What is ERP Implementation?
ERP implementation is a process of putting ERP processes in action. In other words, it is a process that brings momentous changes in an organisation’s work, system and practices. It consists of planning, organising and maintaining tasks.
According to Turban et al. (2008), “Implementing ERP typically requires changes in existing business processes. Poor understanding of needed processes changes prior to starting implementation is a main reason for project failure. The problems could be related to the system, business process, infrastructure, training, or lack of motivation”.
Table of Content
Integration of Process Using ERP
As discussed earlier the ERP system integrates all the departments of organization with a single database which leads to various benefits as discussed above if implemented properly.
In the legacy system the order placed by customer travels between different departments manually and step-by-step manner, which requires lots of encryption and decryption at different departments results in chances of order delay or error in order to data the legacy system and ERP systems.
Implementation of ERP System Department of Finance, HR and operations have single standalone computers and data is transferred manually between them but after ERP they all are interconnected and data is available at all department instantly as soon as the order takes place which eliminates the chances of order delaying and order data errors.
ERP Architecture
- Data Warehousing
- OLAP (online analytical processing
- OLAP (online transaction processing
- Data mining
Data warehouse and data mining are important to ERP system as they make the system intelligent. Enterprise with memory is provided by data warehouse and intelligent enterprise is achieved by data mining. Data warehouse provides the known facts and real-time data in proper order; data in warehouse can be any of the following type:
- Time variant
- Integrated
- Non-volatile
- Subject oriented
The data warehouse is capable to make small data packages from large data set available from multiple sources.
Day to day operational activities of the business is supported by an online transaction processing system (OLTP). On the other hand online analytical processing (OLAP) system provides real-time information to an organization that supports inaccurate decision making to achieve competitive advantage.
In expansive terms, a customer is an element that makes a demand to the server for service and the server is the entity that responds to that particular request. These two entities are connected by a third entity called network. For example, the architecture of SAP R/3 software has three layers:
- Database layer
- Application Layer
- Presentation layer
Process layer requires the input from the presentation layer and validate the data to perform the different process by applying various business rules. This further requires the interaction with storage logic to obtained additional data; following are some of the main components:
- Input-output processing
- Communication with storage
- Business transection and rules
- Managing and balancing the loads
Storage layer is responsible for storage and retrieval of data on request from the processing logic component. It is synonymous with database management system. Main components are:
- Data retrieval
- DBMS
- Data storage
- Read-write-update
Reasons for Implementing ERP
ERP has gained importance in the market for its never-ending benefits to organisations. Today, many organisations are changing their key business systems and adopting new ERP packages. The main reasons for implementing ERP systems are given as follows:
Increases performance of the business
ERP helps to reduce manufacturing cycle time, eliminate inventory storage problems and speed up order deliveries.
Increases revenue
ERP increases an organisation’s sales through CRM and sales force automation processes.
Increases productivity
ERP enables an organisation to get more work done with fewer people; thereby, increasing productivity.
Improves the efficiency of business processes
An ERP system automates business processes and eliminates non-value added activities. In addition, an ERP system allows an organisation to match customers’ demands, which results in reduced inventory and carrying costs.
Leverages the available resources
ERP processes lead to the effective utilisation of organisational resources, such as capital and human resource. An ERP system helps an organisation to gain a clear insight of all resources so that they can be utilised more effectively to improve business efficiency.
Provides high security
An ERP system provides security to the critical information of an organisation such as financial and customers’ details. An ERP system does not allow unauthenticated users to access any critical information that can harm the organisation.
Standardises business practices
An ERP streamlines business practices of an organisation; thereby preventing inaccuracies, inconsistencies and delays in work processes.
Combines operational, financial and strategic insight
An ERP system integrates and analyses the data of all the departments of an organisation and delivers crucial operational, financial and strategic insight, which ultimately lead to effective decision making.
ERP Implementation Methodology
The ERP implementation methodology is a sequence of phases involved in the deployment of an ERP system. The ERP implementation methodology varies across organisations depending on their requirements and work processes. Thus, it is not necessary that the methodology of every organisation involves all the mentioned phases.
The following are the different phases of erp implementation methodology:
Pre-evaluation screening
In this phase, all the available ERP systems are analysed and the ones that fulfil the requirements of an organisation are shortlisted. Packages that do not suit the requirements are eliminated.
Package evaluation
In this phase, all the shortlisted ERP systems are analysed in detail. This phase is considered very critical for the successful implementation of an ERP system. Package evaluation is done mainly on the basis of the cost, time and the number of users involved.
