What is Payment Channels?
Payment channels refer to a mechanism in blockchain and cryptocurrency technology that enables users to conduct off-chain transactions. These channels allow parties to make multiple transactions without recording each one on the blockchain. The primary goal is to reduce transaction costs, increase transaction speed, and alleviate scalability issues associated with on-chain transactions.
Table of Content
Types of Payment Channels
Payments can be made using different channels or media. Each medium of payment has different operating characteristics, rules and settlement mechanisms. The three major type of payment channels include: cash-based channels, cheque based channels and card based channels. Let us discuss each of these channels in detail.
Cash-based Payments
Cash-based and cheque-based payments are included in paper-based systems. There are organisations and retailers that accept cash for providing goods and services. Cash payments are very common in C2B transactions; however, cash transactions are almost negligible in B2B transactions. In case an organisation receives large volumes of cash, it generally hires a professional money transporter to move the cash to the bank for deposit on behalf of the organisation.
For this, the company locks the entire cash in a cash box. This cash box is transported by the transporter to the bank. The bank also has a key to this cash box. Using this key, the cash box is opened and all money is taken out, counted and deposited in the bank. Accepting cash comes with certain problems such as bulkiness of cash and it requires significant controls to maintain it in various offices. The cash also does not earn any interest and it is also expensive to deposit.
Therefore, it is ideal for organisations to avoid making payments and accept payments in cash. The payments when made in cash or accepted in cash have a direct impact on the banks and the entire banking system. The use of more cash increases the costs for banks.
The individual who makes payments in cash has to first withdraw cash either from bank or from ATM which involves cost in terms of manpower, fixtures (ATM machines) and the cost of technology. Then again the merchant that sells services or products on cash has to collect all the cash and transport it safely to the banks (for depositing in his/her account). Banks do not encourage the use of cash for making and receiving payments.
Cheque-based Payments
Cheques are still important means of making payments in various parts of the world including India and the US. The payments made and received through cheques are cleared through the cheque-clearing mechanism as shown in Figure:
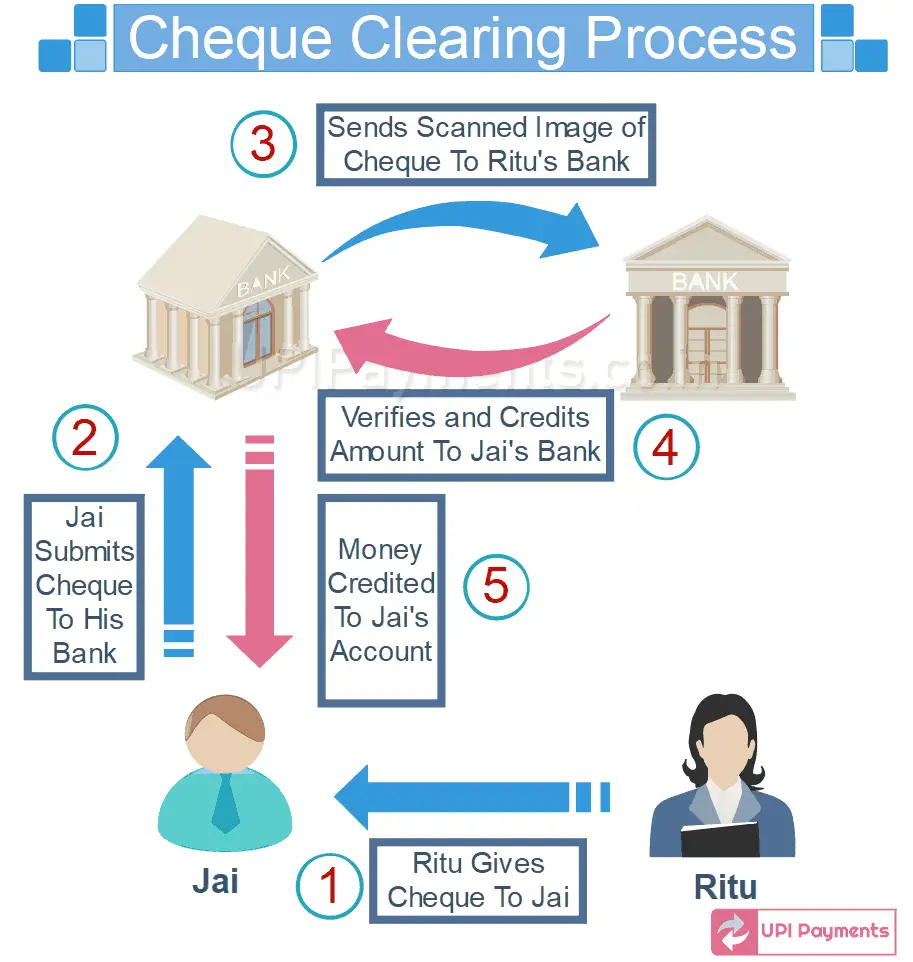
A person who issues a cheque is called cheque payer or drawer or the maker of the cheque. The cheque is given to the payee. The payee deposits this cheque in his/her bank. The payee’s bank presents this cheque or its image (as per new CTS system) to the clearing house. Clearing houses are managed by the RBI.
