What is Depository?
Depository is an organization which holds securities (shares, debentures, bonds etc.) in electronic (also known as ‘book entry’) form, in the same manner as a bank holds money.
Further, a depository also transfers the securities without actually handling securities, in the same day as a bank transfers funds without actually handling cash. Besides holding securities, a depository also provides services related to transactions in securities.
Table of Content
Depository Definition
Advantages of Depository System
The depository system offers following direct and indirect benefits. These are discussed as follows:
- Quick transfer of funds and securities: Depository system leads to quick transfer of funds and securities in the investor’s account.Once the securities are credited to the investors account on payout, he becomes the legal owner of the securities; there is no need to send it to the company registrar for registration. The usual practice is to hold the Securities and not to register the change of ownership.
- Elimination of risks: An investor is always exposed to risks of theft of stocks, damage of certificates, loss in transit or loss of certificates during movement through or from the registrars etc. While dealing in physical securities an investor has to incur costs for obtaining duplicate certificates and advertisements etc. With the introduction of dematerialization of securitiessuch problems are not faced under depository system.
- No stamp duty: No stamp duty is payable by the investors for getting the equity shares and units of mutual funds transferred under the depository system. In case of physical shares, stamp duty of 0.5% is payable on transfer of shares.
- Minimized chances of fraud, theft and counterfeiting of securities: Holding of securities in electronic form minimizes the chances of theft. DPs can affect debit or credit to demat only after receiving valid instruction slip from the client. Thus the risks of frauds, theft and also counter feinting of securities are minimized.
- Provides insurance cover– NSDL has taken up a comprehensive insurance policy to protect the interest of the investors in case the depository participant fails to resolve a genuine loss.
- Statement of accounts: Investors receive statements of accounts periodically from the depository participant. Every month, NSDL sends statement of accounts to investors selected at random, as a counter check.
- Direct disbursement of non-cash benefits: An investor entitled to receive right shares and bonus shares, is directly credited with such number of shares in his demat account. Similarly any dividend or interest receivable is directly deposited by depositories in demat account of the shareholders.
- Faster settlement cycle: A settlement cycle of T + 2 is followed for demat shares i.e. settlement of trading whether for purchase or sale is done on the 2nd working day from the trade day. This not only provides liquidity to the investor but also leads to increased stock turnover.
- Lower brokerage cost: Investors dealing in dematerialized securities pay lower brokerage cost as compared to paper- based securities. Moreover it reduces the back office cost of the brokers who in turn may provide a reduction in the brokerage of 0.25% to 0.50%.
- Convenient for portfolio monitoring: Depository participants (DPs) send periodical status reports to the investors about their holding transaction. This status report shows the consolidated position of investment in all securities. This enables efficient monitoring of portfolio and better control over investment.
Mechanism of Depository System
Worldwide, the depository system adopts either of two routes:
- Immobilization
- Dematerialisation
Both of these are explained as below:
Immobilization
Under the immobilization method, securities in physical form are given credit and the physical certificates are stored or lodged with an organization, which acts as a custodian – a securities depository. Subsequent transactions in such immobilized securities take place through book-entries.
Demineralisation
Dematerialisation is the process by which investor can get physical certificates converted into electronic form.An investor intending to dematerialise its securities needs to have an account with a DP.
The client has to destroy and surrender the certificates registered in its name to the DP. After intimating NSDL electronically, the DP sends the securities to the concerned Issuer/ R&T agent.
NSDL in turn informs the Issuer/ R&T agent electronically, using NSDL Depository system, about the request for dematerialisation. If the Issuer/ R&T agent finds the certificates in order, it registers NSDL as the holder of the securities (the investor will be the beneficial owner) and communicates to NSDL the confirmation of request electronically.
On receiving such confirmation, NSDL credits the securities in the depository account of the Investor with the DP. Stepwise procedure of dematerialisation is shown below:
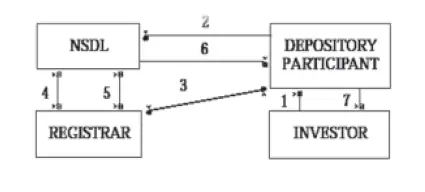
- Inverstor surrenders certificates for Dematerialization to DP.
- DP intements depository of the request through the system.
- DP submits the certificates to the Registrar.
- Registrar confirm the Dematerialization request from depository.
- After Dematerializing Registrar updated Accounts and Informs depository of the completion of Dematerrialization.
- Depository updates its Accounts and informs the DP.
- DP updates its Accouts and Informs invesotrs.
Advantages of dematerialisation
- There is no risk due to loss on account of fire, theft or damage.
- There is no chance of bad delivery at the time of selling shares as there is no signature mismatch.
- Transaction costs are usually lower than that in the physical segment.
- The bonus /rights shares allotted to the investor will be immediately credited into his account.
- Share transactions like sale or purchase and transfer/transmission etc. can be effected in a much simpler and faster way.
Financial Accounting
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Posting In Accounting?
- What is Trial Balance?
- What is Accounting Errors?
- What is Depreciation In Accounting?
- What is Financial Statements?
- What is Departmental Accounts?
- What is Branch Accounting?
- Accounting for Dependent Branches
- Independent Branch Accounting
- Accounting for Foreign Branches
Corporate Finance
Management Accounting



