What is Management by Objectives?
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a strategic management technique in which measurable goals are set by a joint effort of seniors and subordinates and the contribution of each individual is measured in terms of their accomplishment of the goals.
The goals set in MBO are not unilaterally set by the superior or imposed on the subordinates. These identified goals are set in close consultation with subordinates.
In 1954, Peter Drucker coined the term Management By Objective in his book, The Practice of Management.
MBO is an autonomous and participative style of management. The concept has become popular these days as a rewarding style of management. It focuses concentration on the achievement of objectives through partaking and involvement of all concerned persons.
Table of Content
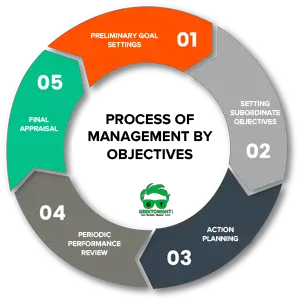
Process of Management by Objectives
The basic assumption behind such a philosophy is that when people are aware of the expectation from them they align their personal goal with the organizational goal and can perform better.
Steps of the MBO process are:
- Preliminary Goal Settings
- Setting Subordinate Objectives
- Action Planning
- Periodic Performance review
- Final appraisal
Preliminary goal settings
The initial stage in the process of MBO is to identify the organizational objectives. The top management generally in consultation with other managers determines it.
The important aspect of determining these is identifying “Key-Result Areas’ (KRA). Once these goals are identified they must be shared with other members.
Setting specific performance objectives
The organization goals can only be achieved if they are divided amongst the individuals and every individual performs the given task. Therefore every individual should be informed about the task that is expected from them.
The subordinate should be consulted before providing with the resources for performing the task. The resources provided should be proportionate according to the goals.
Goal setting is a two-way process it is not imposed on the subordinate by the superior. Superior suggests a goal to subordinate and subordinate accepts it.
Development of Action Plans
After the goals are set, action plans are developed to bring the things into force. Procedures are formed for achievement of set goals.
Under MBO the subordinates and superior jointly and interactively perform a given task. The superior gives suggestion and the subordinates perform. The objectives are so formed that every objective accomplished at lower level contributes to the fulfilment of the greater goal.
Periodic performance review
At specified time interval evaluation of the work is done with joint participation to identify shortcomings or deviations if any. Subordinate and superior sit and discuss the problems area identified Feedbacks and suggestions are made available for the potential development.
The main purpose is to improve the quality instead of focusing on criticism.
Final appraisal
At the end of the year, the performance of the individual is evaluated on the basis of the task completed.
The standards which are set are compared with the actual. The actual work is evaluated based on which the appraisal or rewards of the subordinate is decided.
Advantages of Management by Objectives
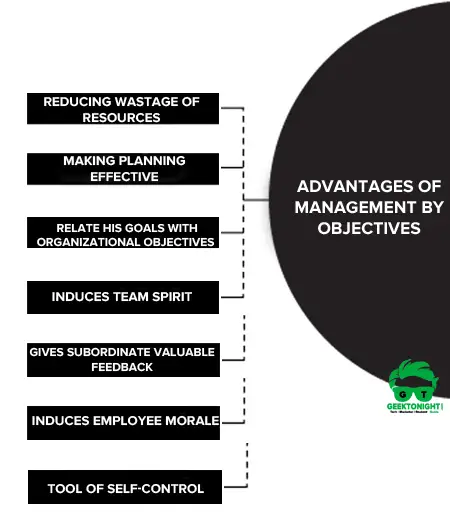
- Helps in reducing wastage of resources as the resources are provided in proportion to goals set.
- Helps in making planning effective with the help of action plans and result oriented planning.
- The subordinate is able to relate his goals with organizational objectives and feels proud of his contribution towards the organizational objectives
- Induces team spirit with a democratic and participative style of work.
- It gives subordinate valuable feedback through the system of periodic evaluation. The employee becomes aware of his progress and can take timely corrective action if he is lacking somewhere.
- Induces employee morale as their participation is given due consideration. Also, the rewards are according to the contribution which raises their morale.
- It acts as an effective tool of self-control as every individual knows what is expected out of him, which helps in self-regulation.
Limitations of Management by Objectives
These are limitations of management by objectives:
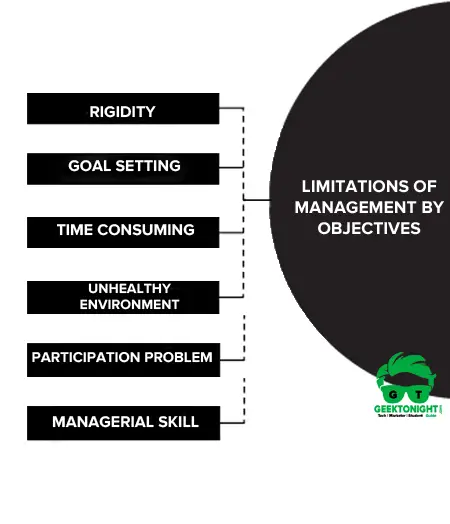
Rigidity
The problem is that it sometimes fails to incorporate prevailing trends and the current scenario of the organization.
Goal Setting
Which criteria should be given more preference quantity or quality? The goal should be long term or short term, these are various issues confronted while setting goals. Sometimes overemphasis on measurable goals can neglect crucial qualitative goals like job satisfaction.
Time Consuming
Setting up of goal that are measurable and that too in participative style requires a lot of time. Instilling confidence, deciding on tasks all these require a lot of time. The process of evaluation and performance appraisal involves considerable paperwork and time.
Unhealthy Environment
Sometimes more emphasis is laid on work rather than improving the quality which produces a lot of pressure and unhealthy competition between workgroup.
Participation Problem
At times to avoid wastage of time, superior do not consult subordinates and set the goals authoritatively which loses the essence of the process.
Managerial Skill
Some managers may not be very good at human skills. They may not be effective in motivating and leading people towards the work.
Key Takeaway
Management by Objectives: It is a technique in which measurable goals are set by a joint effort of senior and subordinate and the contribution of each individual is measured in terms of their accomplishment of the goals.
Reference
- T. V. Rao, “Appraising and Developing Managerial Performance“, Excel Books, New Delhi, 1999.
- D. Grote, “Performance Appraisal Reappraised,’’ Harvard Business Review, Jan- Feb 2000.
- K. R. Murphy, J. Cleveland, “Performance Appraisal”, Boston, M. A: Allyn & Bacon, 1991.
- Scott Snell and G. Bohlander, “Human Resource Management”, Cenpager, New Delhi, 2007.
Go On, Share article with Friends
Did we miss something in Human Resource Management Tutorial? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Types of Training in HRM in the comments section.
Human Resources Tutorial
(Click on Topic to Read)







