What is International Remittance?
A remittance can be defined as money transfer by a foreign worker to an individual in his or her homeland. For example, remittances to India are money transfers from Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) to their families in India. In the banking terminology, remittances are often defined as cross-border person-to-person payments.
Remittances are generally of the following types:
- Cash-based services offered by individuals
- Specialised global money transfer
- Bank-to-bank transfer
Table of Content
The remittances transmission makes funds available to the accounts across borders in just a couple of minutes. This mechanism supports the international business with fast and reliable transfer of funds between two parties. The complete remittance process is not as simple as it looks. It generally consists of a series of electronic messages sent between the financial institutions involved in a remittance transaction.
These financial institutions maintain accounts with their respective banks in their respective country locations. The bank on receipt of complete instructions from the financial institutions for remitting funds to the party in a different country verifies all details as well as compliance of norms and regulations. Then the required amount is debited to the customer’s (sender) account. The debited fund along with electronic messages is sent as foreign remittance to the desired bank for necessary credit to the customer account (receiver).
Credit to the customer account(receiver) completes the process, and instructions are sent back to the remitting bank electronically confirming the successful completion of the foreign remittance. The bank charges the customer (sender)with the agreed commission on handling the complete process along with the foreign exchange rate. These cross-border remittances are a big challenge for banks as they are heterogeneous in nature and involve many small transactions in-between. The complete process passes through a large variety of channels.
The success of the transmission depends on the efficiency of the bank in capturing the required information from the customer and understanding of the transaction channels that are available. The choice of transaction channels is very critical in the complete process of sending and receiving funds into accounts across countries. Other important considerations regarding foreign remittances include the convenience and costs associated with the use of these channels, and the demographic characteristics of senders and receivers.
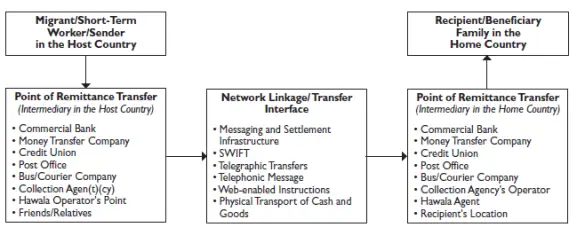
The figure shows remittance channels:
Following are certain underlying factors that need to be taken care of by the banks offering the services of foreign remittances to their customers:
Transparency
It is important for a bank to give complete details to its customer about time, cost, documents, foreign exchange rates, etc., to render remittance services. This helps individuals make informed decisions about which services to use. The bank in return also seeks complete information from the customer.
A complete transparency in the process is arguably very important for an effective and efficient remittance. The customer should be made aware of the fact that the cost of remittance depends on two elements: the exchange rate and any bank fees. Since the exchange rate may fluctuate, the overall fee may also vary on a particular date.
Customer Protection
A bank must ensure that its customer’s confidential information is protected in all respects while seeking details for remittance. Adequate consumer protection is also of prime importance because many senders may have difficulties in understanding the local language or may face problems in providing adequate identification to the bank for claiming the remitted funds.
Infrastructure Support
Inadequate infrastructure needed to support remittance services may result in an ineffective service to the customer. These issues are common in underdeveloped countries that lack in domestic financial infrastructure. Receiving funds in these countries might be slow and unreliable, and in some cases, non-cash payment services may be inadequate.
Correspondent Banking Relationship
It is very critical to the cross-border transfers of funds and might result in an increase of the overall cost of fund transfer. This can make the overall remittance process very expensive for small-value payments.
Statutory Requirements
Remittances are highly regulated for various reasons including countries’ banking norms, prevention of misuse of funds and for purposes such as money laundering.
Commercial banks offer an effective platform for effecting cross-border remittance transactions. These banks have an advantage of extensive networks and settlement systems across countries for sending and receiving international payments. Banks mostly use their own networks for money transfers. In cases where they have limited networks, they may use a franchise transfer service provided by a global operator or utilise a correspondent banking relationship.
The payment formats used by them for foreign remittances include electronic fund transfers or transfers by telegram, fax and telephone. Foreign remittances are sent by the remitting bank via wire transfer to its correspondent bank along with the desired information in the standard format and banking language.
CCIL – Forex Clearing
Set up in April 2001, the Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) supports in the clearing and settlement of foreign exchange transactions. The prime objective of this corporation is to improve efficiency in the transaction settlement process and insulate the financial system from operations-related issues. The corporation also undertakes other related activities to broaden and deepen the money, debt and FX markets across various countries. It started its operations on 15 February 2002 and commenced the settlement services for FX transactions from November 2002.
It started services for the settlement of cross-currency deals from 6 April 2005. It also develops and manages electronic trading platforms for trading in government securities and call money. It has introduced many innovative products/tools for the clearing and settlement of foreign exchange transactions in the international market. Besides, it brings out many publications on a regular basis for the benefit of the market participants. CCIL adopts the ‘payment-versus-payment mode of settlements’ in clearing and settling foreign exchange transactions.
The key benefits associated with this model are summarised as follows:
- Elimination of principal/credit risks
- Maintenance of counterparty limits by members on agreed terms and conditions of the trade agreement
- Trade with counterparties
CCIL, while rendering its services, performs the following validation checks:
- Whether both the parties involved in the transaction are active members of the FX settlement segment of CCIL or not
- Duplication of message
- Correctness of conversion rate
- Valid currency
- Existence of original deal
- Provision for amendment or cancellation of deal
- Ensuring that the trade date is not greater than the current day
- Trade or settlement date is not a holiday or Saturday or Sunday.
- Settlement date is not less than the trade date or reporting date.
- No mismatch of date
- Rounding of the figure involved in the transaction
CCIL offers CCP trade clearing in USD/INR. The settlement is done on Payment vs Payment (PvP) basis, and the underlying risk is mainly the principal risk in the settlement.




