What is World-Class Manufacturing?
World-Class Manufacturing (WCM) is a management philosophy and set of practices that aim to achieve the highest standards of efficiency, quality, and productivity in manufacturing processes. The concept originated in the 1980s and has been widely adopted by organizations around the world.
Table of Content
It is well known that manufacturing sets the bedrock of economic wealth for all nations. Industrial revolution has enabled companies to shift manufacturing from homes and cottages to big factories. However, with latest advancements and growing competition, the emphasis of organisations has shifted from merely earning profits to becoming a world-class manufacturer. The main focus of world-class manufacturing companies is to deliver quality products and satisfy customer expectations.
According to Schonberger, WCM includes techniques and technologies designed to enable a company to match its best competitors. WCM can also be defined as advanced manufacturing techniques that organisations can adopt to uplift their manufacturing performance to world-class levels. Here, the term world-class refers to the best among competitors in global market. Organisations that have successfully achieved WCM are termed as WCM companies.
These companies adopt advanced manufacturing concepts to eliminate obsolete methods, systems and culture that have hampered their success in the past. These companies adopt various advanced systems and practices to attain the goal of continuous improvement. The common attribute of world-class companies is that they have to serve customer needs swiftly by delivering quality goods on time at low costs. Moreover, WCM companies apply latest manufacturing techniques to receive and fulfil customer orders in the market.
Features of Wcm Companies
The main feature of WCM companies is that they strive to excel in the market by delivering best products to their customers.
Focus on innovation
These companies focus on discovering new production and marketing approaches to excel among competitors. For this, they emphasise on innovation to deliver best products and services to their customers.
For example, Ogilvy & Mather (O&M) is a global advertising, marketing and public relations agency that has earned a desirable status through its innovative performance in the advertising industry. The agency is well-known for building and nourishing strong brand equity based on innovation.
Highly responsive
These companies are more flexible in nature than their counterparts. This helps these companies to deal with the changes occurring in the economic conditions and marketplace. This also helps the WCM companies to reach target customers and deliver products/services before their competitors.
For example, Amazon.com, Inc., the world’s largest online retailer is one such company that can be regarded as highly responsive in nature. The company was initially started as an online book store.
However, with changing market conditions and increasing customer demands, the enterprise eventually diversified into different other products also, such as DVDs, CDs, MP3, Computer Software, Video games, electronics, apparels, furniture, food and toys. Extraordinary customer service has helped the enterprise in acquiring and retaining millions of customers over a very short period.
Outstanding leadership
These companies tend to perform exceptionally well in multiple areas at the same time. WCM companies excel in various fields ranging from production, customer service to employee retention policies. Committed and focused leaders help in providing right direction to the employees. This helps the companies to perform remarkably well and attain individual and organisational goals.
For example, Microsoft Corporation is the most valuable company in the world. It is the biggest software manufacturer in terms of revenues. Microsoft has gained value based leadership in developing, licensing, supporting and selling software, services, consumer electronic devices and solutions to help its clients and customers in utilising their full potential.
Sense of ownership among employees
WCM companies also provide an authority of ownership to its employees. This enables employees to feel responsible for their actions and motivated to perform well for the attainment of organisational goals.
For example, Google Inc. is one such multinational technology based company that strongly believes in giving their employees freedom and consider it as the best idea to be progressive. At Google, all that autonomy comes with true accountability and employees routinely exceed management’s expectations for producing exceptional work.
Operational excellence
Another important feature of WCM companies is the accomplishment of operations flawlessly. All systems perform to help the organisation in utilising its resources optimally and attaining corporate goals effectively.
For example, Japanese companies, such as Toyota pioneered various quality control practices to achieve operational excellence. Toyota continuously strives to find out the best practices, which can be used to further improve the operational efficiency in the manufacturing process. This results into creating more customer satisfaction and beating the competitors.
World-class Performance Indicators
The companies that adopt WCM should possess a performance measurement system to help them in making improvements. For this, organisations need to develop world-class performance indicators to evaluate and track their performance on time. Figure 9.2 shows the commonly used WCM performance indicators:
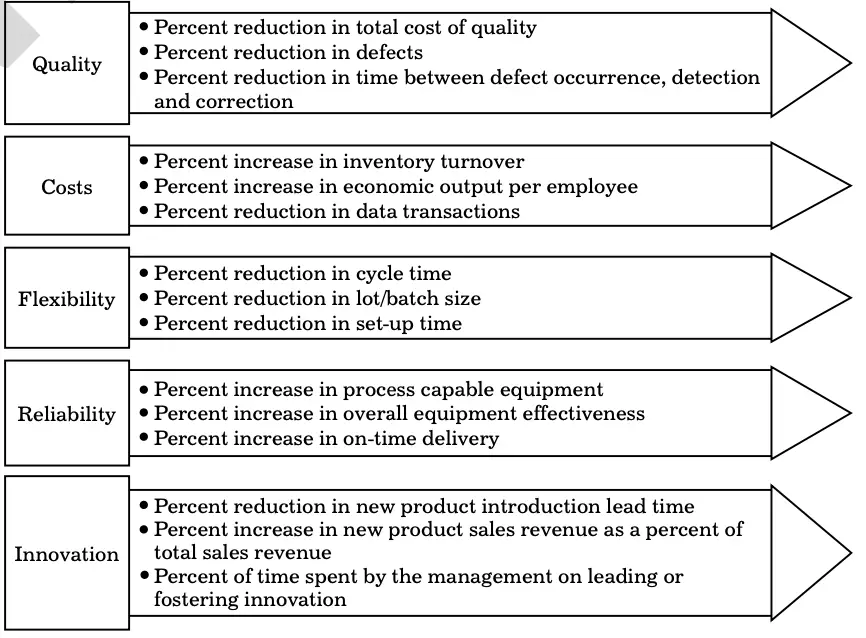
World-Class Performance Indicators
Quality
The performance indicators to measure quality are:
Percent reduction in total cost of quality
It is measured every month and generally represented graphically. The main elements that are measured under costs of quality include prevention, appraisal, internal failure and external failure.