Project planning
At this stage, a detailed plan is formulated for the implementation of the ERP process. The project plan specifies resources required for implementation, the timeline for the completion of the implementation process and the targets that need to be achieved by implementing the ERP system. This stage also involves preparing a contingency plan and deciding control measures and methods for the evaluation of the ERP system.
Gap analysis
This is an important phase in the ERP implementation process. Gap analysis is a critical stage that helps an organisation to identify gaps between its current status and future targets.
Re-engineering
With the emergence of ERP, business processes are restructured, employee roles are changed and new technologies are used. Thus, ERP leads to re-engineering processes. Re-engineering integrates Business Process Reengineering (BPR) with the ERP system.
Configuration
This is a functional phase in the ERP implementation process. The existing systems are synchronised with ERP systems. An organisation should properly analyse all its existing business processes to achieve its overall objectives.
Training
In this phase, employees are trained to use the ERP system. After the implementation of the ERP system, vendors and external consultants leave the organisation. Thus, it is necessary for an organisation to learn each and every detail of the ERP system to avoid any contingencies.
Testing
This stage encompasses the verification of various ERP processes by creating real situations. These situations can be related to system overloads, invalid data entry or hacking attacks. In case some activities fail in the testing phase, the ERP system should be re-evaluated.
Going live
It is the stage wherein the new ERP system is introduced by replacing the older one. The ERP system is now ready to be used technically and functionally and employees are allowed to work on the live system.
Post-implementation
In this phase, a regular follow-up record is maintained for the working of ERP processes. This stage mainly includes maintenance and enhancement processes that are carried out on the basis of the performance reports of the ERP system.
Post-Implementation
Post-implementation is a crucial phase in the lifecycle of an ERP system. It is a continuous process that generally starts after the ERP system has been successfully implemented in an organisation, and the employees have been trained to work on it.
Some of the processes of the post-implementation stage include tracking the performance of the ERP system and maintaining a detailed follow-up record; facilitating the seamless integration of the system with all the work processes of an organisation; training employees on the optimal utilisation of the ERP system and taking necessary steps to further improve its functioning.
To reap full benefits of an ERP system, organisations must keep upgrading the system with new versions or technologies introduced in the market. However, before upgrading the system, organisations should weigh its pros and cons in terms of benefits offered, compatibility with the existing system and costs involved.
Effective post-implementation measures, taken at the right time, contribute significantly in enhancing the productivity and increasing the life of the ERP system.
ERP Implementation Challenges
Every organisation faces challenges while adapting to a new system. The implementation of a new ERP system is not a technical job but requires a lot of planning and proper communication. The common challenges that are faced during the implementation process are given as follows:
Stages to be followed
The ERP implementation process should follow all the implementation phases. It leads to a chaotic situation if the sequence of phases is followed randomly by an organisation, which further leads to confusion in the organisation.
Training
During and after the implementation stage, it is important to impart training to employees. This is because training helps to enhance cooperation and build trust among employees, and prevent situations such as job insecurity or functional inefficiencies.
Lack of proper analysis
For successful ERP implementation, an organisation must analyse its requirements. This is because if the organisation does not analyse its requirements, it may not be able to select the right ERP system.
Lack of support from the top management
Support of top management is necessary for the implementation of an ERP system. Lack of support from top management may lead to ineffective decision-making.
Compatibility issues with ERP modules
Any incompatibility issues in ERP processes with respect to existing systems pose a major problem for organisations. Different companies come in partnership with different vendors of ERP; thus, it is their responsibility to solve any compatibility issues.
Infrastructure investment
It is important for an organisation to make investments in infrastructure development for ERP implementation. Lack of proper infrastructure slows down the progress of application development. This further leads to the wastage of resources.
Factors for Success of ERP Implementation
Apart from the implementation process, the success or failure of any ERP project depends on the vendor selected by an organisation for purchasing software. Some factors responsible for the success of ERP implementation are explained as follows:
Focus on business processes and requirements
The focus of an organisation to check business operations and identify key requirements helps to formulate a more effective ERP software selection process.
Strong project management and resource commitment
The top management also plays a vital role in providing the required resources for ERP implementation. Cooperation and coordination among managers and employees are necessary in successful ERP implementation.
Adequate planning
A feasible plan for implementing an ERP system should be taken into account. This would reduce errors and make the process of implementation easier.
A clear understanding of business objectives and a proper vision of what to achieve with an ERP system maximise the business benefits of ERP.
ERP Implementation Cost
Cost ERP Implementation is very high and also requires a detailed analysis of the current business process and practice. Return of investment (ROI) is also not immediate and depends on the successful implementation of ERP.
