The SAP system has multiple layers and is arranged in the form of different functional modules, with each module covering a distinctive function of a business organisation.
Each business task is handled by a specific module, and these modules are linked to one another other according to the requirement. Some of the most commonly used SAP functional modules are Financials and Controlling (FICO), Human Resources (HR), Materials Management (MM), Sales & Distribution (SD) and Production Planning (PP).
Table of Content
SAP Application Modules
There are 12 major application areas or SAP application modules, as they are called. These 12 SAP application modules are further divided into a number of sub-modules. From the business point of view, SAP application modules are the centre of a SAP system. A typical company may not have all these modules, but there would definitely be a relationship among all the modules.
Financial Accounting (FI)
It is one of the most important modules of SAP as it takes care of the data related to financial transactions. It is used for recording, collecting and processing financial data and generating reports for financial decision making. It involves recording information on accounts receivable, payable, ledger account and sub-ledger account. In simple terms, FI aims at designing the books of accounts that show an organisation’s current financial status. This module includes the following sub-modules:
- General Ledger Accounting
- Accounts Receivables
- Accounts Payable
- Asset Accounting
- Bank Accounting
- Consolidation
- Special Purpose Ledger
- Travel Management
Controlling (CO)
This module performs the function of generating internal reports to help the management in decision making. CO processes the financial transactions, which reflect the cost and revenue of a company. This module includes the following sub-modules:
- Cost Element Accounting
- Cost Centre Accounting
- Profit Centre Accounting
- Internal Orders
- Product Cost Controlling
- Profitability Analysis
- Order Contribution Analysis
Asset Management (AM)
This module helps in handling and monitoring individual aspects of fixed assets by acquiring, depreciating, evaluating and retiring assets. The AM modules include the following sub-modules:
- Purchase and Sale of Assets
- Depreciation
- Investment Management
Project System (PS)
This module provides support for planning, managing, controlling and monitoring highly complex long-term, high-risk projects with defined goals. The PS module contains the following sub-modules:
- Payments
- Confirmation
- Costs
- Resources
- Dates
- Documents
- Information System
- Material
- Progress
- Revenues and Earnings
- Simulation
- Versions
Workflow (WF)
This module associates the integrated SAP R/3 application modules with cross-application technologies, tools and services, including e-mail. The WF module helps in designing, modifying and managing the structure of an organisation on the basis of work responsibility, and makes a particular person accountable for each standard workflow template.
Industry Solutions (IS)
This module is specifically designed for particular industries. It merges the SAP application modules with modules that are specifically designed for a particular industry. For instance, separate techniques have been designed for special industries, such as banking, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, retail, healthcare, automotive, utilities, insurance, wholesale distribution, chemical, media, etc. The various sub-modules of the IS modules are as follows:
- SAP Banking
- SAP Aerospace and Defense
- SAP Automotive
- SAP Engineering and Construction
- SAP Chemicals
- SAP Consumer Products
- SAP Telecommunication
- SAP Utilities
- SAP Service Provider
Human Resources (HR)
This module is focused on all the events related to Human Resource management of the organisation, starting from the entry to the exit of an employee. The SAP HR module is an integrated system that manages the employee lifecycle and payroll, and provides support for the planning and controlling of personnel activities. The sub-modules of the HR module are as follows:
- Organisational Management
- Personnel Administration
- Personnel Planning and Development
- Recruitment
- Time Management
- Travel Management
- Payroll
- Benefits
- Compensation Management
- Personal Cost Planning
- Budget Management
- Training and Event Management
Plant Maintenance (PM)
This module takes care of the plant maintenance function. It consists of the planning activity for plant maintenance, which includes scheduling daily routine maintenance activities so that they do not disrupt plant operations. This module also takes care of processing and implementation of the plant maintenance plan as per the schedule, and lastly, the completion of all the maintenance activities in conjunction with the Production Planning (SAP PP) module. The sub-modules of the PM module are as follows:
- SAP PM-WOC: Maintenance Orders Management
- SAP PM-SM: Service Management
- SAP PM-EQM: Equipment and Technical Objects
- SAP PM-IS: PM Information System
- SAP PM-PRM: Preventive Maintenance
- SAP PM-PRO: Maintenance Projects
Materials Management (MM)
This module helps in processing information related to day-to-day procurement and inventory functions. It is designed to record data on the following:
- Purchasing
- Goods Receiving
- Material Procurement
- Inventory Management
- Consumption-based Planning
- Reorder Point Processing
The procurement process of the MM module is depicted in Figure below:
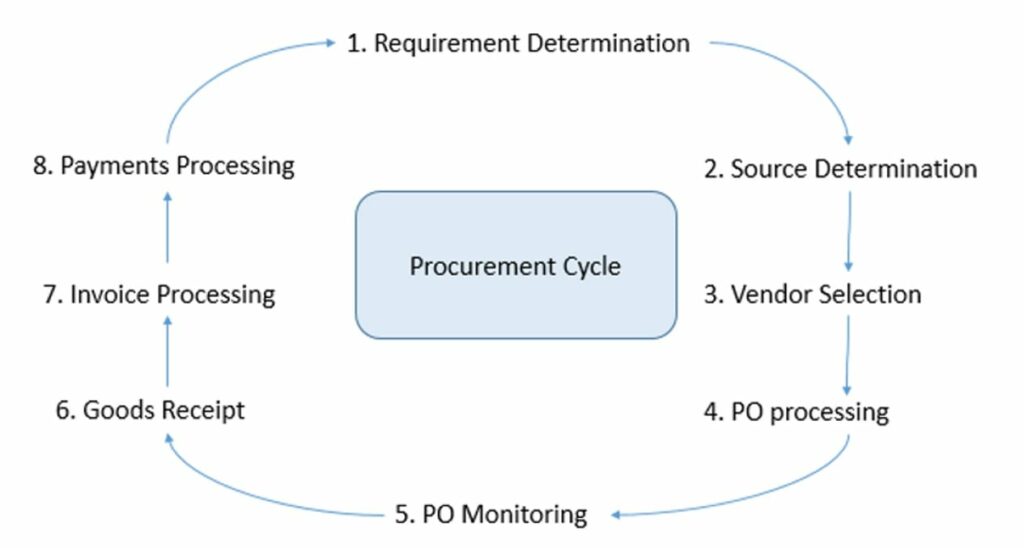
Figure illustrates the procurement function of a business, which includes an eight-step process, where each step depicts the sub-module of this particular business process. Here, the procurement function starts by determining the demand and source of material.
This is followed by the selection of the supplier, preparation and processing of the purchase order, monitoring of the order, receiving of the goods, verification of the invoice with the purchase order and, finally, making the payment. The SAP MM module records information at each step of the procurement function and generates reports of the inventory available to the organisation.
- Quality Management (QM): This module deals with the quality aspect of the organisation or business, including business units such as sales, purchase, production, R&D, procurement, etc. Quality control is the most important concern of the SAP QM module. This module consists of the quality planning activity, followed by quality inspection and quality control activities. The sub-modules of the QM module are as follows:
- SAP QM-QP: Quality Planning
- SAP QM-IM: Quality Inspection Processing
- SAP QM-QC-AQC: Quality Control
- SAP QM-IT: Test Equipment Management
- SAP QM-PT-RP: Control in Logistics
- SAP QM-QN: Quality Notifications
- SAP QM-CA: Quality Certificates
- SAP QM-CR: General Functions
- Production Planning (PP): This module is used for processing information related to planning and controlling of the production function of an organisation. The module is designed to record data on bills of material, work centres, routings, shop floor control, product costing, etc. The sub-modules of the PP module are as follows:
- SAP PP-SOP: Sales and Operations Planning
- SAP PP-CRP: Capacity Requirement Planning
- SAP PP-MP: Master Planning
- SAP PP-ATO: Assembly Orders
- SAP PP-BD: Basic Data
- SAP PP-IS: Information System
- SAP PP-KAB: Kanban/Just-in-Time
- SAP PP-MRP: Material Requirements Planning
- SAP PP-PDC: Plant Data Collection
- SAP PP-PI: Production Planning for Process Industries
- SAP PP-REM: Repetitive Manufacturing
- SAP PP-SFC: Production Orders
- SAP DS: Detailed Scheduling
The manufacturing process of the Product Planning module is depicted in Figure below:
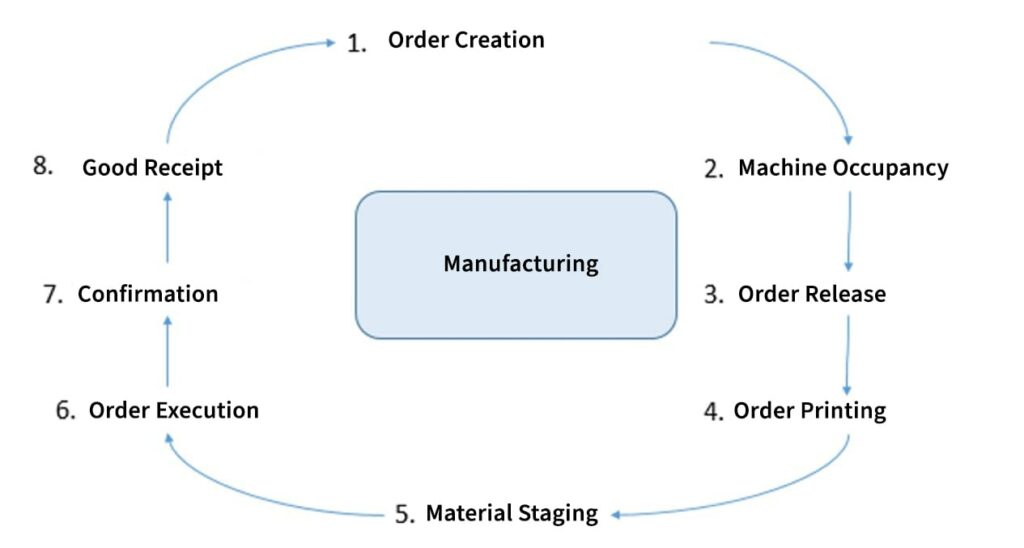
Figure illustrates the manufacturing function of the business, which includes an eight-step process, and each step depicts the sub-module of this particular business process. Here, the manufacturing module involves creation of the order, which leads to the occupancy of machine or equipment.