Percent reduction in defects
It is measured in parts per million and is calculated as defects per unit comparative to the number of chances possible for the occurrence of defects. It is represented through trend charts and is measured weekly and monthly in organisations.
Percent reduction in time between defect occurrence, detection and correction
This measure is evaluated in terms of defect occurrence, defect detection and defect correction. To measure these three indicators, a chart is placed with the operators in each work area. The time is displayed horizontally and defects are indicated vertically on the chart. Operators need to record the time of occurrence, detection and correction of defects. Every week or month, the results on the chart are summarised for further evaluations.
Costs
The performance indicators to measure costs are:
Percent increase in inventory turnover
This indicator is measured by dividing the annual Cost of Sales (COS) by current total inventory. Inventory turns is represented on the trends line and is measured on a monthly basis. While calculating inventory turns, raw materials and finished goods are measured separately from the inventory of finished goods.
The formula to calculate inventory turns is:
Inventory turns = Annual cost of sales / Average raw materials and WIP inventory
Percent increase in economic output per employee
This measures the productivity of an organisation. It helps in ascertaining the degree of utilisation of people and resources while manufacturing a product. It is calculated by dividing annual sales by total number of employees in an organisation.
The formula is:
Output per employee = Annual cost of sales / Total number of employees
Percent reduction in data transactions: Data transactions include activities like inventory movement and labour movement, etc. Organisations measure these transactions on monthly basis and take appropriate steps to reduce them. This measure is calculated against a baseline of business activities, such as total units produced.
For total number of units produced, data transactions per unit are calculated as:
Transactions per unit = Total transactions / Total units produced
Flexibility
The performance indicators to measure flexibility are:
Percent reduction in cycle time
Cycle time reduction is measured by dividing the actual cycle time by theoretical or hypothetical cycle time. Actual time is calculated based on the average work-in-process throughput time. On the other hand, cycle time includes value add time required for a single lot size.
Percent reduction in cycle time is calculated as:
Cycle time ratio = Actual cycle time / Theoretical cycle time
Percent reduction in lot/batch size
It is used to measure the reduction in batch or lot size of products. Reduction in lot size is calculated as the average lot size by production process on monthly basis.
Percent reduction in set-up time
It is an important measure to judge the continuous improvement and flexibility of an organisation. Reduction in set-up time includes substitution of the production line or equipment. The measurement of set-up time is based on the frequency of changeover that can be weekly or monthly.
Reliability
The performance indicators to measure reliability are:
Percent increase in process capable equipment
To calculate this, first of all, one needs to understand whether the equipment is statistically under control or not. The capability of equipment is calculated as:
Percent capable equipment = Total process capable equipment / Total piece of equipment
Percent increase in overall equipment effectiveness
The effectiveness of equipment is measured to ascertain—(i) the machine has run as per the scheduled time, (ii) the machine can be run at the speed it is designed to run and (iii) whether the machine is producing quality material. The effectiveness of equipment can be calculated as:

Percent increase in on-time delivery
It indicates if a product has been delivered to a customer on time as promised. On-time delivery is calculated by dividing order shipped on time by total orders shipped.
Innovation
The performance indicators to measure innovation are:
Percent reduction in new product introduction lead time
It measures the time taken by an organisation to introduce a new product as compared to competitors in the market. It can be calculated as the extra time taken to release in huge volumes in the market. To get correct measure, the total time as well as individual phases in production must be considered.
Percent increase in new product sales revenue as a percent of total sales revenue
It ascertains the amount of new product sales revenue needed for a company. The information received through this indicator can be incorporated in strategic and annual plans of a company.
Percent of time spent by the management on leading or fostering innovation
It is measured on individual basis through personal calendars and estimates. The information is then summarised in monthly reports.
Gaining Competitive Edge Through World-class Manufacturing
World-class manufacturing emphasises on product quality, manufacturing techniques, workforce management and promptness in meeting customer requirements and feedbacks. By adopting these practices, organisations can not only deliver best-in-class products, but also remain ahead in the competition worldwide.
Let us discuss the measures that help world-class manufacturing companies in gaining a competitive edge over others in the industry and market:
Delivering best quality products
Quality is related to the degree to which a company’s product adheres to specifications and satisfaction of customer requirements. World-class manufacturing companies emphasise on delivering quality products to their customers in order to enhance customer satisfaction; thereby, increasing sales.
Reducing delivery lead times
Delivery lead time can be defined as the time taken by a company to deliver an order. It denotes the time period between order placement and order delivery. The practices of world-class manufacturing help companies in reducing their delivery lead times by eliminating unwanted activities from production.
This further helps companies in delivering products in less time and serving more customers. It also helps in attracting customers who do not like to wait for a long time to receive their products/services.
Offering low-cost products
Customers always like to receive best quality products at affordable prices. This has also become a major criterion for companies to remain competitive. World-class manufacturing practices can reduce production costs; thereby, enabling organisations to provide products at competitive prices to customers and increase their market share.
Bringing flexibility in production
World-class manufacturing also brings flexibility in production. Companies can produce either a variety of products (termed as mix flexibility) or various types of outputs (termed as volume flexibility). Mix flexibility helps companies to offer products on time whereas volume flexibility enables to offer products at reduced prices.