However it is hard to decide the correct cost of ERP execution because it depends on the size and type of organization and the requirements of individual organizations. Following are the several cost associated with ERP implementation:
- Purchase Cost
- Cost of Training and Education of Personnel
- High Salary to the Skilled Worker
- Testing Cost
- Data Conversion and Analysis Cost
- Customization Cost
- Post-ERP Depression
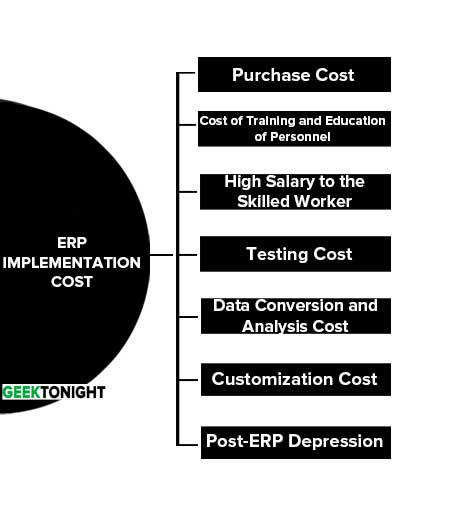
Purchase Cost
Implementation not only includes the purchase cost of ERP system but it also requires some sophisticated software and hardware tools to help support the successful implementation of ERP.
Cost of Training and Education of Personnel
As all the modules are integrated with ERP which is different from older practice, data entered by a person from one department affects the decisions of other departments so to avoid mistakes and for better cross-functionality knowledge of personnel training is required.
High Salary to the Skilled Worker
Implementation of ERP demands technical, interpersonal and multi-functional skills which is difficult to available in all personnel. For that company has to pay high wages to special employees with the above qualities.
Testing Cost
Testing of ERP system to check its integrity with different systems of organization and integration among the different modules of ERP is required for successful implementation. Above costs are the direct costs associated with ERP implementation but there are also some indirect costs associated with it as explained below.
Data Conversion and Analysis Cost
Data related to the material, design of product and supplier resources in the legacy system are required to convert incompatible format of ERP system. Along with that the data of ERP combine with external systems for analytical processing which stored in the data warehouse. It is also difficult to refresh data every day in a big data warehouse, this problem can be solved by custom programming but that may disturb the budget.
Customization Cost
Many organizations want some modules of ERP to work on their unique ways but as all the modules are integrated it is not always possible that ERP handles all these changes easily, for that extra staff with special skill is required to customize the software as per their own needs.
Post-ERP Depression
As ROI of ERP is not instant and the working procedure is different from the old process it creates panic among the employees and business goes into sudden involuntary muscular contractions.
Challenges in ERP Implementation
As the package of ERP is very complex it may take several years and
thousands of dollars for successful implementation. An execution without proper planning will end up being corporate root channels, not the upper hand.
Following are the major encounters in ERP implementation:
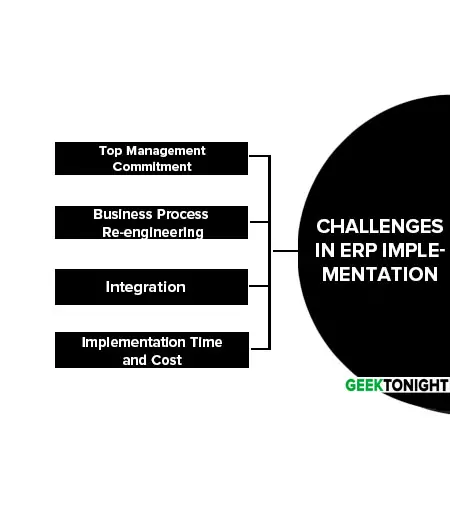
Top Management Commitment
Implementation of ERP is not just a changing of software systems but it is the effort to reposition the company and business process transformation. So, a very visible and well-defined commitment of top management is must require.
Business Process Re-engineering
While implementing the ERP re-engineering of the current corporate process is required to the finest corporate process standard because ERP is developed on the finest practices followed in industries. So if the ERP package cannot adopt the organization’s unique processes than the organization must have to change its procedures.
Integration
Sometimes the unique needs of the company may not be covered by ERP than the company must have to use specialized third-party software to complete the software for satisfying the unique needs. ERP acts as a backbone in this case and this integration is most challenging in ERP implementation.
Implementation Time and Cost
ERP software has lots of modules that may or may not be implemented at a single time. The global implementation team needs to determine a common requirement for all plants. Typically on an average ERP implementation time is 14 months and needs 150 consultants. Corning Inc.
Plans to implement ERP in all ten plants expecting five to eight years, for this long period of time a huge amount of money has to invest in retaining the trained personal. As far as the total cost is concerned total implementation cost will be four to five times higher than the purchase cost due to the various factors
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in BCOM/BBA Study Material or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on ERP Implementation in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)