The clearing house presents the drawer’s bank and the drawer’s bank cheques whether sufficient funds are available in the drawer’s account or not. If sufficient funds are present, the drawer’s bank honours the cheque issued by its account holder and debits the drawer’s account and credits the pay- ee’s account. Please note that the process of cheque clearing after Jan 2013 (when CTS was introduced) has been shown in Figure above.
The payments that are made (or received) through cheques also impact the banks and the banking system. When cheques are received, they need to be cleared. Clearance of cheques requires coordination between three entities namely the drawer bank, the drawee bank and the clearing house.
The entire process of clearing and coordination among these entities requires manual processing apart from the cost of technology implementation for clearing (such as CTS). This in- increased the costs of processing payments for banks. In addition, the banks also incur costs related to printing of cheque books and sending them to the customers. Please note that the use of cheques and cash has an overall negative impact on the banks.
Card-based Payments
In India, there are three types of cards that are used majorly. They are debit cards, credit cards and prepaid cards. Cards can be issued by various organisations that are authorised by the RBI (such as American Express) and banks (such as HDFC); however, the cards are issued by banks are most widely used. A debit card can be used only when a cardholder has sufficient amount in his/her account.
On the contrary, the credit card is a type of card that is issued by a financial institution or bank against a line of credit. In prepaid cards or stored value cards such as gift cards, payroll cards are a special kind of debit cards that are not linked to any particular bank account. They are stored with the sum of money that can be exhausted. However, there are stored value cards which can be reloaded with money to extend their usability. The normal process of a payment using the card is shown in Figure below:
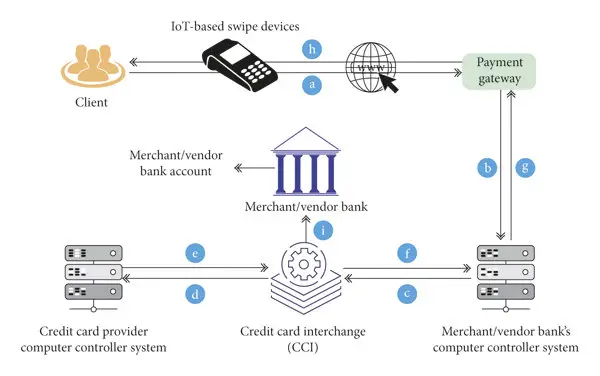
A cardholder presents the card at any of the merchant shop/store that accepts cards. The merchant captures all transaction information along with the amount to be debited. This information is sent for validation and authentication to the merchant acquirer (usually a bank). The transaction is authenticated through the appropriate card network and the status is sent to the merchant. In case a transaction is denied, the payment stands failed and the customer has to make payment either in cash or through other card.
A merchant sends the transaction information to the merchant acquirer either the single transaction or at end of day in bulk by combining various transactions. The card networks (such as VISA, Master etc.) settles each day’s card transactions between its member banks usually through a separate batch payment system such as Automated Clearing House (ACH). The card issuing bank charges the cardholder’s account and credits the merchant’s account including transaction fees. Merchants usually have a swipe machine at their end which generates two receipts one for merchant and one for the customer.
A merchant has to get the receipt of payment signed by the card holder as proof that only valid charges have been deducted and no extra amount has been deducted. It is important because the cardholder may dispute the transaction within a specified time window claiming that excess amount has been debited from his/her account. Nowadays, credit cards are also PIN-based for security purposes. The process of signature-based transactions is common in the case of credit cards. Although debit card transactions can also be signature based; they are usually PIN-based and are processed through an EFT or ATM network.
The use of cards (debit and credit cards) has a direct impact on the banks. Overall these have a positive impact on the banks and the banking system. The banks encourage the use of electronic means of payments because in such payments, the value of the transaction is moved electronically in the books of account of the banks and not physically.
The online banking and automation makes it possible for the customers to carry out most of the payment processing themselves which helps in reducing the cost of bank staff, the branch, branch fixtures etc. In other words, use of cards helps in decreasing the operational costs for the bank.




