What is DMAIC?
DMAIC is an acronym that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a problem-solving methodology used in the context of Six Sigma, a data-driven approach for process improvement and quality management. DMAIC provides a structured framework to tackle complex problems and drive improvements in various industries.
Table of Content
A data-driven quality improvement technique is DMAIC (define, measure, analyse, improve, and control). The letters in the acronym stand for the five stages of the procedure, as well as the tools needed to accomplish them. It is a crucial part of a Six Sigma project, but it can also be utilised as a stand-alone quality improvement technique or in conjunction with other process improvement projects such as lean.
DMAIC Methodology is shown in Figure:
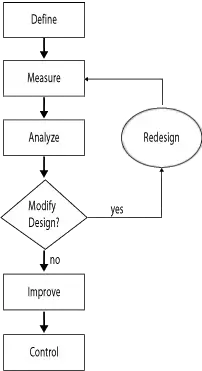
DMAIC Process
- Define the problem, the improvement activity, the improvement possibilities, the project goals, and the client requests (internal and external).
- Use the voice of the customer to understand what existing and potential customers are saying about offerings that please, delight and dissatisfy them.
- A value stream map shows the entire process from start to finish, beginning and ending with the client, and analyses what is required to meet their needs.
- Use the voice of the customer to understand what existing and potential customers are saying about offerings that please, delight and dissatisfy them.
- Measure process performance.
- Process map for capturing process activities
- Capability analysis for determining a process’ ability to meet specifications
- Pareto chart for analysing the frequency of problems or causes
- Process map for capturing process activities
- Analyse the procedure to identify the sources of variation and poor performance (defects).
- Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) for identifying a prospective product, service, and process failures
- Root cause analysis (RCA) to reveal causes
- A multi-vari chart can be used to detect many sorts of variations in a process.
- Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) for identifying a prospective product, service, and process failures
- Improve the efficiency of the process by addressing and eliminating the root causes.
- Design of experiments (DOE) is a method for resolving problems arising from complicated processes or systems in which many variables influence the outcome and it is hard to isolate one aspect or variable from the others.
- Kaizen events are used to bring about rapid change by focusing on a specific project and utilising the ideas and motivation of those who perform the task.
- Design of experiments (DOE) is a method for resolving problems arising from complicated processes or systems in which many variables influence the outcome and it is hard to isolate one aspect or variable from the others.
- Maintain control over the enhanced process and its future performance.
- Quality control plan to document what is required to maintain an improved process at its current level
- Process behavior is monitored using statistical process control (SPC).
- 5S to create a workplace that is conducive to visual control
- Mistake proofing (poka-yoke) to eliminate or detect errors immediately
- Quality control plan to document what is required to maintain an improved process at its current level
DMAIC and DMADV are the two most extensively utilised Six Sigma methods. Both strategies are intended to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of a business process. While both approaches have some key traits, they were created for different business processes and are not interchangeable.
Let’s take a closer look at the acronyms before we compare these two ways:
- DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control
- DMADV: Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, Verify
How Are DMAIC and DMADV Similar?
There are a few similarities between DMAIC and DMADV that are worth noticing. They both use statistical methods and facts to solve common quality-related challenges while focusing on an organisation’s commercial and financial objectives. Green Belts, Black Belts, and Master Black Belts use DMAIC and DMADV to minimise defects to less than 3.4 defects per million available opportunities, or Six Sigma. Their solutions are data-driven and solely based on facts.
How Are DMAIC and DMADV Different?
Even though their names share the first three letters, they have some significant variances. The key distinction is in how the process’s final two steps are handled. The Design and Verify parts of DMADV are concerned with creating a process to meet the needs of customers, as opposed to the Improve and Regulate steps, which are concerned with finding ways to readjust and control the process. DMAIC normally outlines a business process and its applicability; DMADV specifies a customer’s needs as they apply to a service or product.
Both are data-intensive and based only on hard facts. In terms of measurement, DMAIC assesses a process’s current performance, whereas DMADV assesses client specifications and wants. With DMAIC, control systems are built to keep a close eye on the business’s future performance, whereas with DMADV, a proposed business model must go through simulation testing to ensure its efficacy. DMAIC focuses on making improvements to a business process to decrease or eliminate faults; DMADV creates a business model that is tailored to the needs of the consumers.
When Should DMAIC and DMADV Be Used?
DMADV is typically connected with new services and product designs; however, it may or may not be compatible with existing goods and processes. DMADV can be used to create a new product or process if there is not one already on the market. When a process improvement falls short of expectations or fails, another approach to look at is to use DMADV.
The DMAIC method is used to improve an existing product or process that no longer satisfies the needs and/or standards of the client. Companies without prior Six Sigma experience may wish to employ the assistance of professionals such as Six Sigma Black Belts and Master Black Belts, who can assist in determining the appropriate DMAIC and DMADV approaches.




