What is House of Quality?
The House of Quality is a fundamental tool in Quality Function Deployment (QFD), a method used in product development and design to ensure that customer needs and desires are incorporated into the final product.
Table of Content
An essential tool for deploying QFD is House of Quality (HOQ). It is a diagrammatic representation of the relationship between the customer desires or requirements and the product characteristics.
HOQ is a collection of several quality deployment hierarchies, including the quality hierarchy, the quality characteristics hierarchy, the relationship matrix, the quality planning table and the design planning table. HOQ is used by cross-functional teams for translating various customer requirements, using market research and benchmarking data in an appropriate number of prioritised engineering targets to meet a new product design.
HOQ helps organisations in interpreting customer needs into design specifications. Further, through HOQ, effort is made to match the design requirements with the organisation’s capabilities. HOQ is also considered the primary chart in quality planning. The figure below shows the framework of HOQ:
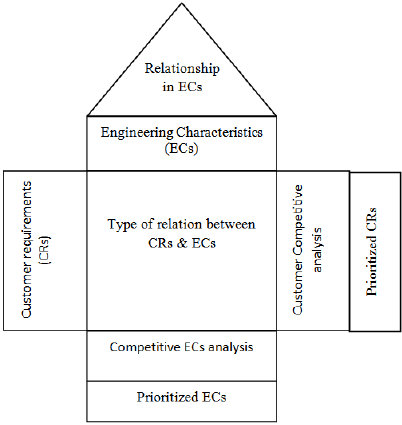
House of Quality
As shown in Figure 8.3, HOQ is depicted as a house. The left wall of the house depicts customer requirements, also called the voice of the customer. The wall to the right depicts prioritised customer requirements. The ceiling of the house represents the technical descriptors, which are the technical specifications of products (also called engineering requirements).
The interiors of the house indicate the relationship between customer requirements and the technical descriptors. The roof of the house represents the interrelationship between technical descriptors (independent technical requirements). Finally, we have the foundation of the house, which is built on prioritised technical descriptors. These technical descriptors are needed to fulfil customer requirements improve quality of the product. Items such as technical benchmarking, degree of technical difficulty, etc., are listed here.
Steps in Building HOQ
Let us now discuss the process of building HOQ. The steps involved in the process are:
Define customer requirements
The first step is to define the expectations of the customer in a product. The main objective is to translate the needs of the customer into engineering specifications. Customers buy products that most closely match their expectations or requirements and organisations try to create products that fulfil those requirements.
Define technical descriptors
In this step, the organisation must define the technical descriptors of the product, that is, the technical specifications, including design constraints and parameters to create customer-oriented products. These descriptors must be expressed in measurable terms.
Establish relationship between customer requirements and technical descriptors
Relationships between customer requirements and technical descriptors can be weak, moderate, or strong. The strength of the relationship depends on the degree to which the organisation has been in addressing the customer’s requirements. Has it been able to address all customer needs? Or perhaps there are product requirements or technical characteristics stated that do not relate to customer needs.
Establish interrelationship between technical descriptors
In this step, a relationship is sought to be established between the various technical descriptors and required adjustments made in them so that they fulfil the requirements of the customers.
Perform competitive assessments
In this step, two types of competitive assessments are performed: customer assessment and technical assessment. In competitive assessment, the organisation determines if the customer requirements have been met and also identifies the areas requiring further improvement. The assessment also helps an organisation to know its position relative to its competitors in the market.
Technical assessments, on the other hand, are conducted to check the technical specifications of the product and see how well these have been able to conform to the specified requirements. Technical assessments also help in judging the quality of the product.
Define prioritised customer requirements
In this step, the requirements of the customer are prioritised according to importance. A priority is a quality characteristic that, by incorporating it into its products, an organisation is able to deliver more value to the customer. Target value, sales point, etc., are example of prioritised customer requirements.