This is followed by release of the order, printing of the order, material staging, order implementation, order confirmation, and finally, receiving of the goods. The SAP PP module records information at each step of the manufacturing process and generates reports on the available raw material, goods produced, etc., to the organisation.
- Sales and Distribution (SD): This module processes information related to the sales, delivery and billing functions of an organisation. It is designed to record data about sales orders processed, sales quotation processed, sales inquiry processed, pre-sales support, delivery process, etc. The sub-modules of the SD module are as follows:
- SAP SD-MD: Master Data
- SAP SD-CAS: Sales Support
- SAP SD-SLS: Sales
- SAP SD-SHP: Shipping
- SAP SD-TR: Transportation
- SAP SD-BIL: Billing
- SAP SD-SIS: Sales Information System
- SAP SD-EDI: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
- SAP SD-GF: General Sales Functions
- SAP LE: Logistic Execution
The order processing phase of the Sales and Distribution module is depicted in Figure below:
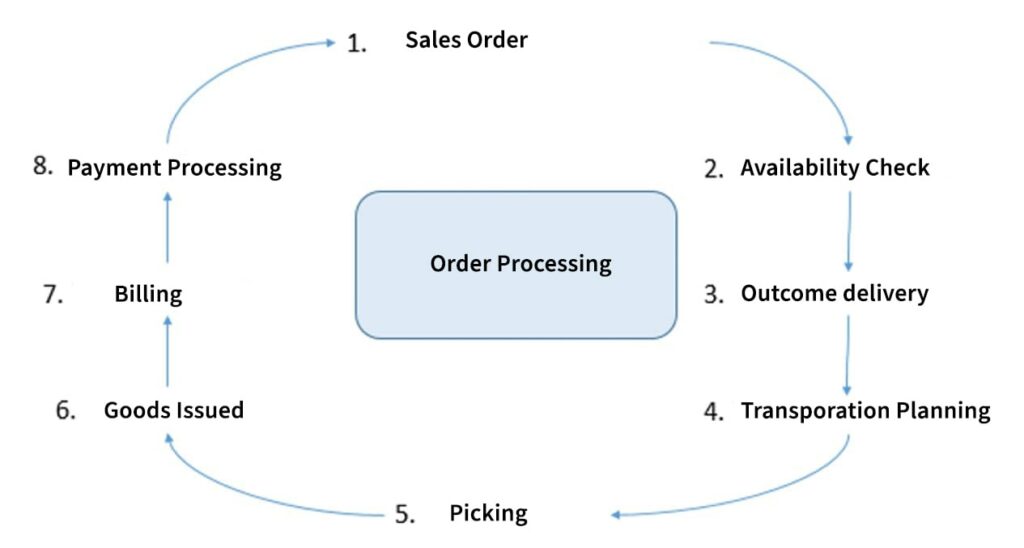
Figure illustrates the order processing function of a business, which includes an eight-step process. Here, order processing starts with the receipt of the sales order.
After this, the sales order is checked for availability of the required goods or services; the subsequent activities include processing the outbound delivery, planning for the delivery of the order, picking the goods to be transported, issuing and billing the goods for delivery and finally, processing the payment.
The SAP SD module records information at each step of the sales order processing and distribution function and generates reports on the goods or services sold, billed, and delivered by the organisation to the customers.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Tutorials
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Enterprise Resource Planning?
- Benefits and Advantages of ERP & Reasons for Growth
- Success Factors of ERP Implementation
- ERP Implementation Life Cycle
- Risk in ERP Implementation, Cross Function, ERP Technology
- Maintenance of ERP
- What is Business Model?
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
- Types of Information Systems: TPS, MIS, DSS, EIS
- What is SAP?
- Modules of ERP Software
- SAP Application Modules
- SAP R/3 System
- ERP Modules
- ERP in Manufacturing
- ERP Purchasing Module
- What is SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD)?
- ERP Inventory Management Module
- ERP Implementation
- ERP Vendors, Consultants and Users
- BaaN ERP
- Oracle Corporation
- PeopleSoft ERP
- Edwards & Company ERP
- Systems Software Associates ERP
- QAD ERP
- What is ERP II?
- ERP Implementation at Rolls-royce



