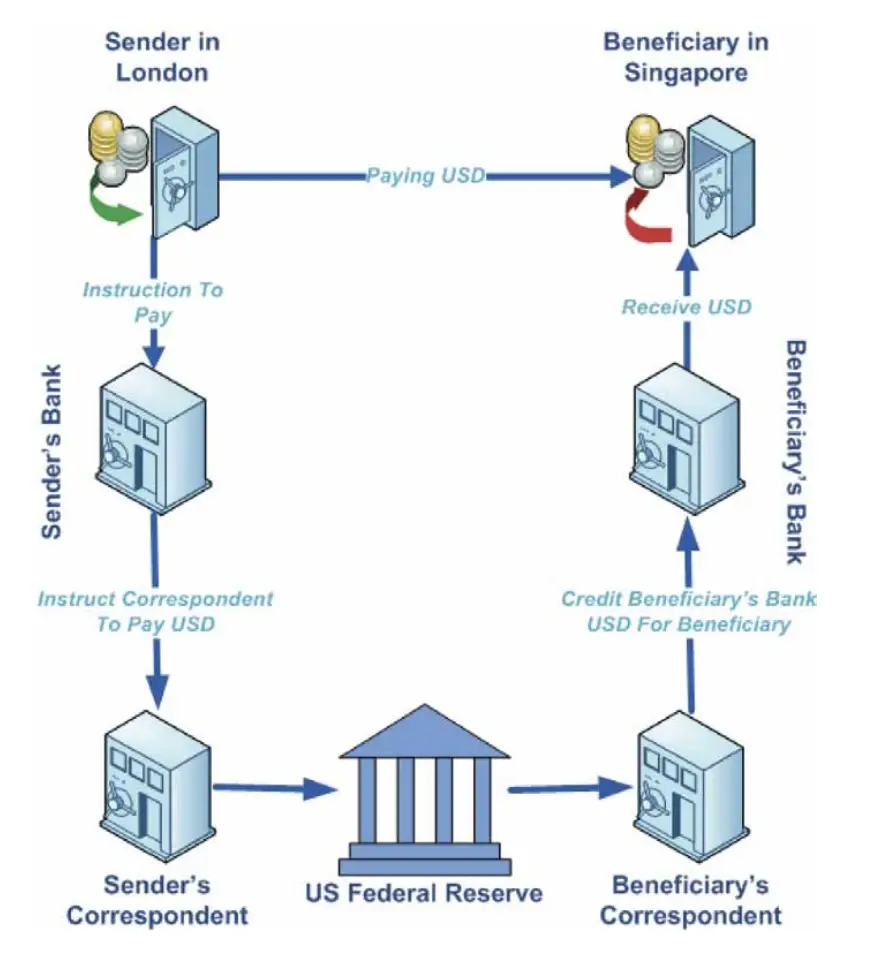
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) System
The RTGS system can be defined as a continuous settlement system of funds transfer prioritising each settlement based on the timing of the order. ‘Real time’ implies that the processing occurs at the actual time and not at a later time. ‘Gross settlement’ implies that the settlement takes place individually based on the received instructions. The funds settlement takes place in the books of the RBI and is irrevocable. The RTGS system is mainly used for carrying out large value transactions. The minimum amount that can be transferred through the RTGS system is ` 2 lakhs. No upper ceiling has been specified for RTGS transactions. The mechanism through which payments are processed through RTGS system is shown in Figure:
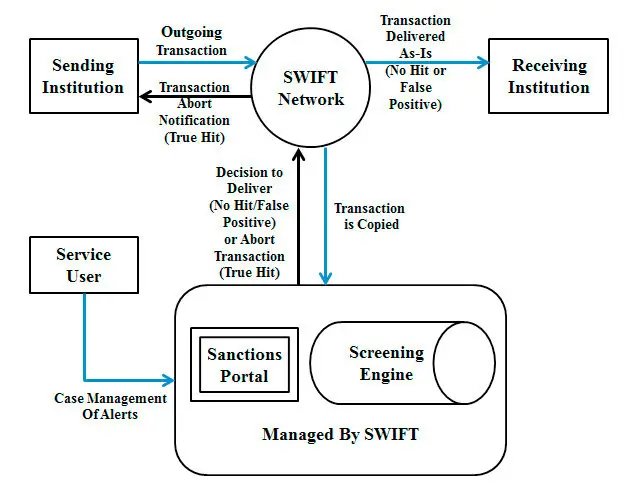
Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT)
SWIFT was introduced in the year 1973. It uses a standardised registered communications platform for the transmission of information related to financial transactions. This information is mainly related to payment instructions to be safely exchanged between financial institutions. SWIFT neither holds any fund nor is responsible for managing client accounts. It is instead a member-owned cooperative that offers secure financial information to its members. The society began its operations in 15 countries and has expanded to 210 countries at present, delivering an average of 18,306,753 messages per day.
SWIFT is based in Brussels and is the most commonly used term in international banking transactions. It is basically exchange of standardised financial messages between financial institutions and corporations through a telecommunication platform to facilitate foreign transactions in the banking sector. Established by major financial institutions, SWIFT is the messaging standard used in many payment and settlement systems. It is not itself a payment or a settlement system. SWIFT messaging standards are used by banks, brokers, dealers, corporates, investment managers, etc., to transmit desired information underlying foreign transactions.
SWIFT is the banking language that is widely accepted and understood globally in the banking sector. SWIFT messages typically result in monetary transactions between institutions. With a view to securing appropriate governance and improving risk management, the central banks of the Group of Ten (G10) countries have been cooperating internationally in the oversight of SWIFT. The SWIFT Oversight Forum was established in 2012 to share information on SWIFT oversight activities among G10 and 10 other central banks.
In addition to strengthening operational management as mentioned above, it is important for SWIFT, as a provider of international messaging services for financial transactions, to continue to enhance its cyber-security management in a steady manner against the background of growing sophistication and complexity of cyber-attacks in recent years.
To increase the speed and transparency of cross-border payments and enhance customer experience in correspondent banking, a new global payment initiative is planned for year 2016 by SWIFT. This initiative will focus on business-to-business (B2B) payment service. This new service would be based on the growth of international business, improved relationships and greater efficiencies in treasury management. Businesses will be able to achieve enhanced services directly from banks.
The key features will be the transparency of funds, end-to-end payments and transfer of rich payment information. The policies related to this initiative will operate on the basis of multilateral Service Level Agreements (SLAs) between banks. SWIFT is also planning to work with the industry for carrying out research on additional SLAs. This is done for reducing costs and friction that arise from cross-bor- der payments.
According to Gottfried Leibbrandt, the CEO of SWIFT, Correspon- dent banking serves the industry with millions of secure cross-border payments day in, day out; with this initiative we are building on those strengths, enabling banks to provide distinctive cross-border payments services and providing real benefits to end customers. This is a critical step in cross-border payments innovation.