What is Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as the quantity consumed of a commodity continues to increase, the utility obtained from each successive unit goes on diminishing, assuming that the consumption of all other commodities remains the same.

Table of Content
To put simply, when an individual continues to consume more and more units of a commodity per unit of time, the utility that he/she obtains from each successive unit continues to diminish.
Also Read: Law of Demand
Law of diminishing marginal utility Example
For example, the utility derived from the first glass of water is high, but with successive glasses of water, the utility would keep diminishing. The law of diminishing marginal utility is applicable to all kinds of goods such as consumer goods, durable goods, and non-durable goods.
Let us understand the law of diminishing marginal utility with the help of an example.
An individual consumes only one commodity X and its utility is measured quantitatively. The total utility and marginal utility schedules are as shown in Table 1.
| UNITS OF COMMODITY X | Total Utility (TUx) | Marginal Utility (MUx) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 30 |
| 2 | 50 | 30 |
| 3 | 60 | 20 |
| 4 | 65 | 10 |
| 5 | 60 | 5 |
| 6 | 45 | -5 |
Table 1 shows that as the number of units of commodity X consumed per unit of time increases, TUx increases but at a diminishing rate while marginal utility MUx decreases consistently. The rate of increase in TUx as a result of increase in the number of units consumed has been depicted through the MUx curve in the graph shown in Figure
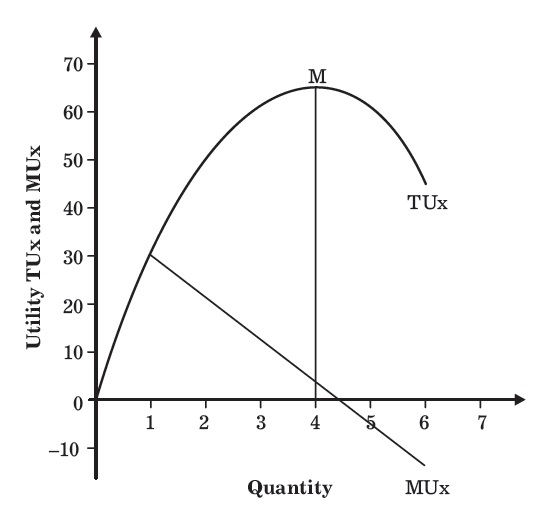
In Figure, the downward sloping MUx curve shows that the marginal utility of a commodity consistently decreases as its consumption increases. When the consumption reaches to 4 units of commodity X, TUx reaches its maximum level (the point of saturation) marked as M.
Beyond the point of saturation, MUx becomes negative and TUx begins to decline consistently. The downward slope of MUx explains the law of diminishing marginal utility. Therefore, according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, the utility gained from a unit of a commodity is dependent on the consumer’s desire for the commodity.
When an individual continues to consume additional units of a commodity, the satisfaction that he/she derives from the consumption keeps decreasing. This is because his/ her need gets satisfied in the process of consumption. Therefore, the utility derived from successive units of the commodity decreases.
Also Read: Law of Supply
Assumptions of Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Assumptions of law of diminishing marginal utility are as follows:
- Rationality
- Measurement of utility
- Constant marginal utility of money
- Homogeneity of commodity
- Continuity
- Ceteris paribus
Rationality
The law of marginal utility assumes that a consumer is a rational being who aims at maximising his/her utility at the given income level and the market price.
Measurement of utility
The utility of a commodity can be measured using quantifiable standards like a cup of tea, a bag of sugar, a pair of socks, etc.
Constant marginal utility of money
The marginal utility of consumer’s income is constant.
Homogeneity of commodity
The successive units of a commodity consumed are homogenous or identical in shape, size, colour, taste, quality, etc.
Continuity
The consumption of successive units of a commodity should be continuous without intervals.
Ceteris paribus
Factors, such as the income, tastes and preferences of consumers; price of related goods; etc. remain unchanged.
Also Read: What is Indifference Curve
Exceptions of Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Following are the exceptions of law of diminishing marginal utility:
- Drunkard – Utility from each additional peg of wine increases for the drunkard. The law does not operate in his case.
- Money – The law docs hold good in case of money. The utility of money does not diminish.
- Hobbies– Hobbies like stamp collection is an exception. A man who has hobby of collecting stamps feels more satisfied with every successive stamp he is able to collect.
- Rare collections
- Money
- Knowledge and Innovation
- Precious goods
- Utility increases due to a demonstration
Also Read: Movement and Shift In Demand Curve
Importance of Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Importance of law of diminishing marginal utility are as follow:
- Basis for law of demand
- Basis of the Progressive Tax-policy
- Basis for Re-Distribution of Wealth Policy
- Determining optimum level of consumption
- Forms basis for production of things
Basis for law of demand
The law of diminishing marginal utility is one of the fundamental laws of Economics. The basic law of demand is, in fact, totally based on the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Basis of the Progressive Tax-policy
The government can formulate a progressive tax-policy on the basis of the law of diminishing marginal utilIty.
Basis for Re-Distribution of Wealth Policy
The government’s public expenditure policy is also based on the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Determining optimum level of consumption
This law helps in the determination of the optimum level of consumption. it is attained at a point where the marginal utility of a commodity equals its price.
Forms basis for production of things
According to Taussing, only due to this very law, are the various things produced or manufactured.
Also Read: Inflation in Economics
Business Economics Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Business Economics Tutorial? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility | Business Economics in the comments section.
Business Economics Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)











